Move Selection
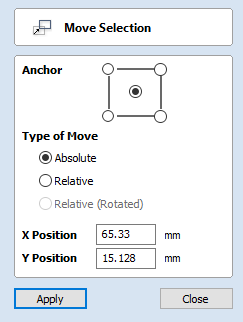
Selected items can be accurately moved and positioned using this option.
Anchor
The anchor position determines the point on your selected object's bounding box that will be moved to the absolute position entered.
Type of Move
Absolute
In this mode, the X Position and Y Position values will be used to position the object's anchor point directly
Relative
With this option selected, the values entered in the X Position and Y Position fields will incrementally offset the object from its current position, by the distances entered. The Anchor options are not relevant in this mode and so will be disabled.
The keyboard shortcut Mopens the Move form in interactive mode.
SketchUp Files
SketchUp files with a .SKP extension (see www.sketchup.com) can be imported as 2D data suitable for machining into a Aspire for ALPHACAM job using the File ► Import Vectors... command from the menu bar or the import vectors icon on the Drawing tab. To import data from a SketchUp file you must already have created or opened a job to import the data into.
As a SketchUp model is usually a 3D representation of the part, the SketchUp importer offers a number of options to allow you to start manufacturing the model.
We will illustrate the two main choices for how the model will be imported using the SketchUp model shown to the left.
The model shown in the screenshots is a cabinet constructed by following the instructions in the Fine Woodworking 'Google SketchUp guide for Woodworkers: The Basics' DVD which is available via the Fine Woodworking site at www.finewoodworking.com. Vectric have no affiliation with Fine Woodworking, we are just using screenshots of the model constructed while following their tutorials to illustrate the process of importing a SketchUp model.
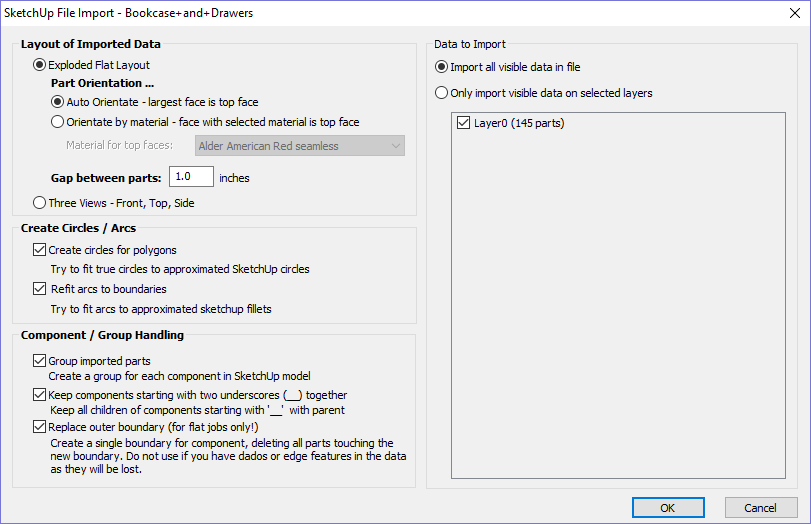
Layout of Imported Data
In the first section there are two main choices for how the data from the model will be imported, 'Exploded Flat Layout' and 'Three Views - Front, Top, Side' as shown below.

Exploded Flat Layout
This option will take each component in the model and orientate it flat ready for machining.
Once this option is selected a number of sub-options also become available.
Part Orientation
This section controls what Aspire considers to be the 'top' face of each part.
Auto Orientate
If this option is selected, for each part in the model, the 'face' with the largest area based on its outer perimeter (i.e. ignoring holes etc.) is considered to be the 'top' face and the part is automatically rotated so that this face is facing upwards in Z. This strategy works very well for models which are to be manufactured from sheet goods where there are no features on particular faces which need to be on the 'top' (such as pockets).
Orientate by material
This option allows the user to control more explicitly the orientation of each part in the model. Within SketchUp the user can 'paint' the face of each component/group with a material/color of their choice to indicate which face will be orientated on top when the model is imported. When this option is selected simply chose the material which has been used to indicate the top face from the drop down list. If a part is found in the model which does not have a face with the specified material, that part will be oriented by making the largest face the top.
Gap between parts
This field lets the user specify the gap between parts when they are first imported. After importing, the nesting functions within Aspire for ALPHACAMcan be used to layout the parts with more control and across multiple sheets
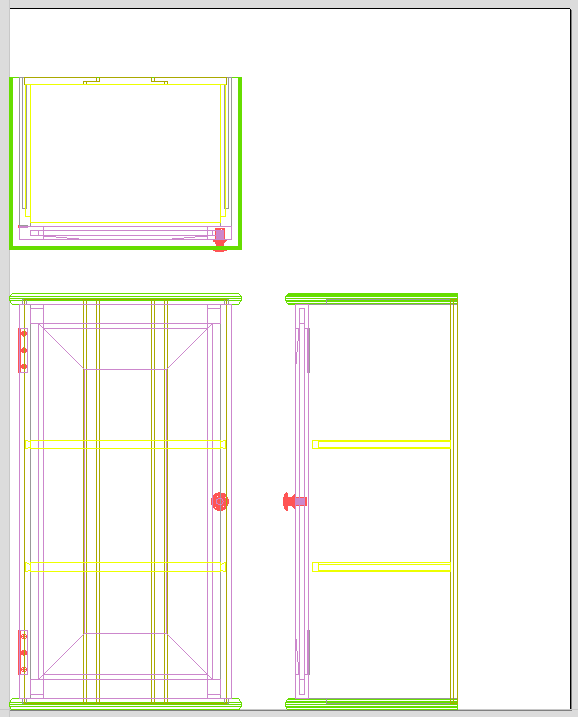
Three Views - Front, Top, Side
This option will create an 'engineering drawing' style layout of the SketchUp model as shown in the screenshot below.
The size of the model is preserved and it is relatively simple to pick up dimensions for parts you are going to manufacture from the various views. The colors of the lines you see are taken from the colors of the original SketchUp layers the various parts of the model are on.
Create Circles / Arcs
SketchUp does not maintain true arc or circle information for the boundaries of its parts. This is a problem when it comes to machining as the 'polygonal' SketchUp representation can give very poor machining results. For this reason, Aspire for ALPHACAM offers the option to refit circles and arcs to imported data.
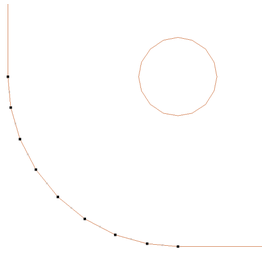
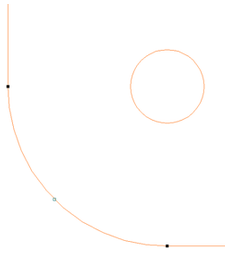
The screenshot above left shows the results of importing a part with a filleted corner and hole with these options unchecked. The 'fillet' is made up of a series of straight line segments and the circular 'hole' is actually a polygon made up of straight lines.
The screen shot above right shows the same part imported with both these options checked ✓. The 'fillet' now consists of a single smooth arc and the circular 'hole' now also consists of arcs rather than straight line segments. Both these features will machine more cleanly in this form.
Data to Import
A SketchUp model will often contain parts that you do not wish to machine (such as hinges, knobs etc.) or data which will be cut from different thicknesses of material and hence different parts need to be imported into different Aspire for ALPHACAM jobs. To allow control over what is imported you can choose to only import parts of the model which are on particular layers using this section of the dialog.
To only import data from selected layers, choose the 'import visible data on selected layers' option and click the check box next to each layer to indicate if you want to import data from that layer. Note that the number of parts on each layer is displayed next to the layer name.
It is very easy to assign different parts of the model to different layers within SketchUp to help with the import process into Aspire for ALPHACAM. The screenshot below shows the result of only importing data on the 'Door' layer from the example.
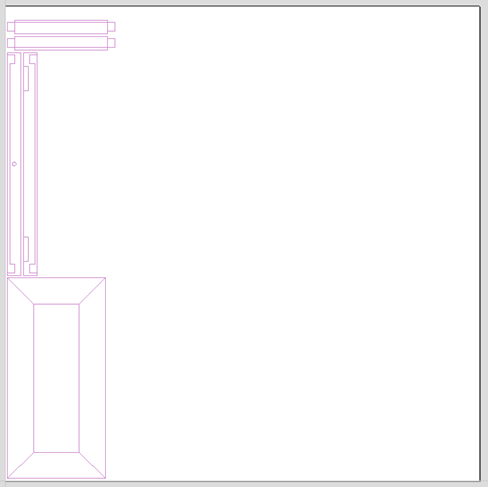
Component / Group Handling
This section of the form allows advanced handling of how 'parts' within the SketchUp model are identified and treated on import.
Group imported partses
This option is normally selected for all but the simplest models as it allows each 'part' of the model to be selected, moved and nested easily after import. You will need to ungroup the imported data after nesting etc. to allow individual features to be machined. By default, Aspire for ALPHACAM will treat each SketchUp group / component as a single part UNLESS it contains other groups or components within it, in which case each lowest level group / component will be treated as a separate part.
Items which you retain in groups can be ungrouped at any time in the usual ways.
If the right-click menu-option to Ungroup back onto original object layers is used (which is the default option when using the icon or shortcut U) then the software will place the ungrouped items back onto the original layers they were created on in SketchUp.
Keep components starting with two underscores (__) togetheres
If you have a complex model which contain 'parts' which are made up of other groups / components, you will need to do some work on your model to identify these parts for Aspire for ALPHACAM. The way this is done is by setting the name of the groups / components that you wish to be treated as a single part to start with__ (two underscore characters). For example, if you had a model of a car and you wanted the wheels / tires / hub nuts to be treated as a single part even though the Tire, Wheel and other parts were separate components, you would group the parts together and name them something like __WheelAssembly in SketchUp. When this model was imported, and Aspire for ALPHACAM reached the group/component with a name starting with __ it would treat all subsequent child objects of that object as being the same part.
Replace outer boundary (for flat jobs only!)
There is a style of 'building' with SketchUp where individual 'parts' are made up of several components 'butted' against each other. The screenshot below shows such a component.
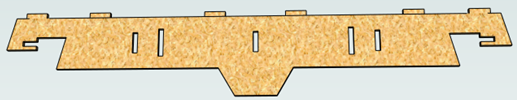
This object is made up of many smaller components representing the tabs on the top, the connectors at the end and the support at the bottom as shown below.
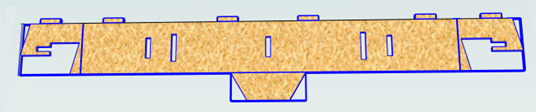
Although when can treat this as a single 'part' when imported by starting its name with __ (two underscores), the imported part is still going to be difficult to machine. The screenshot below shows the part imported into Aspire for ALPHACAM without the 'Replace outer boundary' option checked ✓. The part in the image has been ungrouped and the central vector selected.
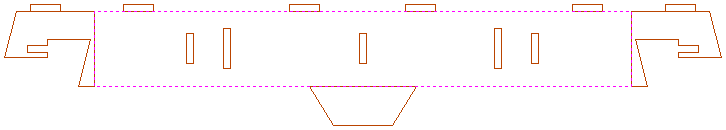
As you can see, the outer boundary is made up of separate segments for each 'feature'. Aspire for ALPHACAM does have the ability to create an outer boundary for vectors but this can be time consuming if it has to be done manually. If the 'Replace outer boundary' option is checked, ✓ for every part Aspire for ALPHACAM will try to create a single outer boundary and delete all the vectors which were part of this boundary. The screenshot below shows the result of importing the same data with this option checked, ✓ this time the part has been ungrouped and the outer vector selected.
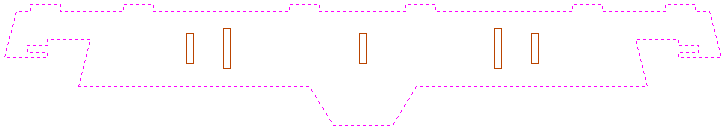
This data is now ready to be machined directly. It is important to understand the limitations of this option. It can be substantially slower. Creating robust boundaries for each part can consume a lot of processing power. Any feature which shares an edge with the boundary will be deleted. If the tabs on the top of this part were to have been machined 'thinner', this approach would not have been suitable as the bottom edge of the tabs has been removed.
IMPORTANT
The new features will help a lot of SketchUp users dramatically reduce the time it takes to go from a SketchUp design to a machinable part using Vectric Software. It is important to understand though that while these options provide a useful set of tools, in many cases there will still be additional editing required to ensure the part is ready to toolpath. Understanding the options and how they work will allow the part to be designed in SketchUp with these in mind and therefore help to minimize the time to machine once the data is imported.
Note
Sketchup files will only open in the same bit version you are running e.g. A file saved in a 32 bit version of Sketchup will only open up in a 32 bit version of the software.
Join Open Vectors
The icons to join and close vectors are located under the Edit Vectors section of the Drawing Tab.
Open vectors are automatically identified and closed or joined to other vectors where the end points lie within the user definable tolerance.
Distort Object
This tool allows you to bend and flex a vector or component by manipulating a distortion envelope using standard node editing tools. You can select one or more vectors or components and then use one of the three different tool modes to create your initial distortion envelope.
Multiple Objects
You can distort several vectors or components at once but you cannot distort a mixture of vectors and components together in a single operation.
Once the distortion envelope has been created, you can use the node editing tools to add or edit its nodes and spans. As you alter the shape of the envelope the associated object will be distorted to reflect the changes.
Layers
When distorting a selection of objects which fall on different layers, the result will be created on the layer of the first object in the selection.
Use Rotated Bounds
This option is only supported if you only have one object selected to distort. It makes use of the local rotation of the object as shown in the Selection Tool.
When this option is ticked,
- The initial distortion envelope is created along the transformed bounds of the selected object.
- When distorting along a curve (or two), the object is distorted on the curve in its local transformation. This is useful if you're distorting a rotated object onto a rotated curve, for example.
Bounding Box Distortion
This option is available if you have a selection of vectors or components (Note that you cannot mix vectors and components in this mode). It creates a distortion envelope based on the closest bounding box that can be drawn around your selection. Thus the resulting envelope is always initially a rectangle, comprising four line spans and a node at each corner. Using the normal node editing tools, however, you can modify this envelope as much as you like and the shape within it will be distorted accordingly.
Along a Single Curve
This option is only available if the last item in your selection is an open vector that can be used to define a curve, above which the other selected objects will be distorted. The distorted object can comprise one or more vectors or one or more components, but not both.
Using this option, you will usually end up with your objects bent to match the curve in your original selection. The distortion curve itself is left unchanged by this operation.
Between Two Curves
This option will become available if the last two objects in the current selection are open vectors, between which the other objects can be distorted.
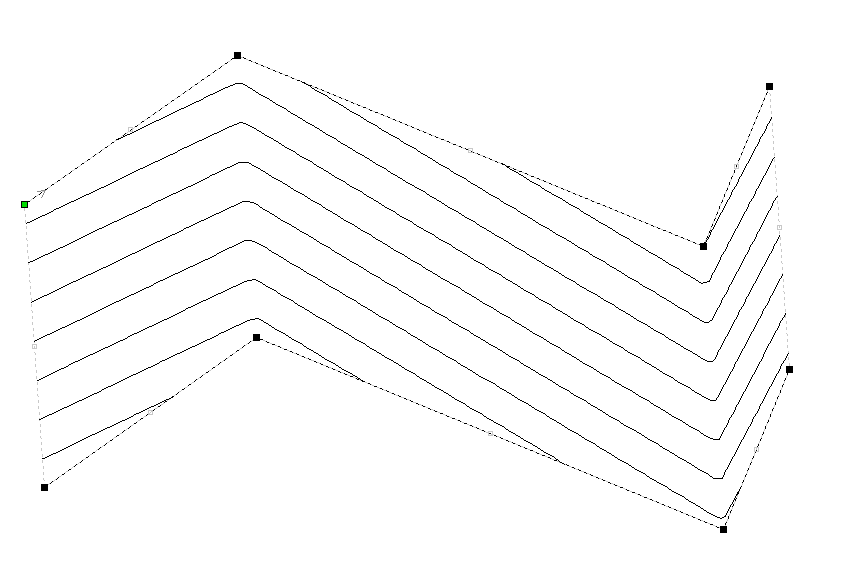
Baking Distortion into an Object
Once an object has been distorted, node editing will always relate to the object's distortion envelope. If you wish to edit a distorted vector directly again, you will first need to permanently apply the distortion to the shape.
If you select an object that already has a distortion envelope while in the Distort Object tool, the button will be available. Clicking this button will permanently apply your current distortion and you will then be able to either distort the object again (with new settings), or node edit the shape directly.
Baking Components
If you try to use this tool to modify multiple, grouped or distorted components you will first be prompted to 'bake' your selection components into a single object. For more information on what this means, please see the section Baking Components.
Redo Operation
Clicking this option steps forward through design steps that have been Undone using the Undo command (see above) to get back to stage that the user started using the Undo function.
Modelling 3D Rotary Projects
Elaborating 2D designs with 3D clipart pieces
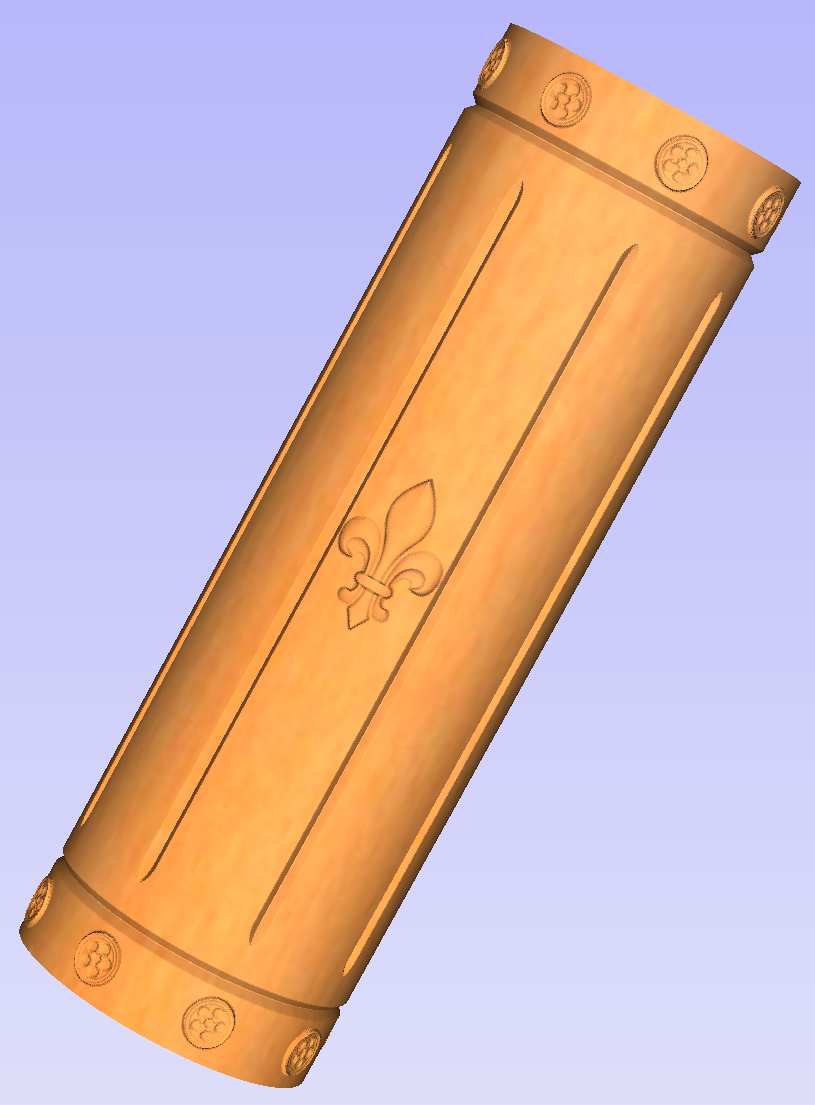

This section will present how to add 3D clipart to basic fluted column presented in Simple rotary modelling using 2D toolpaths.
A simple way to start with 3D rotary models is to use add pieces of decorative clipart that is provided with Aspire. This process is very similar to adding clipart to single- or double- sided project, however there are some additional considerations that are specific to wrapped rotary machining.
To start, switch to the Clipart tab. Then choose a piece of clipart and drag and drop it into the workspace. Aspire will show following message:
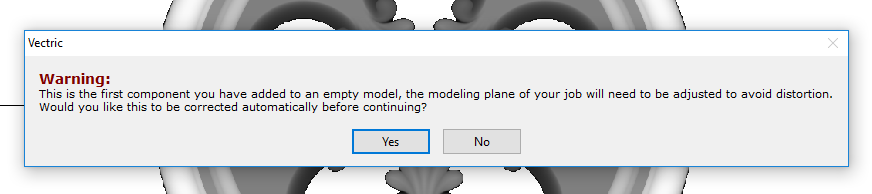
To understand this message, we need to consider the flat view of our model, after importing the clipart. Flat view can be accessed by clicking Auto Wrapping button.
As can be seen, the model contains only the selected decorative piece on the flat plane. Although the column is obviously a cylindrical solid, so far we only used 2D toolpaths to carve details on the surface of cylinder. So the fact that machined piece is a cylindrical solid, derives only from fact that the blank is a cylindrical solid itself. Aspire allows the 3D model to also describe a solid body.
In this example the intent is to only place a decorative piece on the surface, rather than define body of the column. Aspire can see that we did not model a body and we are placing a piece of clipart, that is likely to be placed at the surface. By responding 'Yes' to the message we can confirm that it is our intent to use the component to decorate a surface.
Note
The above message is only displayed when the 3D model is empty. Regardless of user choice, this message will not be displayed again for this project.
More clipart can be placed as desired. Then the 3D view can be inspected. Once design is finished it is time to create toolpaths. In order to create 3D roughing toolpath, use 3D Rough Toolpath. Then create 3D finishing toolpath, using 3D Finish Toolpath. Select settings that are most appropriate for given application, while remembering which axis is rotating. The choice of axis may be particularly important if rotation axis speed is slower than linear axis.
In this example the decorative clipart that was added was not recessed. That means that after 3D machining the flat areas around clipart will be recessed due to clipart 'standing out' of the flat surface. Therefore existing 2D toolpaths needs to be projected. This can be accomplished by selecting Project toolpath onto 3D model option and recalculating the toolpaths.
Making a tapered column
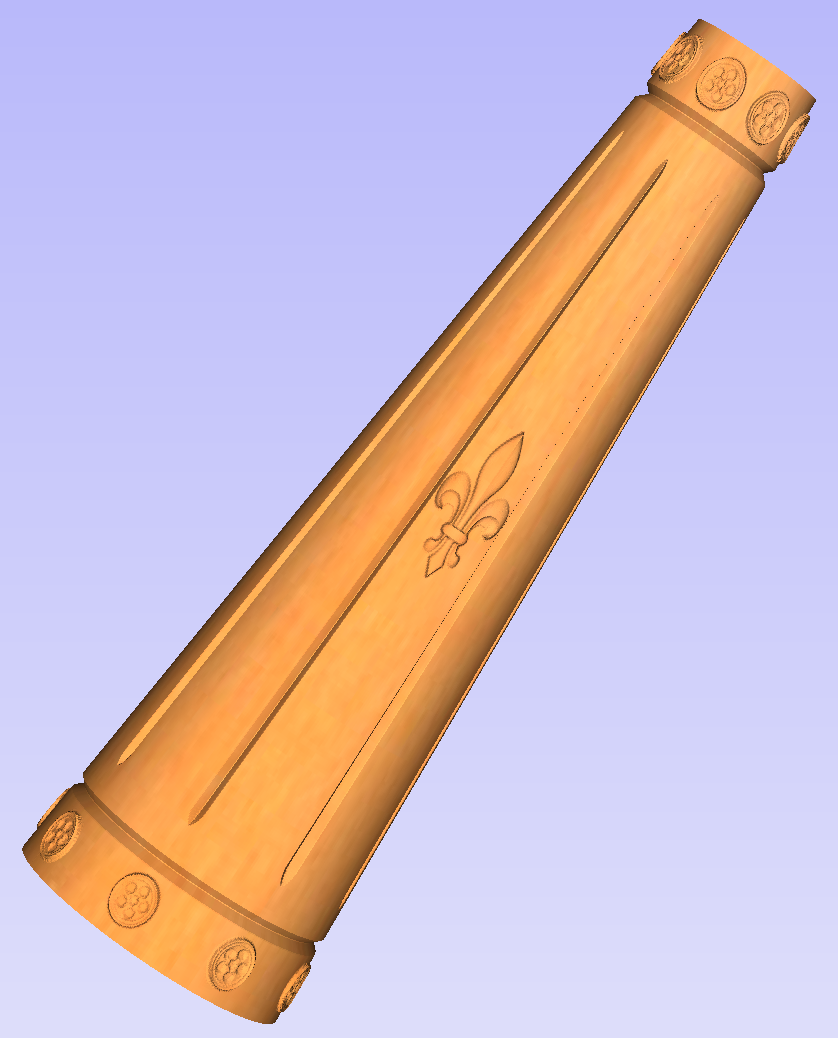

This section will explain how to make a tapered column by modifying the basic design from previous section.
So far only the surface details were modelled. In order to make a tapered shape, we need to model 'body' of the shape in addition to surface details. For that purpose, zero plane component can be used. It is added automatically for rotary jobs.
Double-click zero plane component to open Component Properties. Enter 0.8 in the Base Height box. Select Tilt option. Click Set button in Tilt section, then switch to 2D view and then click in the middle left and then in the middle right. Set angle to 3 degrees.
Since the modelling plane was adjusted for placing component on the surface, it needs to be adjusted again, so the component body is not 'inflated'. To do that open Material Setup form. Adjust modelling plane by moving slider down, until Gap Inside Model is 0.
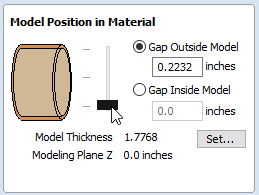
After modelling a tapered shape, the 3D model of column will have a desired shape. However clipart pieces in the narrower parts have been distorted, as can be seen below. To fix that, one need to stretch the components in the wrapped dimension, to compensate for distortion.
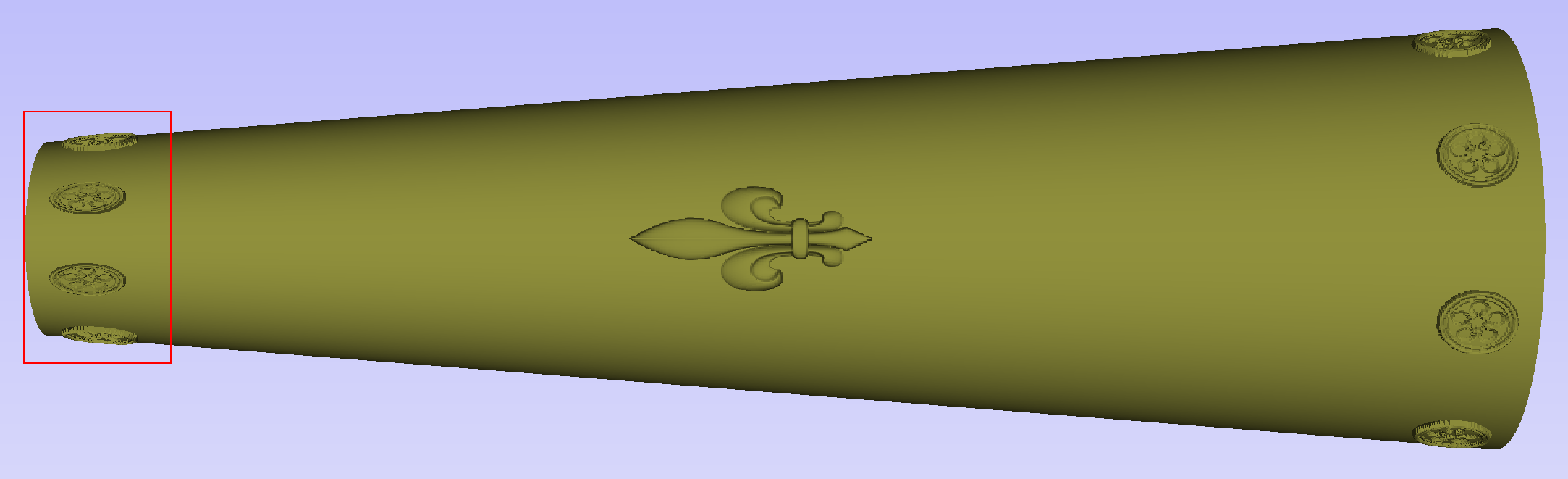
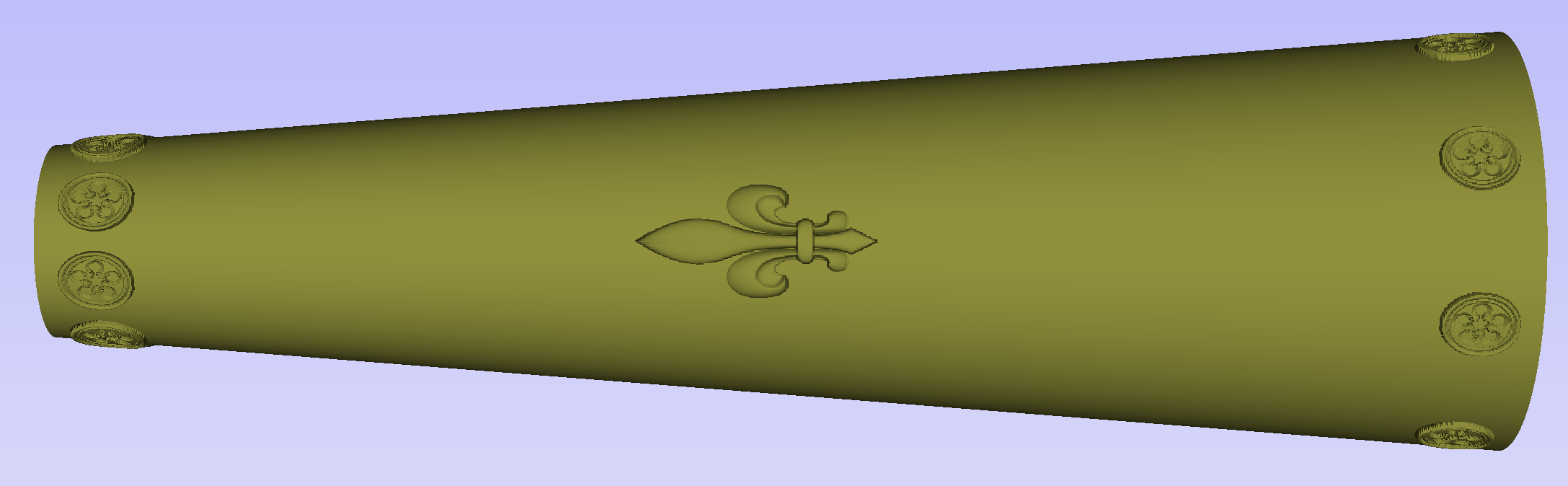
The distortion that has been demonstrated above, applies also to toolpaths. That means that wrapped toolpaths will match flat toolpaths only at the surface of the blank. The closer to the rotation axis (i.e. deeper) the toolpath is, the more it will be 'compressed'. This fact have a profound implication for 3D toolpaths. Consider the example shown below.
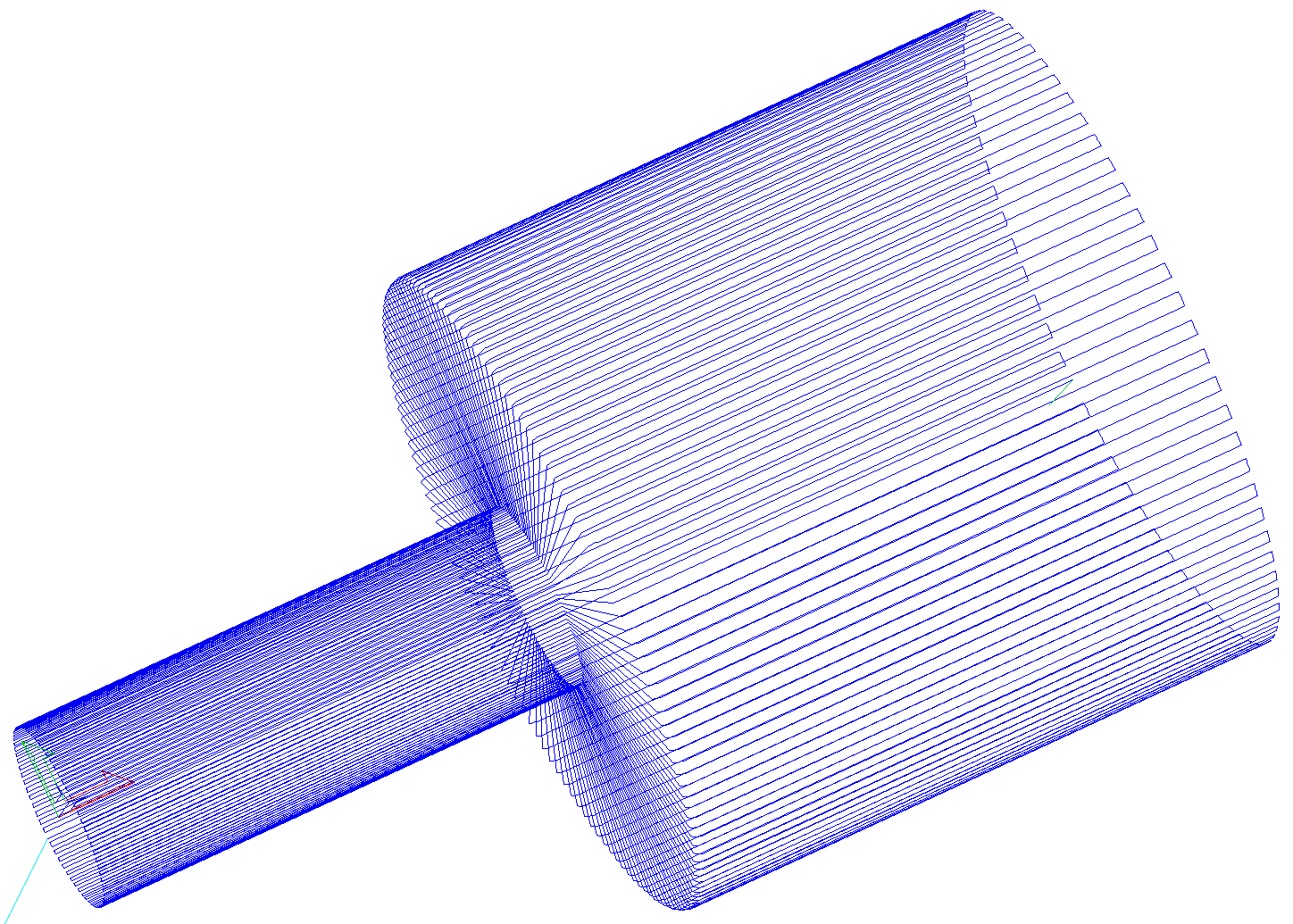
As can be seen if there is substantial difference in diameter in different parts of model, generating one 3D toolpath for whole model will result in wrapped toolpath being overly compressed. Thus it is usually better to create boundaries of regions with significantly different diameter and generate separate toolpaths using correct settings for each diameter.
Modelling turned shapes
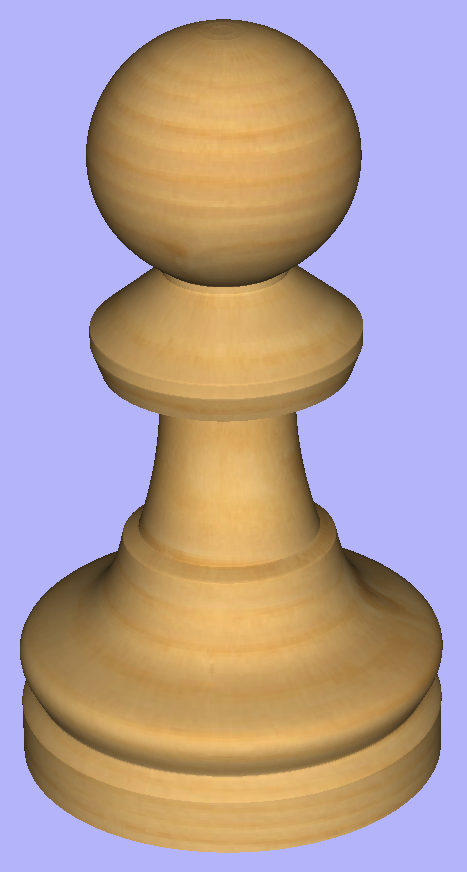

This section will present a basic technique for creating turned shapes.
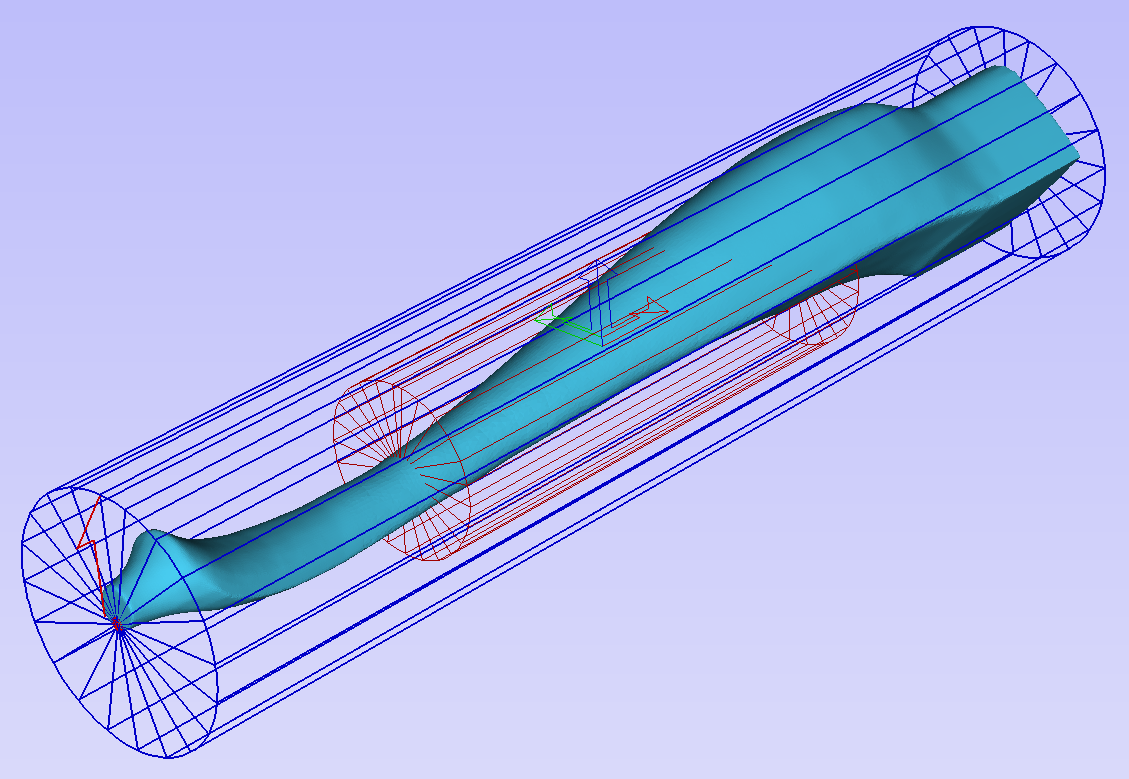
Modelling turned shapes is quite easy. It requires a vector representing a profile of the desired shape and a Two Rail Sweep tool.
To start, create a new rotary job. Then either draw a profile using available drawing tools or import profile vector. This example used a chess pawn profile, as can be seen below.
Open the Two Rail Sweep tool. When the rotary job is created, the software inserts a special layer called '2Rail Sweep Rails'. It contains two blue lines on the sides of the job, that are perpendicular to the rotation axis.
Select both of those rails and click Use Selection button. The rails will be highlighted. Then select the profile vector and click apply. Inspect the 3D view to verify the results.
Modelling cross section
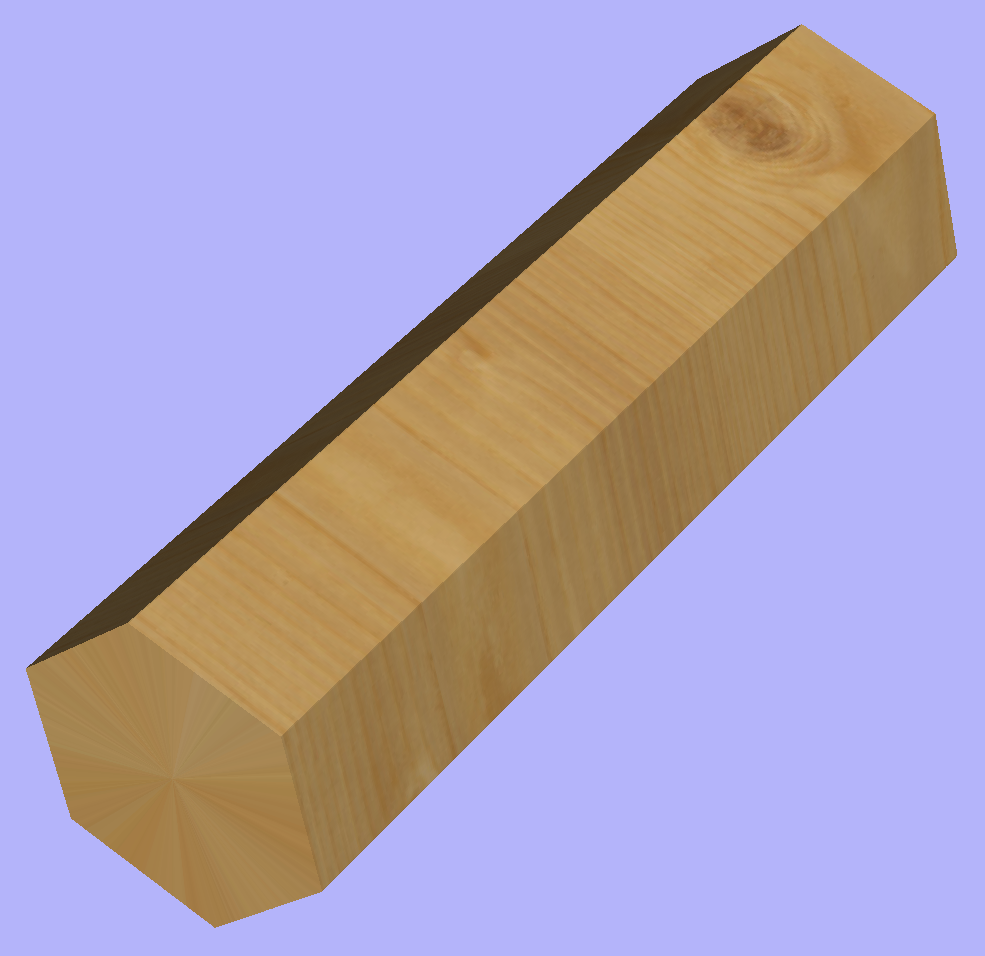

This section will explain how to model desired shape using Vector Unwrapper.
Vector Unwrapper is useful when rather than modelling a profile along the rotation axis, it is more intuitive to specify desired cross section. The tool transforms a vector, representing a cross section, into a profile vector that can be subsequently used with Two Rail Sweep tool.
Suppose we would like to create a hexagonal-shaped column. Let's start by creating a new rotary job. In this example job has a diameter of 6 inches and is 20 inches long. X axis is the rotation axis and Z origin has been placed on the cylinder axis.
We need to create a hexagon using Draw Polygon tool. This vector will serve as a cross section and can be placed anywhere in the 2D view. In this example the material block diameter is 6 inches, so the radius of the shape cannot exceed 3 inches.
When the shape is created, select it and open Vector Unwrapper. The tool will display a cross hair in place where the rotation axis is crossing the profile and a circle with the diameter of the material block. This will help you determine whether the shape with such cross profile will fit in current material block.
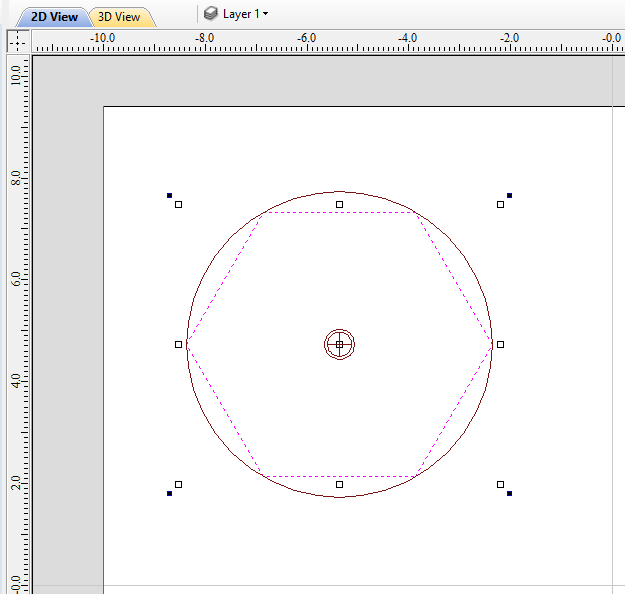
In this example, Use Center of contour option was used. That means that rotation axis will be placed in the centre of vector's bounding box. One can also tick Simplify unwrapped vectors option to fit bezier curves, instead of using series of very short line segments. After apply is pressed, the unwrapped version of the selected cross section will be created, as have been shown below.
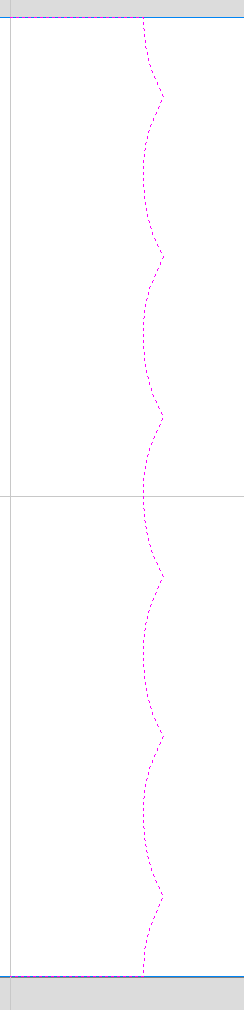
This example shows the unwrapped vector for a cylinder rotating around the X axis. If your rotary axis is aligned along Y the unwrapped vector will be horizontal. It is worth noting that unwrapped profile have 'legs' on each end. Those are needed to ensure that correct height will be used in the next step.
The tool automatically creates layer called 'Unwrapped Vectors Drive Rails' on which it places two blue line vectors on job sides, parallel to the rotation axis. In order to extrude the profile, open the Two Rail Sweep tool. Then select top and then bottom rail (left and right when Y axis is rotation axis) and confirm selection by clicking Use Selection button. Rails will become highlighted. Now click on unwrapped vector and press apply. The 3D view will show a hexagonal column, that can be seen at the beginning of this section.
Modeling Plane
The desired cross-section will only be achieved if modelling plane is positioned in cylinder centre. That means that Gap Inside Model is reported as 0 in Material Setup form. Otherwise the resulting model will have incorrect diameter and the cross section will become rounded.
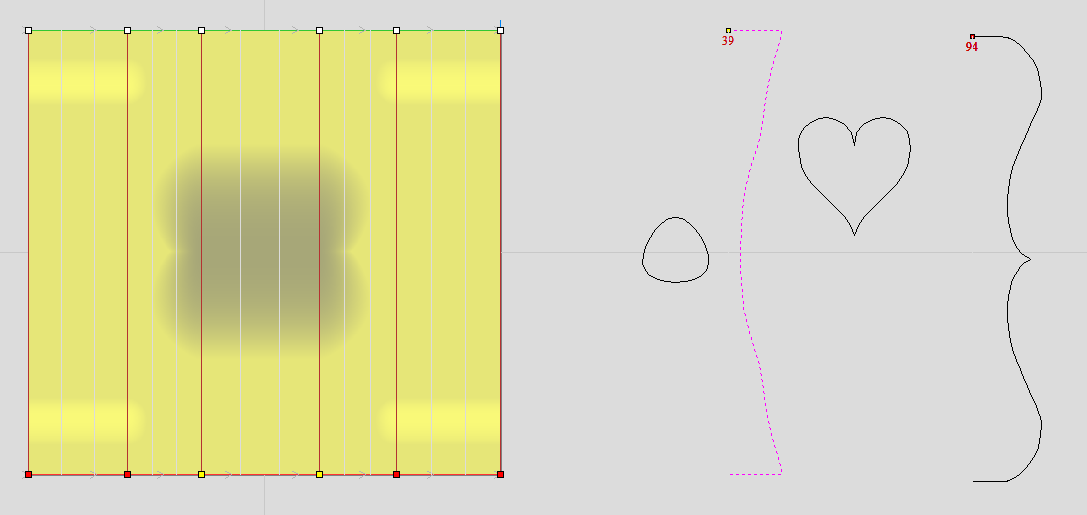
Vector unwrapper is not restricted to simple shapes. In principle it is always possible to use convex shapes and certain concave shapes. The example below shows a heart profile unwrapped.
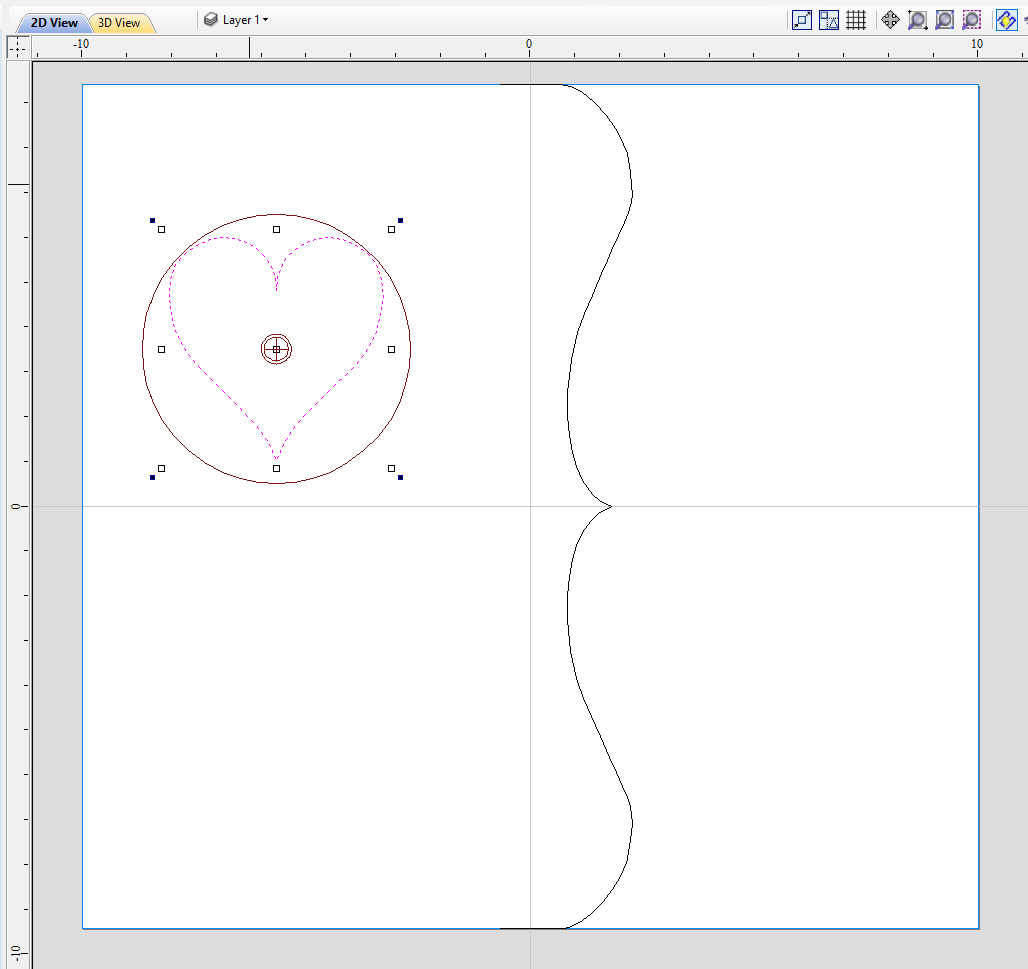
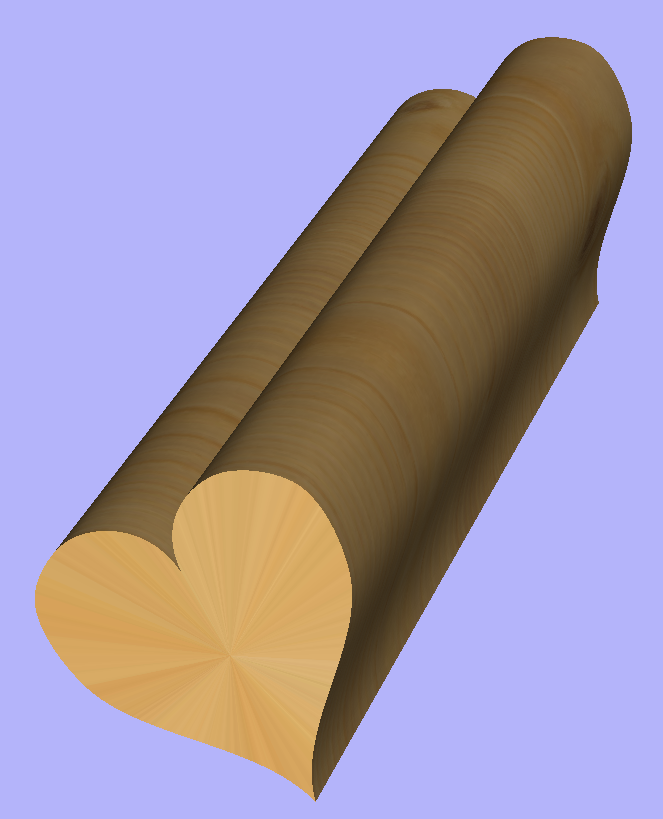
If cross section in question is concave, one could imagine straight line starting in the center of the shape and touching a point on the boundary. If the second points keeps travelling along the boundary and each line is not crossing another point on the boundary, then it is possible to use this cross section. If the line does cross more than one point on the boundary, this part of the cross section will not be represented correctly.
All the examples so far used a single cross section. However it is also possible to use multiple cross sections.
Let's take another cross section and open Vector Unwrapper. Then drag the rotation axis handle a bit down from the center. If snapping is enabled, it can be used to help position the rotation center, as can be seen below.
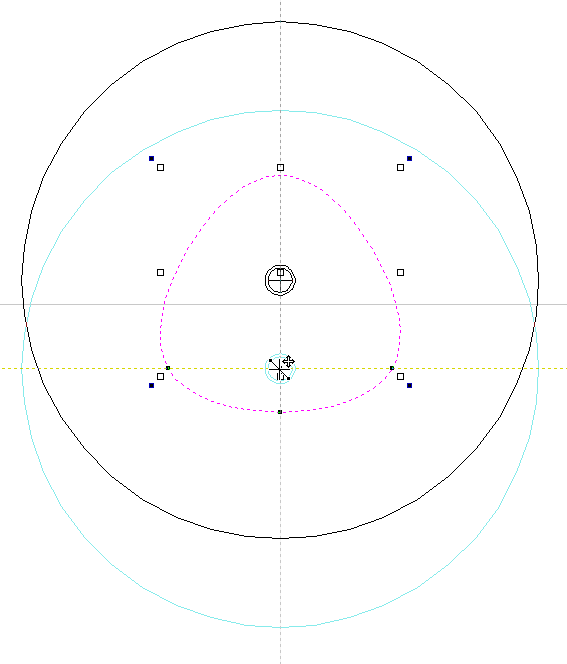
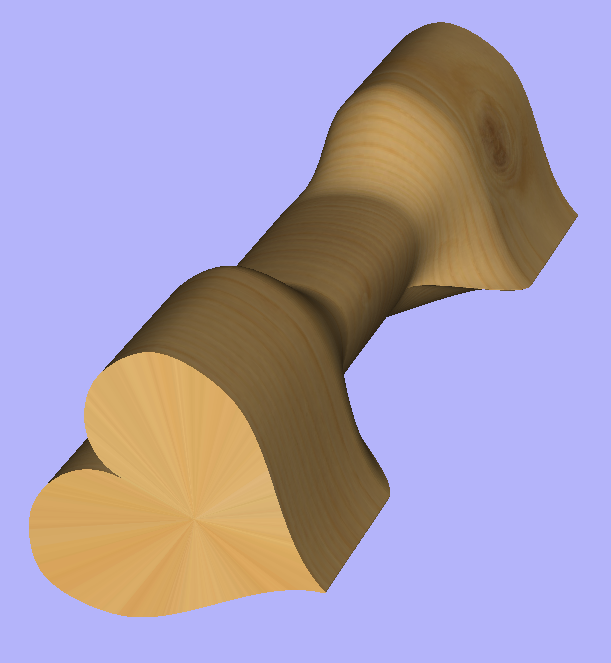
Once we have another unwrapped cross section, it is possible to use both during Two Rail Sweep. For example unwrapped heart profile can be placed twice on the left and twice on the right. The second unwrapped profile can be placed twice in the middle. Such arrangement may result in shape morphing, as can be seen below.
Text Selection
The Text Selection tool allows the user to adjust kerning, line spacing and bending the text on an arc. The text will be displayed as magenta lines with 2 Green handles in the middle for arching the text.
If the selected text was placed on a curve the handles will not appear, as such text cannot be arched.
Letter Kerning
The interactive kerning and line spacing cursor is shown when placed between letters or lines:
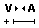
The interactive letter kerning allows default text to be modified so that adjacent pairs of letters sit more naturally together. A typical example is shown above where the capital letters W A V are placed next to each other and the default space is excessive.
Place the cursor between 2 letters and click the Left mouse button to close the gap.
Holding a Shift key and clicking the Left mouse button moves the characters apart.
Holding a Ctrl key when kerning doubles the distance each letter moves on each click.
Holding Shift and Ctrl keys together and clicking the Left mouse button moves the letters closer together in larger increments.
Line Spacing
Line spacing can be modified by placing the Edit Text cursor between lines. It will change to the line spacing cursor:
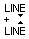
Clicking Left mouse button will move the adjacent lines of text closer together.
Holding the Shift key and clicking the Left mouse button will move the lines apart.
Holding the Ctrl key doubles the distance each line moves on each mouse click.
Holding the Shift and Ctrl keys together and clicking the Left mouse button moves the lines apart in larger increments.
Text Arching
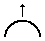
The interactive rotation and movement cursor is displayed when the cursor is placed over either of the Green Handles to indicate that the text can be arced either Upwards or Downwards:
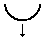
Click and Drag the Bottom Green box to arc the text Downwards.
Click and Drag the Top Green box to arc the text Upwards.
The text can easily be dragged back into the horizontal position again.
After arcing text, additional Red and Blue handles are displayed for Rotating and Moving the text.
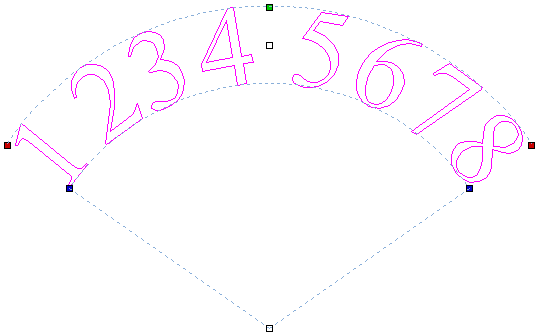
Moving
There are two white handles for moving the text, one in the middle of the text, and one in the center of the arc, though that may be off-screen for very shallow arcs.
Rotating
Clicking and dragging the Red boxes rotates the text around the center point of the arc.
Holding the Ctrl key forces the rotation to be in 15° increments. This allows the text to be positioned exactly on the horizontal or vertical quadrants, even after it may have been moved slightly.
Changing arc radius
Clicking and dragging the Blue boxes changes the radius without moving the arc center.
Circular Copy
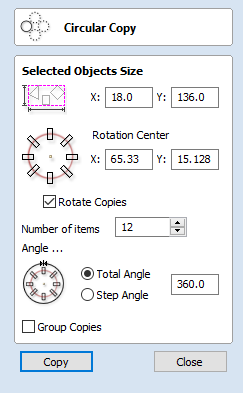
This tool will automatically create a repeating pattern by making copies of the selected object and positioning them around a full or partial circle. The number of copies to be made can be entered directly.
Selected Objects Size
Reports the current size of the selection that you are intending to copy. This is for information only, but the values can be selected, copied and pasted to use in other calculations.
Rotation Center
This is the absolute XY coordinate around which the objects will be rotated when copied and pasted. The default Rotation point is the middle of the selection. You can set the rotation center coordinates explicitly using the X and Y edit boxes on this form or by clicking the selected geometry to show the transform grips, then double-clicking the center one to show the pivot-point and dragging the Pivot Point handle associated with the selection in the 2D View:
Rotate Copies
This option controls whether the copied objects are each rotated as they are placed around the circle, as shown in the diagrams below. If this option is selected, each copy is rotated according to its position on the circle. If the option is not selected then each copy maintains the orientation of the originally selected object.


Angle
Total Angle
With this option selected the number of items is divided into the Total Angle to give the incremental angle between each object.
Step Angle
With this option selected this angle is used to copy the selected vector(s) by this angle x the number of Items.
Note
A negative step angle pastes the copies in a counter-clockwise direction. A positive step angle pastes in a clockwise direction.
Turn and Spin

The Turn and Spin tool allows you to create a 3D component by turning or spinning a cross section (an open vector)
Turn
Turn takes a profile and turns (rotates) it around line from start point to end point to create a rounded symmetrical shape. To turn a shape select the vector cross section you want to turn and use the Turn (Rotate) option, this cross section should represent the silhouette of the shape you wish to create. You can click to create your 3D turned shape.
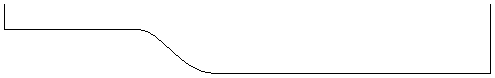
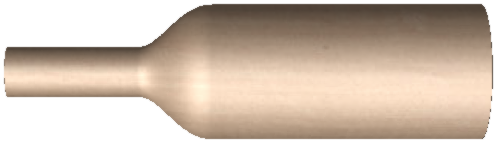
The profile to be turned can run beneath the line between the two end points
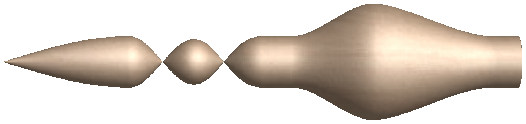
Spin
Spin takes a profile and spins it around the left end point of the cross section to create a circular component based on the profile shape of your cross section. To spin a shape select the vector cross section you want to spin around the left end point and click to create your 3D spun shape.


Note
The Spin Tool will always Spin around the left end point, which may require you to move your vector to the right side of your job to accommodate the vector being spun to create the spun shape.
Scale to Exact Height
Checking ✓ this option scales the shape calculated so its maximum height is the value entered in the Height area of the form.
Common Modeling Options
All of the main modeling tools in the software use a common set of commands to assign a name and combine mode to the component being created along with options to apply the settings in the form, reset the shape, start creating a new component and close to exit the function.
Combine with other components...
This section includes options to allow you to name your Component and control the way it will be combined with other objects in the Component Tree.
Reset
Clicking the button will remove the current shape, doing this before you Close the form will ensure that a component is not created from the current selection. Clicking this does retain the current set of selected vectors or Components.
Apply
Clicking the button will create a shape based on the settings you have chosen. You can continue making edits to the component by choosing different parameters within the form and hitting Apply to update it.
Start New Component
Clicking the button will save the state of the component that has been created, deselect all components/vectors and start the creation process again on a new component. The values and options within the form will be retained in this case until you Close it.
Close
Clicking the button will close the form returning to the Modeling Tab icons and the updated Component Tree, reflecting any changes that you have made. If you wanted to remove the shape you just created then you can hit the Undo icon or use the keyboard shortcut to undo, CTRL+Z.
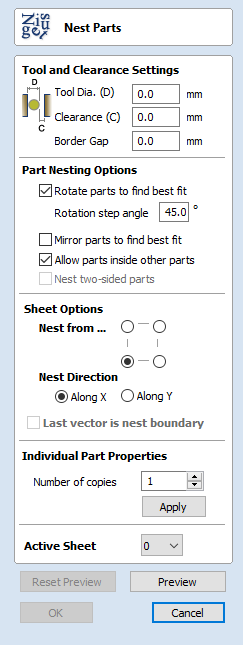
Nest Parts
The Nesting tool will automatically fit vector shapes within the user defined area in the most efficient way it can calculate (based on the user defined parameters). By default the area the vectors will be fitted is the current Job Size but it is also possible to select a vector as the nesting area. This is a powerful way to optimize material usage and increase toolpath efficiency when laying out and cutting a number of shapes.
Object Selection
The Nesting tool allows you to select open vectors, closed vectors, text and components.
Once selected the objects will form parts, with part outer boundary highlighted with a thicker line.
The basis for forming parts is overlapping. If selected object contains another or overlaps with it they will be considered the same part.
Note
Currently it is not possible to nest components and other objects at the same time.
Tool and Clearance Settings
The settings in this section of the form will determine the spacing which will be left between each of the nested vectors and also control how close they are to the edge of your nesting area.
Tool Dia. (D)
Enter the diameter of the tool that you will be using to Profile (cut-out) the vectors you are nesting. This is the minimum distance that will be left between shapes once they are nested.
Clearance (C)
The Clearance value will be combined with the specified Tool Diameter to create the final minimum spacing between the nested shapes. For example a Clearance of 0.05 inches combined with a Tool Diameter of 0.25 inches would create a minimum spacing gap of 0.3 inches (0.05 + 0.25 = 0.3).
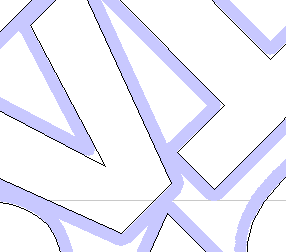
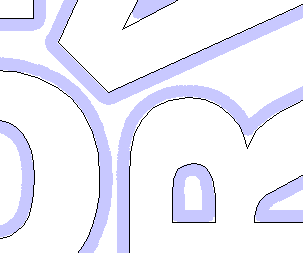
Border Gap
The Border Gap value is applied to the edge of the area which is being used to nest the vectors into. It will be added to the Clearance value around the edge of this shape to create the minimum distance that parts will be nested in respect to the nesting boundary.
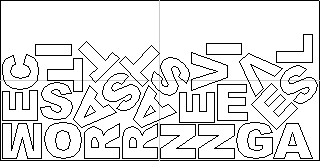
Part Nesting Options
The options in this area of the form will all directly affect how many parts or how efficiently it is possible for the software to fit shapes into the defined nesting area.
Rotate Parts to find best fit
Checking ✓ this option will allow the software to rotate the selected vectors in order to try and better fit them. The increments of rotation the software will use is based on the Rotation step angle.

Mirror parts to find best fit
Checking ✓ this option will allow the nesting to mirror (flip) the vectors in order to try and more efficiently nest the selected shapes. This should only be checked ✓ if the direction the parts are cut in is not important.
Allow parts inside other parts
Checking ✓ this option will allow the software to nest within the internal areas of shapes that have gaps in the middle.
When this option is active, the internal areas that will be considered in nesting will be highlighted.

Nest two-sided parts
This option is only available for double-sided projects and allows nesting on both sides simultaneously. When this option is active, any visible objects on the other side will be included, if they intersect with objects selected on active side.
When using this mode it is recommended to perform selection on the side that contains cut-out contours.
When part is selected, the included vectors on the other side will be highlighted as can be seen below.
Sheet Options
Nest From
This area of the form is used to define which corner the nesting will start in. There are four options which can be selected from the options in the form.
Nest Direction
The options in this area of the form are used to select how the parts will progress as they are positioned within the sheet. The best way to think of this (for the purposes of this section) is that they 'pour' out of the selected corner filling the sheet in one axis then advancing along the other defined axis (X or Y) .

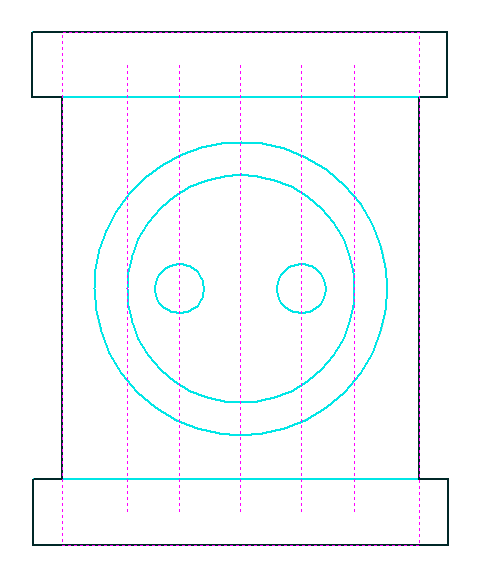
Last vector is nest boundary
Checking ✓ this option means the last vector selected will be used as the boundary for the nesting area. This can be useful if you need to define a non-rectangular shape to Nest Parts into, such as large off-cuts from a previous job. It's important to note that using this option will not respect the currently defined Job Area if the selected boundary vectors goes outside of it.
Note
If you need to represent a sheet with holes or other features which can't be represented with a single selected vector as the new boundary it is possible to also use a Grouped vector for the last selected item then the shapes will be nested within the spaces in this.
Individual Part Properties
If you want more than one incidence of a particular item then select it from the 2D view. In the box where it says Number of Copies enter as many copies as you want and hit and the selected vectors will be marked with a green number indicating how many copies of that item will be made when they are nested. Different shapes or groups of shapes can be assigned different numbers of copies. To stop an item being copied multiple times just set the Number of Copies back to 1 and click .
Active Sheet
This option lets you choose which Sheet of vectors is currently active, either for editing or applying toolpaths onto.
Slice Model
The slicing feature allows the user to divide the Composite Model into Z-Slices each of which will become a Component. This is for customers who need to cut a part which exceeds the Z depth of their machine gantry, the cutting length of their tools or the thickness of the material they are using. Once the slices have been cut on the CNC then they can be re-assembled to make the finished full depth part.
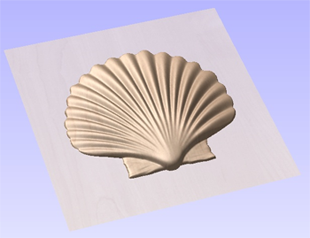
When this function is executed each slice will become a Component in the Component Tree and can then be moved into position and have toolpaths calculated on it. An example of this is shown in the images below, on the left it shows a scallop shell component that is 3 inches thick, the image below right shows this divided into two separate components, each a 1.5 inch slice of the original.
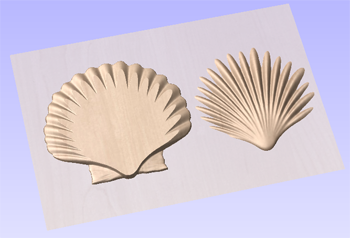
Note
Before using the Slice model command it is important to make sure that you hide any components that you do not wish to include in the operation.
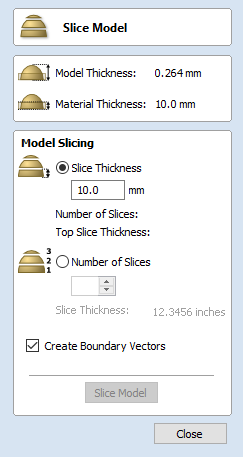
When the icon is clicked the Slice Model form will appear. This can be used to control the number and thickness of slices which will be created. At the top of the form it will display some reference information showing the thickness of the current Composite Model and also the currently defined Material Thickness (for machining).
Model Slicing
Slice Thickness
Checking ✓ this option will let you define a particular value for each slice. Right below this the Number of Slices will be displayed which is determined by the Composite Model thickness divided by the Slice Thickness. The model will be sliced from the bottom up and if the Composite Model thickness does not divide exactly by the Slice Thickness then the top slice may not be a whole number. To help indicate how the part is going to be divided the Top Slice Thickness is displayed in the form.
Example
If the Composite Model is 4.75 inches thick and you define a Slice Thickness of 2 inches then the software will create 3 Component slices - the bottom and middle slice will both be 2 inches thick and the top slice will be 0.75 inches thick.
Number of Slices
Checking ✓ this option will divide the model into a specific number of slices. The slice thickness will be determined by the Composite Model thickness divided by the Number of Slices defined. This may be a good option to use if the specific slice thickness is not important (for instance if it does not relate to material thickness).
Example
If the Composite Model is 3.96 inches thick and you define 3 Slices then the software will create 3 Component slices each 1.32 inches thick.
Create Boundary Vectors
Checking ✓ this option will cause the slicer to create vector boundaries for each slice. These can be useful for defining the subsequent machining regions required to cut each part. The boundary vectors will be placed on the same layer in the 2D View as the component preview for their associated model slice.
Slice Model
Clicking will apply the choices made in the form and create the Components which represent each slice of the Composite Model.
Note
The Component Tree will retain a copy of the original Components in the part as well as the new Slice Components. This may result in a very thick looking model as all the slices will be added to the original shapes. At this point you can delete, undraw or move Components before proceeding with any additional operations.
Close
Clicking will close the Slice Model form without completing the operation.
Trace Bitmap
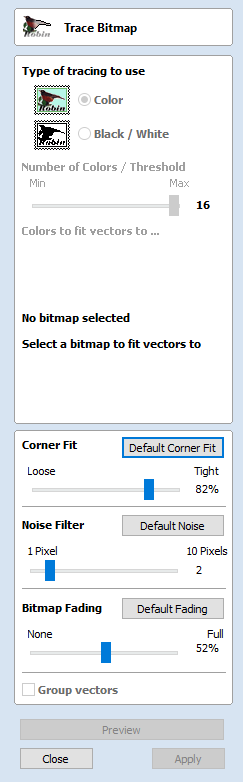
This tool automatically traces or fits vectors to image files so they can be machined. Use the Import Bitmap tool and select the image in the 2D view, then open Fit Vectors to Bitmap.
After importing an image the Tracing option allows vector boundaries to be created automatically around colored or black and white regions in the image.
Tracing a Selected Area of the Bitmap
You can define an area within the bitmap, such that only that part of the bitmap will be traced. This can be done by selecting the bitmap (if this hasn't been done already), and then clicking and dragging the mouse over the area you want, to define a rectangular region on the bitmap. This will be highlighted with a dashed black rectangle.
Clicking on the Bitmap again will remove a selected area if one has been specified, in which case, the entire bitmap will have vectors fitted to it.
Tracing Black and White Images
When working with Black and White images the slider can be used to change the Threshold and merge the levels of gray between all white (min), and all black (max).
When the image being displayed in the 2D view looks correct then clicking the button automatically creates vector boundaries either around the selected Trace Color or the grayscale.
Tracing Color Images

Color images are automatically reduced to 16 colors and the slider allows the visible number of colors to be set as required. Colors are merged with the closest match.
Colors can be temporarily linked together by clicking the check boxes next to each of the colors displayed. This changes the color displayed in the 2D view to the selected Trace Color. This is very useful for merging similar color's together to allow complete regions to be traced.
If a new Trace Color is selected the linked colors are displayed using this color in the 2D view.
The Reset button unlinks all the checked ✓ colors and the image displayed in the 2D view reverts back to the original 16 color image.
2D View
You can select the colours directly from the image in the 2D View.
Tracing a Selected Area of the Bitmap
You can define an area within the bitmap, such that only that part of the bitmap will be traced. This can be done by selecting the bitmap (if this hasn't been done already), and then clicking and dragging the mouse over the area you want, to define a rectangular region on the bitmap. This will be highlighted with a dashed black rectangle.
Clicking on the Bitmap again will remove a selected area if one has been specified, in which case, the entire bitmap will have vectors fitted to it.
Fitting-Options
The options available on this form control how closely the vectors fit / follow the selected color boundaries and these can be modified to obtain improved results.
Corner Fit
The Corner Fit control determines how accurately the vectors are fitted to the corner edges in an image.
Noise Filter
The Noise Filter slider controls the minimum size of pixels that are traced / vectorized, preventing small unwanted vectors or noise being created.
Bitmap Fading
Preview
This will preview the result of the tracing of the bitmap. If you are not happy with the result provided, you can alter the settings and click on the button again to get an updated result.
Apply
When you are happy with the result of the preview you can click on the button to keep it.
How to Get Started
The first stage in any project is to create a new blank part or import some existing data to work with. At this stage a number of parameters need to be defined relating to the size of the part and its position relative to the datum location on the CNC machine. Later, once the part has been defined and you have started working, you may want to change the size of the material, import additional data and generally manage the project operation. In this section of the manual the initial creation of a part will be covered along with all the icons which appear under the File Operations section of the Drawing Tab.
When you first start the program you will see the Startup Task options on the left hand tab and also a list of your 4 most recently opened Aspire parts (this is a rolling list that will be populated each time you run the software and may initially be empty).
Startup Tasks and Recently Opened Files
When you first start the program you will see the Startup Task options on the left hand tab and also a list of your most recently opened Aspire parts.
The first choice is whether you want to Create a new file or Open an existing one. Creating a new file allows you specify a size and location for a blank work area, set your material thickness and also set the model quality and even the shading color/material. The process to do this will be covered in the next section (Job Setup Form Options).
The second choice, Open an Existing File, will allow you to open a pre-created file from your computer. This may be a file you previously created (*.crv3d or *.crv). Alternatively, it might be a 2D vector layout from another CAD system (*.dxf, *.eps, *.ai and *.pdf). A CRV3D or CRV file will have the necessary information for material size etc. already embedded in it. The 2D formats will import the data at the size and position it was created but will require you to go through the Job Setup form to verify/edit all the parameters for the part.
Video Tutorials
The Tutorial Video Browser will open your default web browser (typically Internet Explorer, Chrome or Firefox - depending on your Windows setup and personal preference). The web browser offers a number of tutorial videos and associated files, presented either by project or feature category to help you to learn about the software. You will initially need internet access to watch or download the videos or files, but, once downloaded, the materials can be used offline.
Online Resources
This section includes direct links to useful websites and web resources - including clipart and projects for you to purchase, download and incorporate into your own designs. These links will also open in your default web browser and you will need internet access to use them.
Interactive Vector Trim
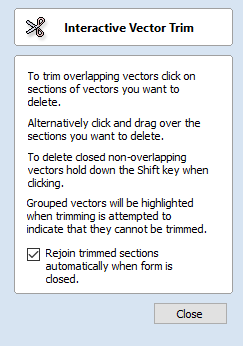
The interactive trimming tool allows the user to just click on sections of vectors they want to delete.
The program finds the closest intersections either side of the clicked portion of the vector and removes the piece of the vector between the intersections. Optionally, when the form for this command is closed, the program can rejoin all the remaining trimmed pieces automatically.
Without using this tool, to remove an overlapping section of a vector, the user would need to insert extra nodes into both vectors, manually delete the intermediate sections and then manually join the resulting pieces. These operations can be performed with a single click using this tool.
When the tool is selected the cursor changes into a 'closed' scissor shape. When the cursor is moved over a vector suitable for trimming the scissors 'open' to show you can click and trim.
If there are lots of vectors to trim then the left-click mouse button can be held down and then when the cursor is dragged and hovers over a vector then it will also trim the vectors. This can be much quicker than individually clicking spans.
Note
If you try to trim a group then the group will flash pink. This indicates that it cannot be trimmed unless it first has to be ungrouped
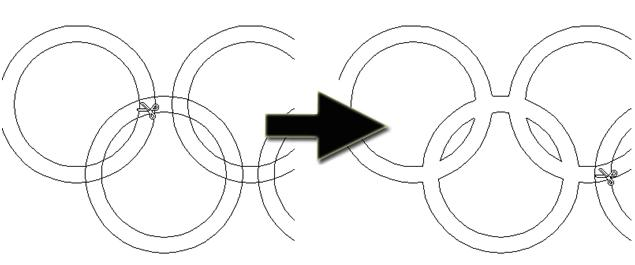
Rejoin Trimmed Sections
Allows the user to select whether the program will automatically try to rejoin trimmed vectors when the form is closed. For most simple cases like that shown above with the overlapping rings, this option can be left checked ✓. If you have an example where for instance many trimmed lines meet at the same point, you may want to uncheck this option and rejoin the vectors manually.
Job Setup - Single Sided
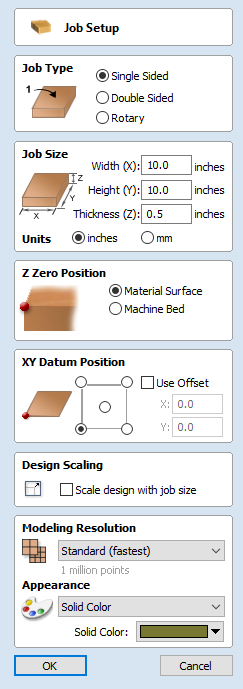
The Job Setup form is displayed whenever a new job is being created, or when the size and position of an existing job is edited.
The size forms may be limited
In most cases a new job represents the size of the material the job will be machined into or at least an area of a larger piece of material which will contain the part which is going to be cut. Clicking OK creates a new empty job, which is drawn as a grey rectangle in the 2D View. Dotted horizontal and vertical Grey lines are drawn in the 2D design window to show where the X0 and Y0 point is positioned.
Job Type
Single Sided job type should be used when design only requires the material to be cut from one side. This is the simplest type of job to design and machine.
Double Sided Job type is useful when it is desired to cut both sides of your material. Aspire allows you to visualise and manage the creation and cutting process of both sides of your design within a single project file.
Rotary job type enables the use of a rotary axis (also called a 4th axis or indexer).Aspire will provide alternative visualisation, simulation and tools appropriate for rotary designs.
Job Size
This section of the form defines the dimensions of the material block you will be using for your project in terms of width (along the X axis), height (along the Y axis) and thickness (along the Z axis).
It also allows you to select which units of measurement you prefer to design in - either inches (Imperial/English) or millimeters (Metric).
Z-Zero Position
Indicates whether the tip of the tool is set off the surface of the material (as shown in the diagram) or off the bed / table of the machine for Z = 0.0.
XY Datum Position
This datum can be set at any corner, or the middle of the job. This represents the location, relative to your design, that will match the machine tool when it is positioned at X0, Y0. While this form is open, a red square is drawn in the 2d view to highlight the datum's position.
Use Offset
This option allows the datum position to be set to a value other than X0, Y0.
Design Scaling
When editing the Job Size parameters of an existing job, this option determines whether any drawings you have already created will be scaled proportionally to match the new job dimensions. If you wish to preserve the existing size of your drawings, even after the job size has changed, leave this option unchecked. With this option checked, your drawings will be re-sized to remain in the same proportion and relative position within your new material extents when you click
Modeling Resolution
This sets the resolution/quality for the 3D model. When working with 3D models a lot of calculation and memory may be required for certain operations. Setting the Resolution allows you to choose the best balance of quality and speed for the part you are working on. The better the resolution quality chosen, the slower the computer will perform.
As this is completely dependent on the particular part you are working on and your computer hardware performance, it is difficult in a document like this to recommend what the setting should be. Generally speaking, the Standard (fastest) setting will be acceptable for the majority of parts that Aspire users make. If the part you are making is going to be relatively large (over 18 inches) but still has small details, you may want to choose a higher Resolution such as High (3 x slower) and for very large parts (over 48 inches) with small details then the Highest (7 x slower) setting may be appropriate.
The reason that the detail of your part needs to be taken into account is that if you were making a part with one large item in it (e.g. a fish) then the standard resolution would be OK but if it was a part with many detailed items in it (e.g. a school of fish) then the High or Highest setting would be better. As previously stated these are extremely general guidelines as on slower/older computers operations with the highest setting may take a long time to calculate.
As the Resolution is applied across your whole work area it is important to set the size of your part to just be big enough to contain the part you plan to carve. It would not be advisable to set your material to be the size of your machine - e.g. 96 x 48 if the part you plan to cut is only 12 x 12 as this would make the resolution in the 12 x 12 area very low.
Importing External Models in a Rotary Project
Importing Full-3D models
This section will present the process of importing the Full-3D STL model into rotary project, using a table leg as an example.
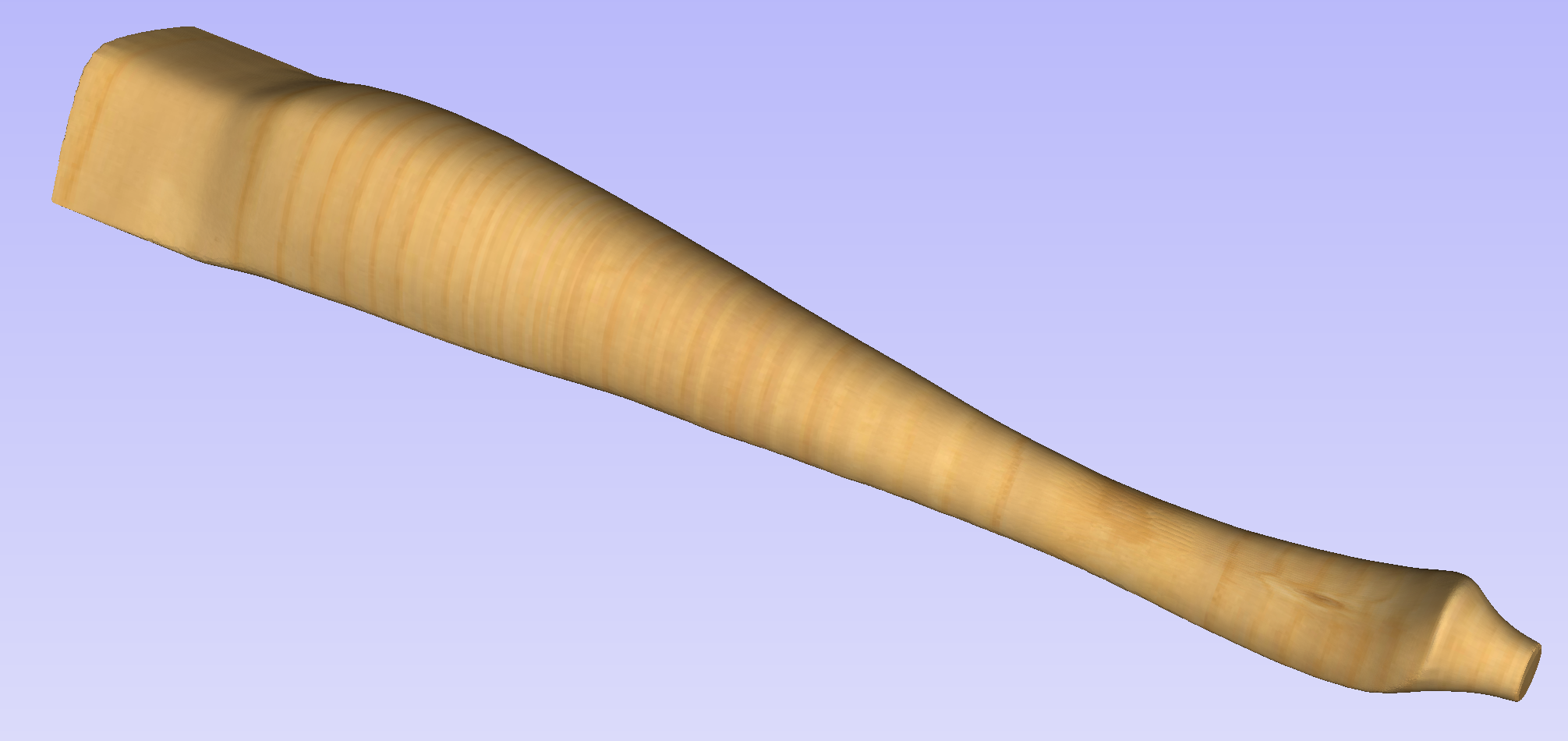
Overview
There are two basic use cases when importing an external model into the rotary job. The first case involves bringing a model designed for this particular job in another software. Thus the dimensions of the imported piece may already be correct and it can be desired to use them for the size of project. The second use case is when importing a stock model that would have to be scaled to fit on particular machine.
Aspire uses following workflow that covers both of those cases:
- Setting-up rotary project
- Choosing file for import
- Orientating the model in material block
- Scaling the model
- Finishing the import
Setting up a rotary project
Create a new job using the Job Setup form. It is important to set the job type as rotary to ensure a proper import tool is used in the next step.
If the dimensions of the project are already known, they could be specified directly.
If it is desired to fit the model to a given machine or stock available, set both the diameter and length to maximum. During import the model will be scaled to those limits.
If it is desired to use the imported model size, any size can be specified at this time. During the model import the project can be automatically resized to match the model dimensions.
In this example it was desired to fit the model into a specific stock size with a Diameter of 4 inches and a Length of 12 inches. XY origin was set to centre.
Importing the file and orientating it
To start the importing process, use Import a Component or 3D Model tool from the Modelling tab
Make sure that the Imported model type is set to Full 3D model .
The first step is to position the imported model within the material. This step is necessary as this information is not present in the imported file. When the model was opened, the import tool chose the initial orientation, as can be seen below.
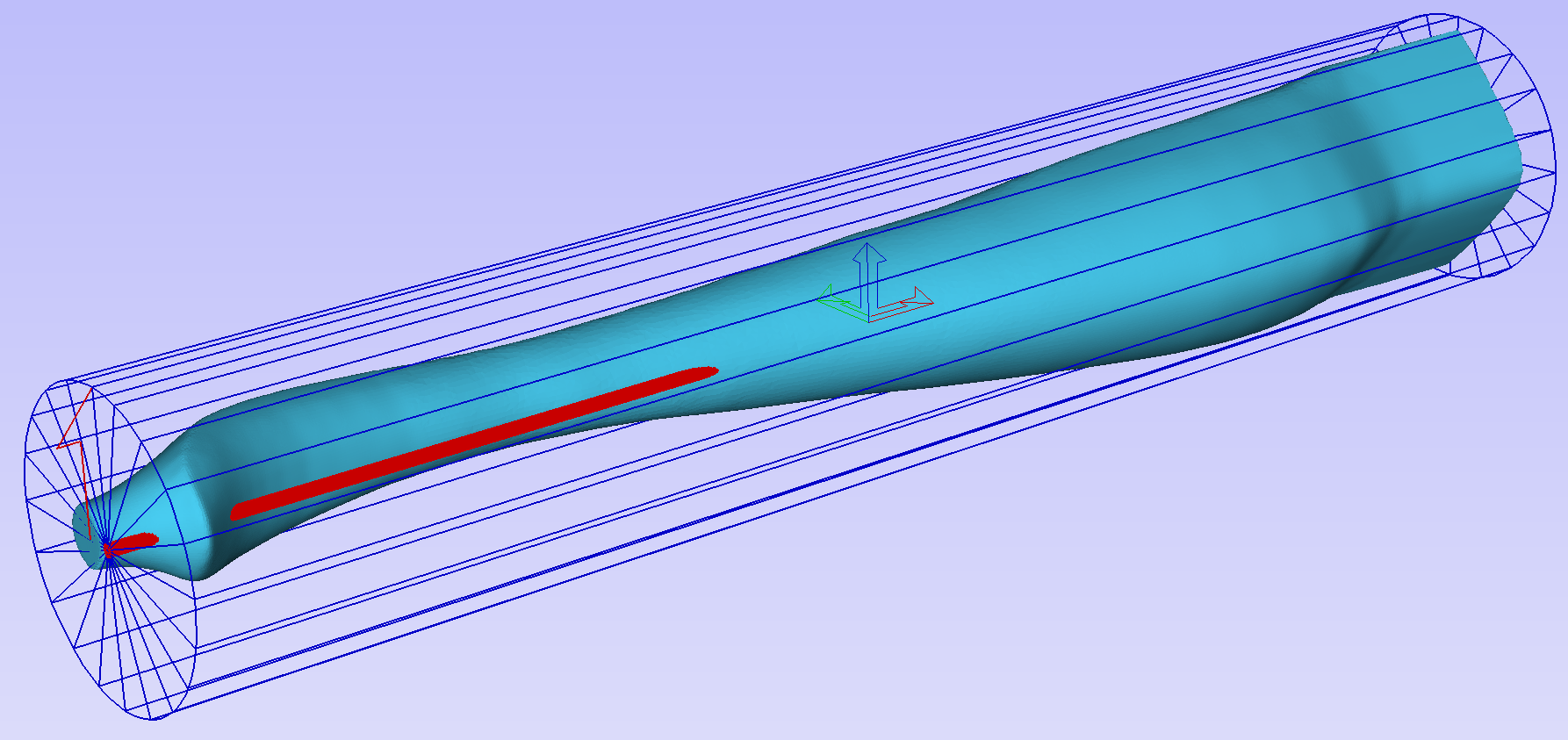
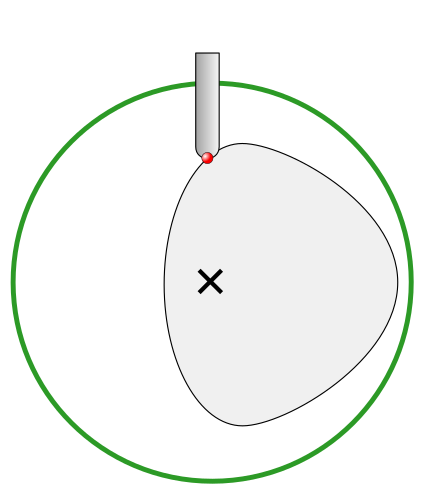
To help with orientating the model, the software displays a blue bounding cylinder. This cylinder has the rotation axis aligned with that defined for the material block and thus can be used as a reference. Its size is just big enough to contain the imported model at the current orientation. When the model orientation is changed, this blue cylinder will shrink or grow so it always contains the model. At this stage its exact dimensions are not important, as we are only interested in positioning the model correctly.
The software also highlights the rotation axis in red. This is particularly important when importing bended models. It is currently not possible to represent areas of model that are entirely below or above the rotation axis. This is the case in the example shown here. If the model was imported as is, the distortion would be created as can be seen below. Therefore it is important to position the model in a way such that the rotation axis is contained within the model.
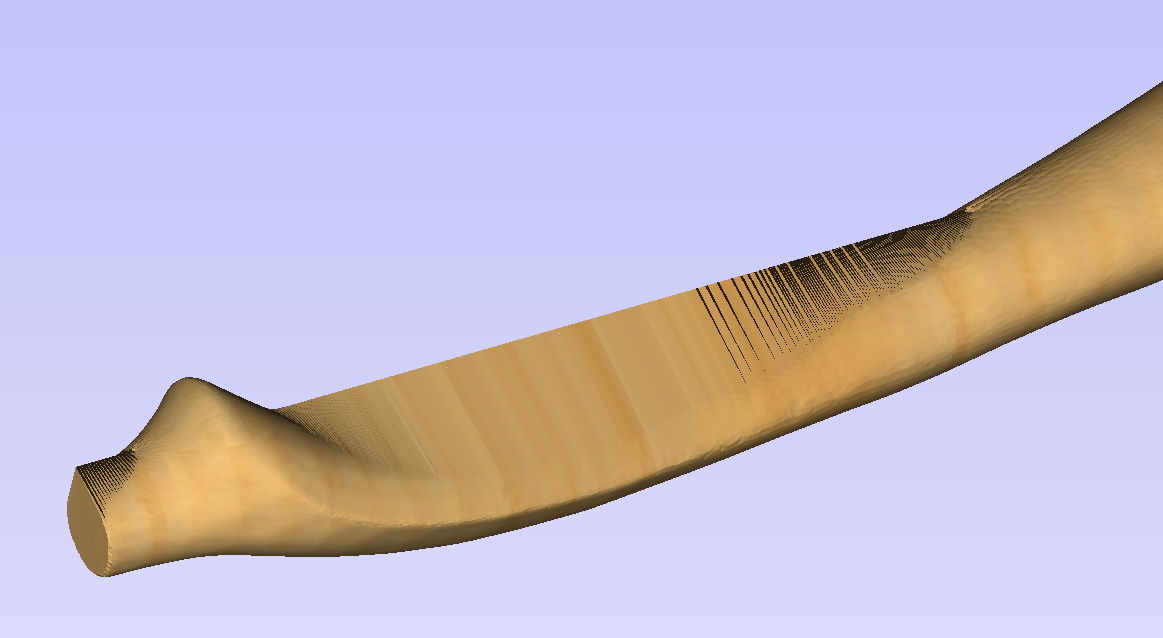
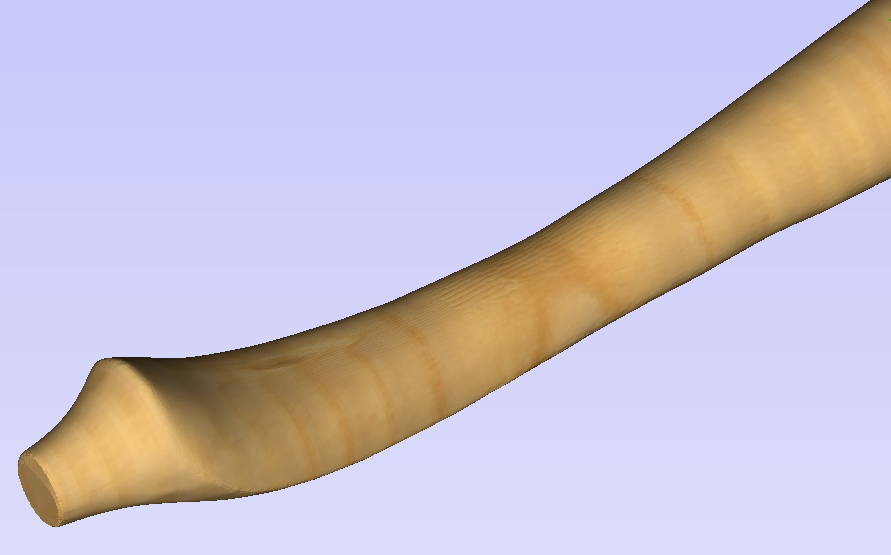
The last guiding element displayed by the software is the red half arrow on the side of the cylinder. This arrow is indicating the position that corresponds to the center of the wrapped dimension in the 2D view. In this example the model is orientated in such a way, that front of the leg would be placed on side of the 2D view, rather than centre. Thus it is better to rotate model so this arrow points to the front of the imported model.
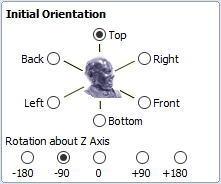
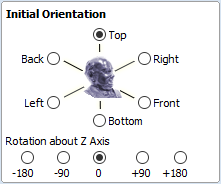
The import tool provides a few ways of adjusting the model orientation. The most basic one is the Initial Orientation. This can be used to roughly align the model with the rotation axis. This can also be combined with the Rotation about Z Axis.In this example the tool chose Left with no rotation. In order to align the front of the leg with the red arrow, one could use the Front and -90 as the Rotation about Z Axis.
Once the initial orientation is decided, further adjustments can be made using the Interactive Rotation. The default option - XYZ View - disables the interactive rotation. That means that the 3D view can be twiddled with a mouse. Selecting other options enables the rotation around the specified axis.
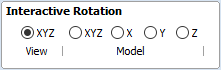
In this example, instead of changing the initial orientation to align the front of the leg with the red arrow, one could select X Model option and rotate the piece manually. When selecting single axis rotation, the 3D view will be adjusted to show that axis pointing towards the screen. If any mistake is made, it is possible to undo rotation using Ctrl+ Z
Notice that whenever the part is rotated, it is always centered in the cylinder. In this example it is not desired, since we need the rotation axis to be contained within the model. In order to move the model in relation to the rotation axis, one can use the Rotation Axis Movement
Similarly to the previously described tool, when Rotation Axis Movement is set to Off, the 3D view can be panned
Correctly positioning the model for importing may require a combination of the Rotation Axis Movement and the Interactive Rotation to achieve desired results with models that bend. It is important to make sure that rotation axis is hidden in order to avoid distortion. However it is also desirable to have the rotation axis being in the center of each segment of the piece to ensure tool has angle close to the optimal during machining. Usually it is also useful to rotate the model in view around the axis after the adjustment, as this allows us to inspect the model from each side without the need to disable the Interactive Rotation before changing the viewing angle.
It is important to understand that Aspire does not support 4-axis machining. That means that while the machined piece can be rotated and tool moves along the rotation axis and in the Z direction, it is not possible to move the tool in the wrapped dimension and thus the tool is always above the rotation axis and cannot be moved to the side.
This limitation is shown below. The first picture presents correct machining of the point. If the tool moves to another location though, the angle will be incorrect and even worse, the tool side will be touching the stock.
Scaling imported model
Once model has been positioned as desired, its size can be taken into account.
By default the tool will assume that imported model is using the same units as the project. If that is not the case, model units can be switched. In this example project was set-up in inches, while imported model was designed in mm. After switching model becomes considerably smaller and a red cylinder, representing current material block is shown, as can be seen below.
At this point it is possible to specify the model size, in terms of diameter and length. This can be done manually by typing desired dimensions, or by fitting to material. If Lock ratio option is selected, the ratio between diameter and length is kept. One can also tick Resize material block option. If it is selected, the material block will be scaled to match current size of the model, after OK is clicked.
If it is desired to use model size as material block size, one can just make sure units are correct, then tick Resize material block option and press OK.
If it is desired for the model to fit material, one could click Scale model to fit material and tick Resize material block.
In this example model was fitted to material. Since in this case length of the piece is limiting factor and lock ratio is maintained, this results in model having considerably smaller diameter than material block. Hence Resize material block option was ticked.
Finishing import
After pressing OK the model will be imported as a component. It is possible to modify it as any other component or add pieces of decorative clipart onto its surface if desired.
It is important to keep in mind the distortion caused by the wrapping process. That means that wrapped toolpaths will match flat toolpaths only at the surface of the blank. The closer to the rotation axis (i.e. deeper) the toolpath is, the more it will be 'compressed'. This fact have a profound implication for 3D toolpaths. Consider the example shown below.

As can be seen if there is substantial difference in diameter in different parts of model, generating one 3D toolpath for whole model will result in wrapped toolpath being overly compressed. Thus it is usually better to create boundaries of regions with significantly different diameter and generate separate toolpaths using correct settings for each diameter.
Importing Flat Models
This section will present a process of importing Flat STL model into rotary project. Flat models are similar to decorative clipart pieces provided with Aspire and are supposed to be placed on the surface of modelled shape.
To start the importing process, use Import a Component or 3D Model tool from the Modelling tab
Make sure that Imported model type is set to Flat model
Again the first step is to select proper orientation of model. The tool will chose initial orientation and display model in the red material box. This box corresponds to the 'unwrapped' material block and its thickness is equal to half of the specified diameter of the blank.
If model is not oriented correctly, that is, does not lie flat on the bottom of the material box, as can be seen above, orientation have to be adjusted. To do that one can change Initial Orientation option and/or Rotation about Z Axis.
If the imported model is not aligned with any of the axes, it may be necessary to use Interactive Rotation. The default option - XYZ View - disables interactive rotation. That means that 3D view can be twiddled with a mouse. Selecting other options enables rotation around specified axis.
Each rotation can be undone by pressing Ctrl+ Z.
Once model is properly orientated, units conversion can be performed. By default the tool will assume that imported model is using the same units as the project. If that is not the case, model units can be switched.
There is also model scaling option included. When Lock ratio option is selected, the ratio between X, Y and Z lengths are kept. Note that once model is imported, it will be added to project as a component. Hence correct placement, rotation and sizing can be performed later, after model is imported.
If the project does not contain any models yet, following message will be displayed:
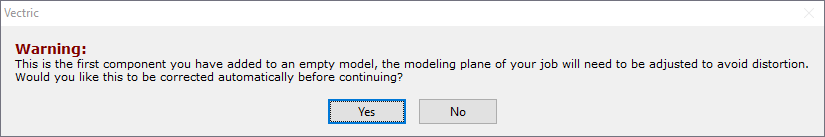
Typically you could simply click Yes.The more detailed explanation about modelling plane adjustment has been provided in Modelling 3D rotary projects
Crash Handling
In the unfortunate event of the software crashing,
- We try to save unsaved changes, so that your data isn't lost.
- Provide an easy way for you to report the crash so that we can work on a fix.
Project Saving
If you're working on a job and the software crashes, the first thing it will try to do is to save your project. The project will be saved alongside your original to avoid accidentally corrupting your original file.
Report the crash
A dialog will pop up asking you to upload the crash information which will help us track down the issue. Any information you can think of would be greatly appreciated and will help us fix the issue in a timely manner.
Description
Please try to remember what you were doing at the time, and describe it for us. Please include any information you can think of. Any bit of information can help us track the issue quicker, so we greatly appreciate that.
Information
You can include your name and e-mail to allow us to get back to you with questions in case we need more information. For example, we may need the project that you were working on. This data will not be used for any purpose other than to help us track down the issue.
Internet
You will need to be connected to the internet for this to work. If not, you can still send the generated zipped report to support@vectric.com. The report can be found in the Application Program Data (Accessible through the menu File ⇛ Open application data folder.... If you try to send the report and it fails, you will get a message of where that path is and possible methods to get that report to us.
The crash reporting is powered by BugSplat (a third-party) company which provides us with the tools that help us analyse them.
Auto Layout Text
This option automatically sizes a block of text to fit inside the boundary box (width and height limits) of a selected vector or vectors. If no vectors are selected the text is scaled to fit the size of the material.
Entering Text
The procedure for Drawing Text in the 2D Window is:
- Select the vector inside which the text is to be fitted
- Click the Draw Text icon
- Enter the required text content
- Select the font either True Type or Single Line as required and alignment options
The button opens a larger text entry window that makes it easier to enter text that needs to run on longer line lengths.
Font Selection
Vertical Fonts
Fonts that start with the @ character are drawn vertically downwards and are always left justified
Engraving Fonts
The Single Line Radio Button changes the Fonts list to show a selection of fonts that are very quick to engrave.
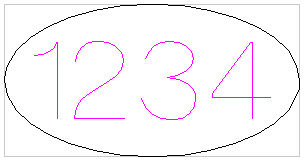
This example shows text (in an Engraving Font) drawn in an ellipse. The bounding box of the ellipse is used for the layout:
Text Alignment
Positions text relative to the selected bounding box or material size with options for left, center and right aligned.
Bounding Box Dimensions
These are the actual size of the box into which the text will be fitted. If the text is scaled interactively (by left clicking twice on the text) or precisely using the scale tool, the new bounding box is updated and displayed as a light gray rectangle.
Margin Size
The distance between the text and the bounding box where:
- None - Scales text to fit the rectangle width or height of the bounding box
- Normal - Scales text to fit within 80% of the bounding leaving a 10% border to the left and right.
- Wide - Reduces the size to 60% of the rectangle width leaving a 20% border to the left and right.
Vertical Stretch
When the text fits the width of the box and there is space above and below it, the text can be made to fill that vertical space using one these methods:



Horizontal Stretch
When the text fits the height of the box and there is space at the sides, the text can be made to fill that horizontal space using one these methods:

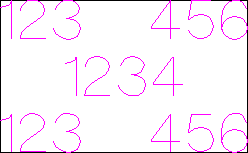
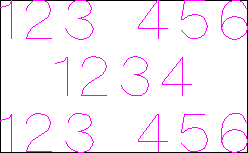
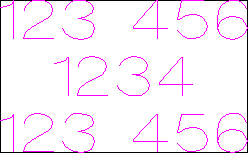
Edit Text
To edit text properties or content of previously created text:
If the Create Text form is open, click the text you wish to edit or
If the Create Text form is closed, click the left mouse button on the text in the 2D View to select it before opening this form. The form will now allow you to edit the properties of the selected text.
Edit Picture
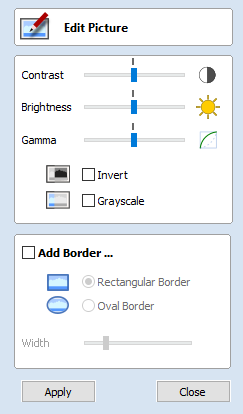
The Edit Picture form allows you to add a border to, and edit the properties of a selected bitmap.
Contrast
This slider adjusts the contrast. A higher contrast emphasises the differences between the light and dark parts of the image.
Brightness
This slider adjusts the brightness of the image.
Gamma
This slider adjusts the gamma correction applied to the image. This can make an image look lighter or darker whilst maintaining detail.
Invert
Inverts the colors in the image. White becomes black and black becomes white
Grayscale
Makes the image black and white.
Add Border


Fades the edges of the image based on the border type and the width of the fading.


Draw Star
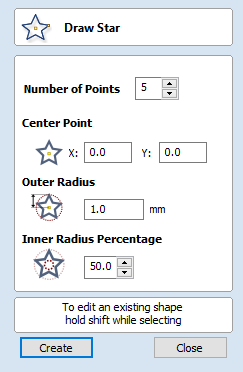
Stars can be created interactively with the cursor and Quick Keys, or by entering the number of points, exact coordinates and outer radius and inner radius percentage using typed input.
Interactive Creation
The quickest and easiest way to create a star is by clicking and dragging the shape to size in the 2D View using the mouse.
- Click and hold the left mouse button to indicate the center point.
- Drag the mouse while holding down the left mouse to required radius.
- Release the left mouse button to complete the shape.
Note
Holding Alt and dragging creates a star from the middle point.
As the cursor is dragged across the screen so the outer radius is dynamically updated. The increments will depend upon your snap radius and the job size.
Quick Keys
Instead of releasing the left mouse button when you have dragged your shape to the required size, you can also type exact values during the dragging process and set properties precisely.
- Left-click and drag out your shape in the 2D View.
- With the left mouse button still pressed, enter a quick key sequence detailed below.
- Release the left mouse button.
Default
By default, entering a single value will be used to set the outer radius of your star. While you are dragging out the star, type Radius Value Enter to create a star with the precisely specified outer radius.
Example
- 2 . 5 Enter - Creates a start with an outer radius of 2.5 all other settings as per the form
Specifying Further Properties
By using specific letter keys after your value, you can also indicate precisely which property it relates to.
Note
When specifying multiple properties with quick keys, it is still important that they are entered in the order indicated in the table below.
- Value D - Creates a start with the outer Diameter (D) specified with all other properties as per the form
- Value I Value R - Creates a star with the inner radius percentage (I) and the outer radius (R). The inner radius is defined in terms of a percentage of the outer radius or diameter. All other properties are as per the form.
- Value P Value R - Creates a star with the specified number of points (P) and the outer radius (R).
- Value P Value I - Creates a star with the specified number of points (P), inner radius percentage (I) and the outer radius (R).
Examples
- 1 R - Outer radius 1, other properties as per form
- 1 D - Outer diameter 1, other properties as per form
- 6 P 1 R - A 6 pointed star with an outer radius of 1
- 6 P 2 5 I 4 D - A 6 pointer (P) star with an outer diameter (D) of 4 and an inner diameter that is 25% of the outer (i.e. 1).
Exact Size
Stars can also be drawn by entering the Number of Points, Center Point, Outer Radius and Inner Radius Percentage.
- Click to update the star.
Help
Help Contents | Displays an online version of the full reference manual that documents every feature and option available in the software. Note The reference manual is not intended as a User Guide or introductory training resource - please don't forget about the Getting Started guides and the extensive video tutorial library on your install media. |
Keyboard Shorcuts | Displays the Shortcut Keys |
Video Tutorial Browser... | Access the tutorials |
What's New | See a summary of the new features added in major and minor updates. |
Release Notes | See the list of issues fixed and enhancements in patch updates. |
Third Party Licences | Display a list of all the third party software used to help create Aspire for ALPHACAM. |
Enter License Code | Displays the License Dialog used for entering license or module details. |
View the Vectric Online FAQ... | Displays the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
View the Vectric User Forum... | Opens the Vectric User Forum in your Web Browser if you have an Internet Connection. Everyone should join the Forum to engage with other users and benefit from each others tricks and tips! |
Visit Vectric Support online... | Opens the Vectric Support Website in your Web Browser if you have an Internet Connection. |
Visit Vectric User Portal... | Opens the Vectric User Portal in your Web Browser if you have an Internet Connection. Download software installation files, activation codes and Clip Art included with the software. |
Post Processor Editing Guide | Opens the page explaining how to create and edit your own post processors. |
Migrate From Older Version | Opens a dialog to enable the settings in the last version of Aspire for ALPHACAM to be copied to the latest version. 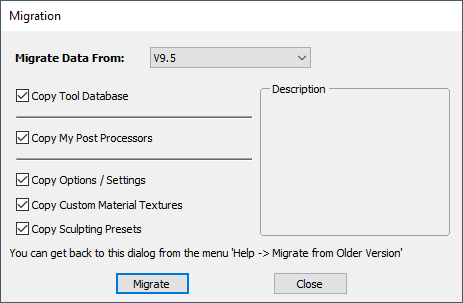 |
Check for Updates | Try this periodically to check (through the Internet) if an update is available for your software. |
About Aspire for ALPHACAM... | This window displays the version of the software being used, to whom the software is license and the type of license. |
License Dialog
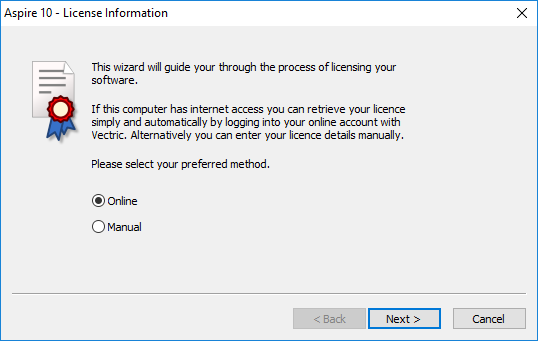
The License Dialog is used to set the details you need to activate the software. This dialog can also be used to activate optional modules. The page that initially appears will give you the option to set your license details either automatically from your V&Co account or manually.
The "Online Method" section below covers the process to follow if Online is selected.
The "Manual Method" section below shows the process to follow if you wish to type in your license details manually or do not have an Internet connection available.
Online Method
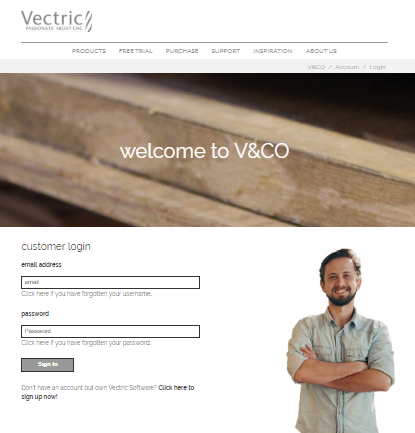
This method will allow you to retrieve your details automatically from your V&Co account. To use this select 'Online' and then click on the form. The online section of the form will then be displayed.
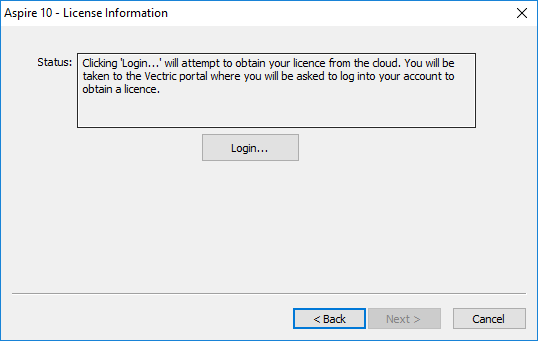
Pressing on this dialog will launch a web browser which will take you to the V&Co login page if authentication is required.
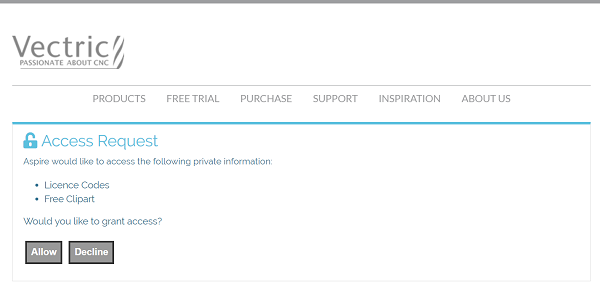
After logging in here with your V&Co account details another page may appear asking for permission for Aspire for ALPHACAM to access your license details.
This page will only appear if you have not already granted access. If this appears you should select "Allow" to enable Aspire for ALPHACAM to retrieve your license details automatically.
At this point Aspire for ALPHACAMshould be being displayed and the dialog should be automatically populated with any licenses available on your account.
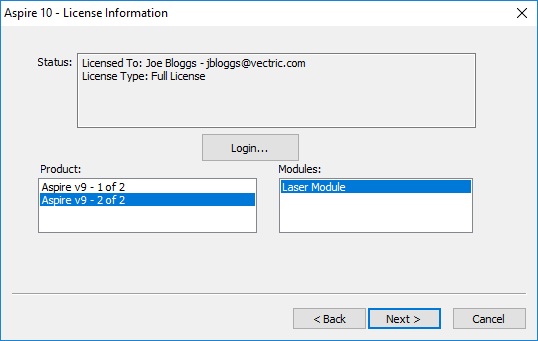
You can select any of the product licenses available and information on the type of license will be displayed in the status area. Once the license and any modules have been selected by clicking on them can be pressed to activate these and proceed to the summary page.
Note
If there is only a single license available on your account the above page is skipped and the summary page (below) will already be displayed.
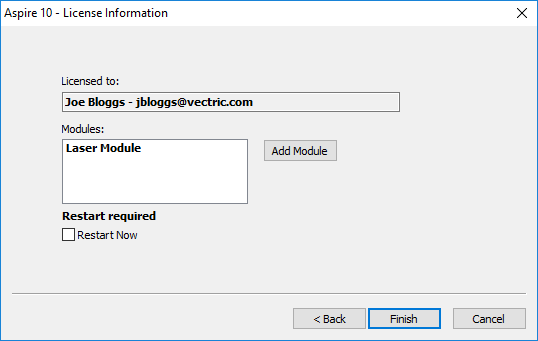
This page displays the selected license and module details. If you are changing current license details or adding a module a restart will be required for these to fully take effect. In this case a check box will appear allowing you to restart automatically. If this is checked then when you press Aspire for ALPHACAM will automatically be restarted to apply the license changes. If you do not select this option the license changes take effect the next time Aspire for ALPHACAM is restarted.
Manual Method
The manual method allows entry of license details without requiring an Internet connection. Selecting "Manual" and clicking will cause the manual entry form to be displayed.
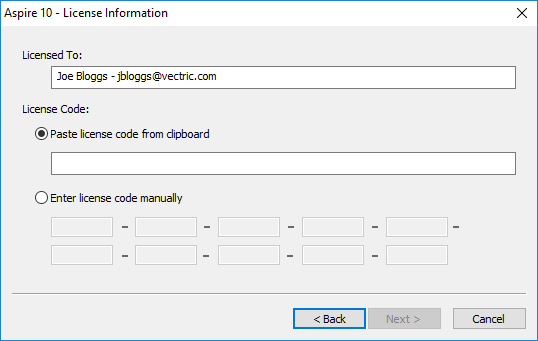
The "Registered User Name" from your license information should be entered into the "Licensed To" area of the form and the license code can either be copied and pasted into the middle row of the dialog or manually typed into the lower section if "Enter license code manually" is selected. The button will become available when a code of the expected length has been entered.
If the product is already licensed then a module code can be entered at this stage instead of the product code. If you wish to manually activate both a product and module code the product code should be added here and there will be an opportunity to add the module code later. Pressing will set the license and display the summary screen.

The summary screen shows the current licensed user and has an button to allow additional modules to be added. Pressing this button will display the manual entry form again and allow the module details to be entered.
If the licensed user is changed or a new module is added a restart will be required for these to take full effect. In this case a check box will appear allowing you to restart automatically. If this is checked then when you press the finish button the program will automatically be restarted to apply the license changes. If you do not select this option the license changes take effect the next time the program is restarted.
Create Component from Bitmap
This tool lets you automatically create a 3D Component from a Bitmap.
If no Bitmap is selected in the 2D View, then a File dialog will open allowing you to select an image file from one of the drives on your computer. This method of component creation bypasses the need to convert the image when importing which potentially reduces the number of color shades, so this second method is the best way to directly convert Bitmap files to components in Aspire.
The Component from a Bitmap is automatically scaled and set to Add to other Components by the software so will typically need to be edited using the Component Properties icon to adjust height or Combine Mode and the Transform tools to adjust its size and position.
Converting selected bitmap
If you have a selected Bitmap in the 2D View this will automatically create a new component derived from that Bitmap, the Component will have the same name as the original image.
Converting without bitmap selected
If no Bitmap is selected in the 2D View, then a File dialog will open allowing you to select an image file from one of the drives on your computer. This method of component creation bypasses the need to convert the image when importing which potentially reduces the number of color shades, so this second method is the best way to directly convert Bitmap files to components in Aspire. This is especially important for 16-bit images.
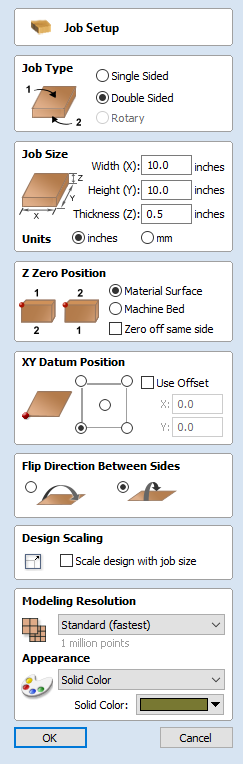
Job Setup - Double Sided
The Job Setup form is displayed whenever a new job is being created, or when the size and position of an existing job is edited.
In most cases a new job represents the size of the material the job will be machined into or at least an area of a larger piece of material which will contain the part which is going to be cut. Clicking OK creates a new empty job, which is drawn as a gray rectangle in the 2D View. Dotted horizontal and vertical Grey lines are drawn in the 2D design window to show where the X0 and Y0 point is positioned.
Job Type
Single Sided job type should be used when design only requires the material to be cut from one side. This is the simplest type of job to design and machine.
Double Sided Job type is useful when it is desired to cut both sides of your material. Aspire allows you to visualise and manage the creation and cutting process of both sides of your design within a single project file.
Rotary job type enables the use of a rotary axis (also called a 4th axis or indexer).Aspire will provide alternative visualisation, simulation and tools appropriate for rotary designs.
Job Size
This section of the form defines the dimensions of the material block you will be using for your project in terms of width (along the X axis), height (along the Y axis) and thickness (along the Z axis).
It also allows you to select which units of measurement you prefer to design in - either inches (Imperial/English) or millimeters (Metric).
Z Zero Position
Indicates whether the tip of the tool is set off the surface of the material (as shown in the diagram) or off the bed / table of the machine for Z = 0.0.
Zero off same side
This option allows Z Zero to reference the same physical location, regardless whether material is flipped or not
XY Datum Position
This datum can be set at any corner, or the middle of the job. This represents the location, relative to your design, that will match the machine tool when it is positioned at X0, Y0. While this form is open, a red square is drawn in the 2d view to highlight the datum's position.
Use Offset
This option allows the datum position to be set to a value other than X0, Y0.
Flip Direction Between Sides
This section gives choice between horizontal and vertical flipping when changing machining side. Aspire uses that information to correctly manage the alignment of the geometry relating to each side.
Design Scaling
When editing the Job Size parameters of an existing job, this option determines whether any drawings you have already created will be scaled proportionally to match the new job dimensions. If you wish to preserve the existing size of your drawings, even after the job size has changed, leave this option unchecked. With this option checked, your drawings will be re-sized to remain in the same proportion and relative position within your new material extents when you click
Modeling Resolution
This sets the resolution/quality for the 3D model. When working with 3D models a lot of calculation and memory may be required for certain operations. Setting the Resolution allows you to choose the best balance of quality and speed for the part you are working on. The better the resolution quality chosen, the slower the computer will perform.
As this is completely dependent on the particular part you are working on and your computer hardware performance, it is difficult in a document like this to recommend what the setting should be. Generally speaking, the Standard (fastest) setting will be acceptable for the majority of parts that Aspire users make. If the part you are making is going to be relatively large (over 18 inches) but still has small details, you may want to choose a higher Resolution such as High (3 x slower) and for very large parts (over 48 inches) with small details then the Highest (7 x slower) setting may be appropriate.
The reason that the detail of your part needs to be taken into account is that if you were making a part with one large item in it (e.g. a fish) then the standard resolution would be OK but if it was a part with many detailed items in it (e.g. a school of fish) then the High or Highest setting would be better. As previously stated these are extremely general guidelines as on slower/older computers operations with the highest setting may take a long time to calculate.
As the Resolution is applied across your whole work area it is important to set the size of your part to just be big enough to contain the part you plan to carve. It would not be advisable to set your material to be the size of your machine - e.g. 96 x 48 if the part you plan to cut is only 12 x 12 as this would make the resolution in the 12 x 12 area very low.
Create Text
This form allows text to be created at any height using the units the model is being designed in.
Entering Text
To enter text:
- Click in the 2D view to choose the anchor position
- Enter the text in the Text box
- Edit the styling options. All changes are automatically applied
Font Selection
Vertical Fonts
Fonts that start with the @ character are drawn vertically downwards and are always left justified.
Engraving Fonts
The Single Line Radio Button changes the Fonts list to show a selection of fonts that are very quick to engrave.
Text Alignment
Positions text relative to the full body of text, this only has a noticeable effect when writing multiple lines of text.
Anchor
Sets the position of your text block. Either enter values directly, or use the mouse cursor to set the position values interactively:
- For new text simply left click in 2D view in the desired location
- For existing text object, left click the anchor point handle and drag it to the desired location
Editing Text
To edit text properties or content of previously created text:
- If the Create Text form is open, click the text you wish to edit or
- If the Create Text form is closed, click the left mouse button on the text in the 2D View to select it before opening this form. The form will now allow you to edit the properties of the selected text.
2D View Controls
See also the Rulers, Guides and Snap Grid section.
 | Pan | Click and hold the Left mouse button and drag the mouse about to Pan - Esc to cancel mode Shortcut: Click and drag the Middle mouse button or if using a 2 button mouse, Hold Ctrl + drag with Right Mouse button. | |
 | Zoom Interactive | Mouse with Middle Wheel - Scroll wheel in / out Mouse without Middle Wheel - Hold Shift + Push / Pull with Right Mouse button. | |
 | Zoom Box | Click top left corner, hold mouse down and drag to bottom right corner and release. Clicking the left mouse button will zoom in, Shift + click will zoom out. | |
 | Zoom Extents | Zooms to show material limits in the 2D window | |
 | Zoom Selected | With objects selected Zooms to the bounding box of the selection |
Undo Operation
Clicking this option steps backwards through the design changes made by the user.
Draw Arc
The Create Arc tool allows a single arc span to be created using precise values, or dynamically within the 2D View.
Through 3 Points
- Left click the mouse in the 2D View to set the start point of an arc.
- Click again to set the end point position.
- Move the mouse and click a third point to set the arc's radius.
Center, Start and End
- Left click the mouse in the 2D View to set the center point of the arc.
- Click again to set the start point of the arc.
- Move the mouse and click a third point to set the end point of the arc.
Note
Clicking the Right mouse button or pressing the Esc key will complete the arc drawing if possible and close the form.
Exact Size
Precise values for the start and end point positions (in absolute X Y coordinates) and either the radius or the height of the arc can be entered in the form directly. Click to draw and arc using these values.
2D Design and Management
The 2D View is used to design and manage the layout of your finished part. Different entities are used to allow the user to control items that are either strictly 2D or are 2D representations of objects in the 3D View. A list of these 2D View entities are described briefly below and more fully in later sections of this manual.
Ultimately the point of all these different types of objects is to allow you to create the toolpaths you need to cut the part you want on your CNC. This may mean that they help you to create the basis for the 3D model or that they are more directly related to the toolpath such as describing its boundary shape. The different applications and uses for these 2D items mean that organization of them is very important. For this reason Aspire for ALPHACAM has a Layer function for managing 2D data. The Layers are a way of associating different 2D entities together to allow the user to manage them more effectively. Layers will be described in detail later in the relevant section of this manual. If you are working with a 2 Sided project you can switch between the 'Top' and 'Bottom' sides in the same session, enabling you to create and edit data on each side, and using the 'Multi Sided View' option you can view the vectors on the opposite side. 2 Sided Setup will be described in detail later in the relevant section of this manual.
Vectors
Vectors are lines, arcs and curves which can be as simple as a straight line or can make up complex 2D designs. They have many uses in Aspire for ALPHACAM, such as describing a shape for a toolpath to follow or creating designs. Aspire for ALPHACAM contains a number of vector creation and editing tools which are covered in this manual.
As well as creating vectors within the software many users will also import vectors from other design software such as Corel Draw or AutoCAD. Aspire for ALPHACAM supports the following vector formats for import: *.dxf, *.eps, *.ai, *.pdf, *skp and *svg. Once imported, the data can be edited and combined using the Vector Editing tools within the software.
Bitmaps
Although bitmap is a standard computer term for a pixel based image (such as a photo) in *.bmp, *.jpg, *.gif, *.tif, *.png and *.jpeg. These file types are images made up of tiny squares (pixels) which represent a scanned picture, digital photo or perhaps an image taken from the internet.
To make 3D models simple to create, Aspire for ALPHACAM uses a method which lets the user break the design down into manageable pieces called Components. In the 2D View a Component is shown as a Grayscale shape, this can be selected and edited to move its position, change its size etc. Working with the Grayscale's will be covered in detail later in this manual. As with bitmaps, many of the vector editing tools will also work on a selected Component Grayscale.
Frequently Asked Questions
Interactive Selection Mode
The Interactive Move, Rotate, Scale Selection tools can be used to quickly and easily modify vectors and components.
Clicking twice on one of the selected objects and the interactive scaling, movement and rotation handles are displayed in the same way as selecting this icon. Lines, Arcs and Bezier spans will be displayed as dotted magenta lines and text and grouped objects will be displayed as solid magenta lines:
When in this mode the mouse is used to click on one of the handles which has appeared on the selected Vector/s. Each handle is used for a specific editing operation as detailed here:
- Middle - Move the vectors (Hold +Alt Move the selected objects in one axis)
- Corner (White) - Scale the vectors proportionally (Hold +Alt Scaling non-proportionally, +Shift Scale around the centre)
- Edges (White) - Scale the vector in one axis (Hold +Shift Scaling proportionally)
- Corner (Black) - Rotate the vectors (Hold +Alt Rotate in 15° increments)
To deselect objects,
- Click the white background unless Shift is pressed.
- Press Esc
- Right click menu ► Unselect All
Import Vectors
This opens the File Open dialog window and allows 2D DXF, EPS and AI and PDF files to be imported into the 2D View. The imported vectors will always be read in at the size and scale they were created in their original design software. Once open they can be scaled and edited in the same way as vectors created in Aspire. All the Vector tools will be dealt with in that section of this manual.
To import toolpaths from PhotoVCarve and Cut3D (.PVC and .V3D file extensions), use File ► Import... ► Import PhotoVCarve or Cut3D Toolpaths from the file menu bar. Any Toolpath data saved as .PVC or .V3D files can be imported and will be visible in the Toolpath List.
See the 3D Toolpath Files section for detailed instructions on importing PhotoVCarve(*.pvc), Cut3D(*.v3d) or Vectric 3D Machinist(*.v3m) files.
Simple Rotary Modelling using 2D Toolpaths
Creating vectors for a basic column
This section will show how to create a simple column, using the profile and fluting toolpaths.
Start by creating a new rotary job. Please note that settings shown here are only an example and should be adapted to match your machine setup and available material.
In this example the blank will rotate around X axis. We will refer to it as the rotation axis. The axis that will be wrapped is the Y axis. We will refer to it as the wrapped axis. That means that the top and bottom boundaries of the 2D workspace will actually coincide. We will refer to them as the wrapped boundaries.
First, create the cove vectors using Draw Line/Polyline tool. Those will run along the wrapped axis at both ends of the design. Snapping may be useful to ensure that the created line starts and ends at the wrapped boundaries.
In this example the coves were placed 1 inch from the job boundaries, leaving 10 inches in the middle for the flutes. The flutes will run along rotation axis. Assuming 0.5 inch gap between the cove and the beginning of the flute, the flutes will have the length of 9 inches. This example will use 8 flutes.
To start, create a line parallel to rotation axis that is 9 inches long. Now select the created flute vector and then select one of the cove vectors while holding down Shift. Then use Copy Along Vectors tool to create 9 copies. The original flute vector may now be removed as it is no longer necessary. Note that first and last copy are both created on wrapped boundaries. That means they will coincide, so one of them can be removed. As the last step select all flute vectors and press F9 to place them in the center of design.
Creating rotary toolpaths
The process of creating 2D rotary toolpaths is very similar to creating toolpaths for Single- and Double- models. This example will use the profile toolpath on the cove vectors. To create the toolpath, select the cove vectors and click on the Profile Toolpath from
To create the toolpath for the flutes, select the flute vectors and click on the Fluting Toolpath. This Example used a 1 inch 90deg V-Bit set to Flute Depth 0.2 and using the Ramp at Start and End and Ramp Type Smooth options. Ramp length was set to 0.25 inches. Both toolpaths can be seen below.
Simulating and saving toolpaths
It is time to simulate toolpaths using Preview Toolpaths. If the option to animate the preview is selected, the simulation will be visualized in flat mode. Once the simulation is complete, the wrapped rotary view will be turned back on automatically.
Contrary to single- and double- sided simulation, rotary simulation is not 100% accurate. For example round holes will appear in rotary view as oval ones, but obviously will be round when part is actually machined.
Although the design can be considered to be finished, in practice it is useful to be able to cut-out the remaining stock. This can be realized by making the design slightly longer and adding profile cuts. In this example the blank length was extended by 2 inches using the Job Setup . Existing vectors can be recentered using F9. After that the existing toolpaths have to be recalculated.
The cut-out vectors can be created in the same way as cove vectors. Two extra profiling toolpaths can be created using the suitable End Mill. In this example we used a tab with a 0.5 inch diameter. In order to achieve that, the user can type the following in the Cut Depth box: z-0.25 and then press = and the software will substitute the result of the calculation. Variable 'z' used in the formula will be substituted by the radius of the blank automatically by software. It is also important to specify Machine Vectors Outside/Right or Machine Vectors Inside/Left as appropriate. Cutout toolpaths and the resulting simulation has been shown below.
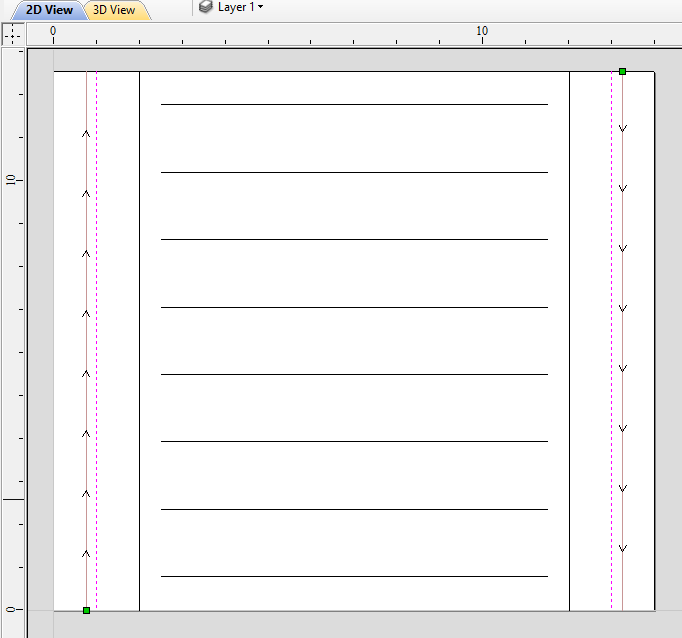
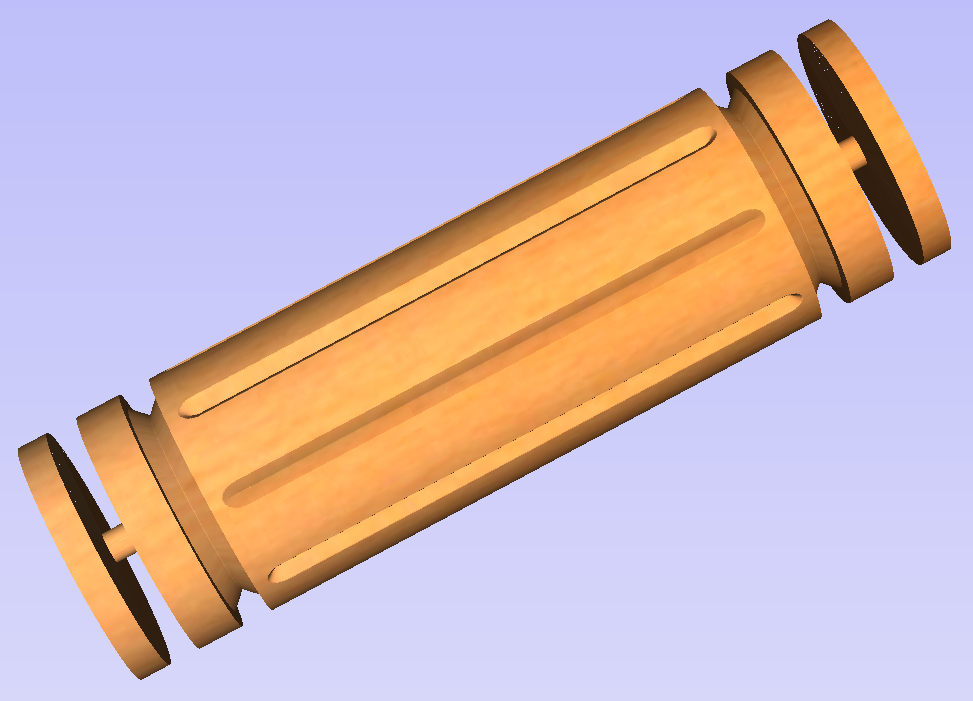
The final step is to save the toolpaths in a format acceptable by your machine. Use the Save Toolpaths and select the wrapped post-processor matching your machine.
Note
Tools and values presented in this example are for illustrative purposes only. Size of tools, feed rate, tabs diameter etc. have to be adapted to the material and machine used to ensure safe and accurate machining.
Spiral toolpaths
This section will explain how to create and simulate spiral toolpaths.
One way of thinking about spiral toolpaths is to imagine a long, narrow strip of fabric. Such a strip can be wrapped around a roll at a certain angle. In order to create a toolpath that wraps around the blank multiple times, one can create a long vector at a certain angle. Such a vector is an equivalent to the strip of fabric when it is unwrapped from the roll.
Although such a toolpath will exceed the 2D workspace of the rotary job, thanks to the wrapping process during both simulation and machining the toolpath will actually stay within material boundaries.
The most crucial part of designing spiral vectors is to determine the right angle and length of the line that would result in a given number of wraps. Suppose one would like to modify a simple column design to use spiral flutes, rather than parallel to rotation axis. The following example will use flutes wrapping 3 times each, but the method can be adapted to any other number.
All but one of the existing flute vectors can be removed. Select the Draw Line/Polyline and start a new line by clicking at one end of the existing flute. This line needs to be made along the wrapped axis with the length being 3 times the circumference of the job. In this example that means typing 90 into the Angle box and typing y * 3 into the Length box and pressing =. If the wrapped axis is not the Y axis, but rather the X axis, then the above formula should be x * 3.
Now one can simply draw a line connecting to the other end of the original flute vector and the newly created one. Using Copy Along Vectors tool this single flute may be copied in the way described earlier. In this example 4 spiral flutes were created, as can be seen below.
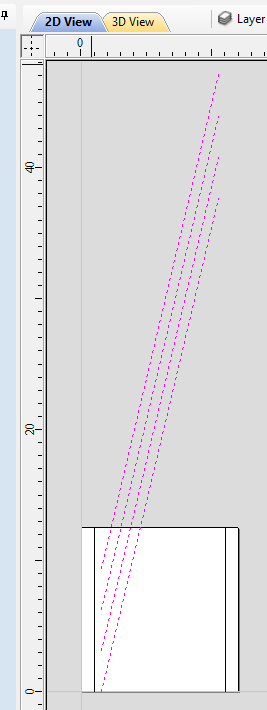
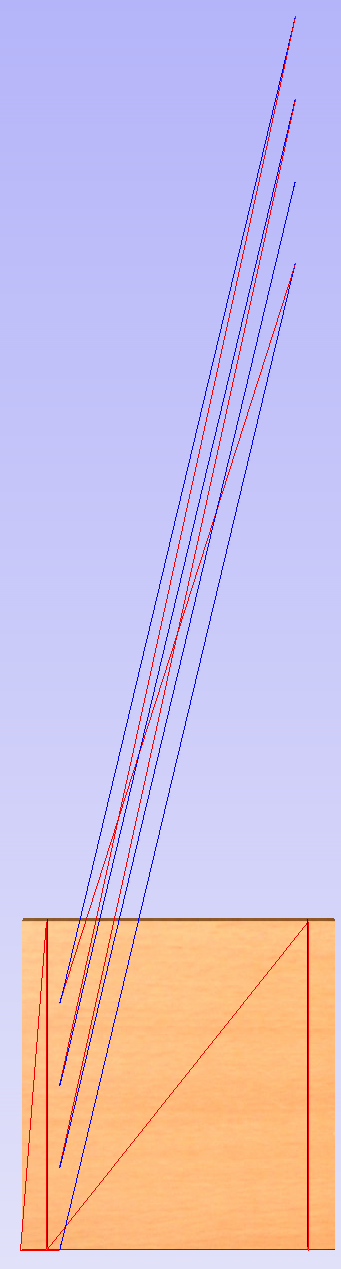
Once the flute vectors are ready, the toolpath can be created again using the Fluting Toolpath. An important thing to note, is the difference between the appearance of spiral toolpaths in the wrapped and flat view. By clicking on Auto Wrapping one can switch from wrapped rotary view to flat view and back again.
As can be seen above, in the flat view the toolpaths will follow the vectors and extend beyond the job boundaries. On the other hand the wrapped view, presented below, will display the toolpaths spiralling around the blank.
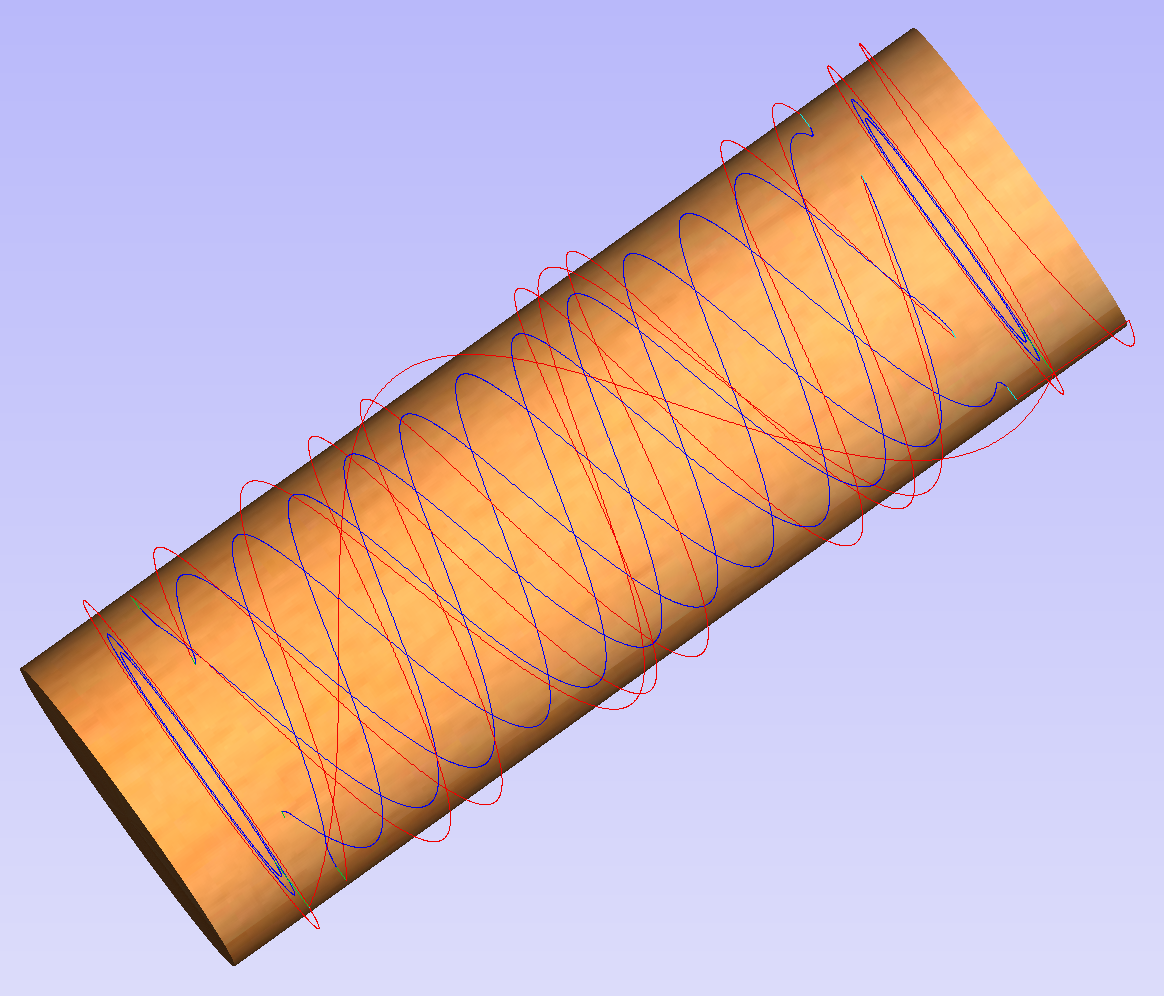
This was just a brief overview of general 2D workflow for rotary machining. Remember to also take a look at video tutorials dedicated to rotary machining, which are accessible from the Tutorial Video Browser link when the application first starts.
Snapping Options Dialog
To help with drawing, construction and layout, the 2D View has Rulers which are displayed along the top and down the left side of the window. In addition to the Rulers there is the option to use Guidelines and The Smart Cursor to help with construction of vectors or positioning of other objects in the 2D View.
Rulers
The Rulers are permanently displayed in the 2D view to help with positioning, sizing and alignment. The graduated scale automatically uses the units set for the project and zooming in / out shows the sizes in 10ths.
Guidelines
Guide Lines are used to help layout designs and make it very easy to sketch shapes by clicking on the intersections of Guides. Guide Lines are easily be added to the 2D view by pressing the left mouse button down on the appropriate ruler (left if you want a vertical guide and top if you want a horizontal guide) then holding the button down and dragging the mouse into the 2D view.
While dragging a Guide into position it automatically Snaps to the units displayed on the ruler. This snapping behavior can be overridden by holding down a Shift key while dragging the guide. After positioning a Guide it can easily be moved to a new position by clicking the right mouse button on the guide to open the Guide Properties form as shown later in this section. If you hover the mouse over a Guideline then its current position is displayed next to the cursor
Additional guide lines can be added relative to an existing guide line by interactively placing the cursor over an existing guide (the cursor changes to 2 horizontal arrows), Holding a Ctrl key and dragging to the required position. The incremental distance between the guide lines is displayed next to the cursor. Releasing a Ctrl key changes to display the absolute distance from the material origin.
Guides can also be added and other edits made by right clicking on the Guideline which will bring up the Guide Properties form:
The exact position can be specified by entering a New Position.
Guides can be given an angle by either entering an angle into the New Angle box or dragging the slider and clicking . Angles are measured in degrees counterclockwise from the x-axis. From an angled guide you can only create relative parallel guides.
Guide lines can be locked in position to stop them from being inadvertently moved by ticking the Lock Guide option.
Additional Guide Lines can be added that are positioned using absolute or incremental coordinates. Enter the Absolute or relative positions and Click .
Guides can quickly be toggled visible / invisible by clicking in the Top Left Corner of the 2D view:
Alternatively the visibility can be changed using View Menu ► Guide Lines from the Main MenuView Menu ► Guide Lines ► Delete All Guides from the Main Menu
Snapping Options
These options can be used to help create and edit vector geometry.
The Snapping Options form can be accessed by selecting Edit ► Snap Options from the Main MenuF4.
Display Text at Cursor
Displays the XY coordinates on the cursor making it easy to see the position for each point
Snap to Guides
When this option is checked ✓ drawing and positioning vectors will snap onto any horizontal or vertical guide lines visible in the 2D view.
Snap Guides to Geometry
When checked, ✓ the Guide Lines can snap to Geometry while being dragged.
Snap to Grid
Displays a grid of points separated by the Grid Spacing which can be snapped to when drawing or editing vectors and other objects in the 2D View.
Snap Distances
Snap to fixed lengths based on your zoom level. This occurs when creating shapes, dragging nodes or vectors.
Snap to Job Center and Corners
Snap to the job corners and center. This, also, control the job smart snapping
Fixed Nudge Distances
Objects can be moved small, fixed distances (nudged) by holding Ctrl + Shift and tapping the arrow keys. The Fixed Nudge Distance specifies the distance to move selected objects with each nudge.
Snapping Radius
The snap radius (pixels) will adjust how close the cursor must get to vector geometry in order to snap it. If you work quickly and grab and throw geometry at speed, you may prefer a larger Snapping Radius to pick up geometry that is vaguely near the mouse. If you work precisely or have complex overlapping geometry, you may prefer a smaller Snapping Radius to avoid having to zoom in to select one geometry in an area that has many nearby vectors.
Geometry Snapping
Used to control the position at which the cursor will snap when drawing and moving objects. When drawing, the cursor will snap to items on vector geometry depending what options you have selected in the form under this section.
Object centers, Span End points, Span Mid-points, Arc centers, intersections Horizontally, Vertically and the specified Angle and Distance Guide lines and the intersection of Guides
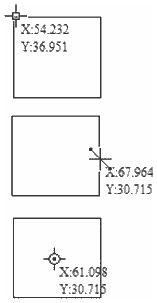
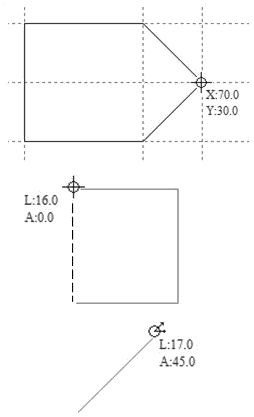
Smart Snapping
Smart snapping works by snapping the cursor to imaginary lines related to vectors and/or nodes. These lines will appear as dashed, and sometimes coloured, lines that go through the vector or node and the cursor point. You can snap to the intersection of those lines by hovering over the nodes that you're interested in. This reduces the need to create construction geometry (for example, for aligning nodes or vectors), and can be used in almost all the shape creation tools, node editing and transforming vectors.
Note
A node is the start, middle, or end point of a span.
Note
The snapping system is watching to see which vectors you hover the mouse over. It remembers that last few vectors as the ones you want to work with and draws the snap lines for those as a priority. There is a maximum number of nodes and vectors that can be "woken up" at the same time to avoid too many snap lines appearing at once.
Snapping lines can be drawn from:
- Nodes that were woken up by hovering the mouse over them or their span
- Vector properties, such as their bounding box or center point
- Material properties, such as extensions from the edge and the middle
Note
It is possible to wake up vectors on the other side of a double-sided job.
Cursor | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | Object Bounds | The theoretical bounding box surrounding the active vector |
  | Horizontal and Vertical Lines | Horizontal and vertical lines passing through a node or a span midpoint. |
 | Tangents | Tangents originating from a node or a span midpoint. |
 | Perpendicular to Tangents | Lines which are perpendicular to tangents from nodes or span midpoints. |
 | Connecting Lines | Lines connecting two nodes. Includes mid-point. |
 | Span Geometry | Snap to the geometry of the vector. |
 | Angular Constraints | Snapping to specific angles, as defined in the snap options F4. |
  | Job | Horizontal and vertical lines through the center of the job. |
Object Bounds
These snap lines appear on the bounding box edges of the vector, and in the middle horizontally and vertically.
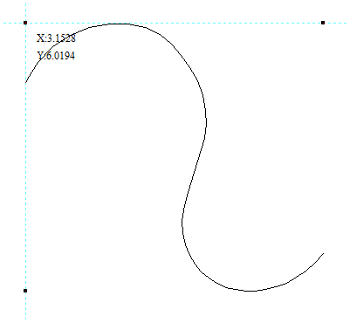
Vertical and Horizontal Lines
Nodes
The snap lines appear when the cursor is near the horizontal or vertical line passing through the woken nodes.
Vectors
Snap lines become available while moving vectors so that it is used for aligning them with other vectors.
Tangents
These snap lines originate from the woken node and will appear as an extension along the end of the belonging span.
Perpendicular to Tangents
These snap lines will be 90° from the tangent snap line.

Connecting Lines
If you wake two or more nodes, you could snap to the line connecting them. You could, also, snap to the mid-point of that line.
Span Geometry
This allows you to snap to the geometry of the vectors.
Angular Constraints
Job Edges & Centre
If you have the job snapping

Toolbar Snapping Options
Geometry Snapping, Smart Snapping and Grid Snapping can be switched on and off from the View Toolbar
Any change to the snap settings F4, through the Main Menu or the toggles on View Toolbar will be remembered for subsequent sessions.
Disable snapping temporarily
Snapping can be temporarily disabled by holding down the Shift key.
Edit
 | Undo | Steps backwards through the last 5 changes made by the user. |
 | Redo | Steps forward through design steps that have been Undone using the Undo command (see above) to get back to stage that the user started using the Undo function. |
 | Cut | Removes the selected objects from the job and places them onto the clipboard. |
 | Copy | Copies selected objects to the clipboard, leaving the original in place |
 | Paste | Pastes the contents of the Clipboard into the model (see cut and copy above). |
| Delete | Deletes the selected object - same as hitting the Delete key on your keyboard |
| Selection► | Select various types of vectors |
| Align Selected Objects ► | Give the user all the options covered under the Align Objects section of the menu. Opens the Alignment Tools form. |
| Join Vectors | Joins open vectors. Opens the Join Vectors form. |
| Curve Fit Vectors | Allows arcs, Bezier curves or lines to be fitted to existing vectors to 'smooth' them. Opens the Fit Curves to Vectors form. |
| Nest Selected Vectors | Opens the Nesting form. |
 | Job Size and Position | Opens the Job Setup form. |
| Notes | Opens a text box where you can record notes regarding this job, such as customer name, material required, special setup instructions or any other relevant text information you would like to keep when you save the job. If the text starts with a period/full stop/dot '.' , the Notes dialog will be displayed automatically each time the file is opened. The text from the Notes dialog can also be optionally output into the toolpath as a comment field. See the Post-Processor Editing Guide. |
| Document Variables | Opens the Document Variables dialog. |
| Snap Options | Opens the Snap Options dialog. |
| Options | Opens the Program Options dialog to allow the customization of certain aspects of the program. |
Selection
| Select All Vectors | Selects all the currently visible vectors in the part (vectors on invisible layers are not selected). |
| Select All Open Vectors | Selects all the currently visible Open vectors in the part |
| Select All Duplicate Vectors | Selects all the currently visible Duplicate vectors in the part - these are vectors which are exact copies of each other in terms of shape and location so that visually they appear to be only one vector. These can cause problems for some toolpath and modeling functions so it can be useful to delete them or move them to a new layer. |
| Select All Vectors On Current Layer | Selects all the vectors on the selected layer. |
| Unselect All | Deselects all the currently selected vectors in the part |
| Vector Selector... | Opens the Vector Selector dialog. |
Join / Close Vector with a Straight Line
Join with a Line finds the closest end points on 2 selected, open vectors and joins with a straight line. Close with a Line closes a single open vector with a straight line between its two end points.
Grouping and Ungrouping
Grouping objects allows you to select, move and manipulate them as if they were one entity. The process is entirely reversible by Ungrouping.
See Grouping and UnGrouping.
Overlap Vectors
Selected closed vectors that overlap can be merged together to create a new shape. These tools consider the closed vectors to be solid areas.
The following examples begin with these five vector shapes where the rectangle was selected last.
Only areas of the first selected parts (the circles) that are covered by the last selected vector (the rectangle) remain after this operation.

Component Tree
The model that you see in the 3D View is the result of progressively combining all of the visible components from the bottom of the Component Tree, to the top. The resulting model is known as the Composite Model. The order in which components are combined can have a significant impact on the final shape of the composite model and so you will often need to move components relative to one another within the Component Tree in order to achieve the end result you are intending.
For more information, see the 3D Design and Management page.
Combine Modes
To help you understand how the components are being combined, each component in the tree has an icon indicating how it is currently being combined with the components below





Grouping
Grouped components are also indicated by their own icon and the presence of a plus or minus control to the left of the visibility checkbox. These controls allow you expand or collapse the group to show or hide the group contents, respectively.
Every component exists on a single Level. These levels can be used to organize your modelling process. During the compositing process the contents of a level are combined first before the levels themselves are combined together.
Selection
Components can be selected in 3 ways:
- By left-clicking on the component's name in the Component Tree
- By left-clicking on the associated grayscale component preview image in the 2D view
- By double left-clicking directly on the component in the 3D view
In all cases, the new selection will subsequently be reflected in all three locations. So, for example, selecting a component in the Component Tree will simultaneously cause the associated 2D component preview to become selected in the 2D View, and the same component to become highlighted in red (or green if the selected component is obscured by another component) in the 3D View.
There are, however, some minor differences between the three methods of selection. Also, depending on the circumstances, there may be some advantages to selecting your components using one method rather than another.
Selection in the Component Tree
The component tree works in a similar way to the Window's file explorer. To select a component, simply click on it. To select multiple components, hold down a Ctrl key while clicking on each component you wish to add to the selection. While in this mode, clicking on a component that is already selected will cause it to be removed from the selection.
Pressing a Shift key allows you to select a range of components. Click on the first component in the range to select it, then holding a Shift key and pressing the last component you want selected will select all the components between the first and last selection.
Double-clicking a component or level in the Component Tree will automatically open the Component Properties tool - see the Component Properties section for more information on how to use this tool to modify the selected components.
Right-clicking an unselected component in the Component Tree will select it, and open its pop-up menu of related commands. Any commands you select will apply to this selected component only.
Right-clicking a component that is already selected, and is also one of several selected components, will open a similar pop-up menu of commands. Any commands you select from this menu will apply to all of the currently selected components.
Selection in the 2D View
The 2D component previews behave exactly the same way as vectors or bitmaps. They can be selected by a single, left-click. Several component previews can also be 'shift selected' (see above). Clicking on selected component previews again activates their interactive transform handles. These can be used to move, rotate or stretch the 2D component preview and its associated 3D component.
Selection in the 3D View
Because the left mouse button is used for twiddling the 3D view itself, a single left-click cannot be used for component selection directly. However, Aspire for ALPHACAM's 3D view supports most of the standard selection concepts described above, using double-clicks instead. Therefore, to select a component in the 3D view it must be double-clicked with the left mouse button. To select multiple components in the 3D view, hold down a Shift key and double-click each of the components you wish to add to the selection. To access the pop-up menu of commands associated with a component, double right-click it in the 3D View.
Because components may overlap or merge through one another when forming the composite model, you may find that some components become difficult (or are even impossible) to select directly from the 3D view using the double click method. In this case you may use the right click menu. If you right click on a point above the component you wish to select then you are presented with a list of all the components that lie under this point.
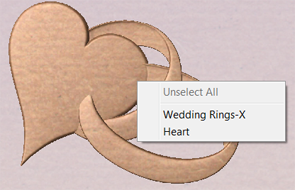
You can also double right-click the selected component (highlighted in red) in the 3D view. The options offered include showing/hiding components, or setting their combine mode within the composite model.
In the 3D view selected object will often be tinted red. On some occasions parts of some components will be obscured by other components. In this case then the red tint will not be seen. The parts of the objects that are obscured will be tinted green so they are still visible from within the 3D view.
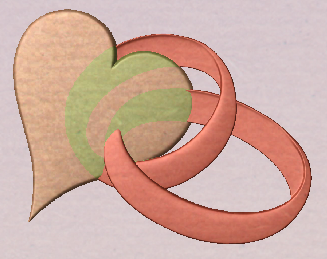
Editing in the 3D View
Many of the dynamic component editing tools can now be accessed directly from the 3D View. Editing the components in the 3D View makes it quick and easy to see the immediate effect of the changes to the Composite Model. To access these editing options a component or components must first be selected. Once selected then either clicking the component again in the 3D view or clicking the Transform Mode icon (Move, Scale, Rotate Selection) will activate the 3D Transform Handles. These take the form of solid and hollow blue squares around the component/s in the 3D View.
The majority of these will function in the same way that they do with objects in the 2D View. The additional larger solid blue square below the middle of the bottom edge of the model can be left-clicked to open a floating form that allows access to some of the components properties. This form can be moved if it is covering an important area of the job. From this form you can adjust the Combine Mode, Shape Height, Base Height, Fade and Tilt for the selected component/s. If you edit Fade or Tilt using this form, then when you click the Set button you must click the positions for this in the 3D View.
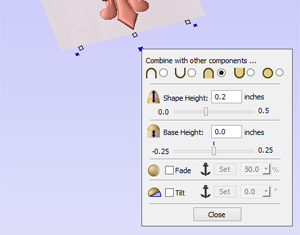
Position in the Component Tree
The position of the component in the Component Tree may affect the resulting combined model. This position can be altered by selecting one or more component(s) and clicking one of the buttons with a blue arrow at the top of the Component Tree. Alternatively, component(s) can be selected and dragged in component tree via mouse. If Ctrl is held when component is being dragged, then the component itself will not be moved, but it will be copied instead and placed at the desired location.
Group Selected Objects
Vectors can be Grouped allowing any number of vectors to be included as a single object that can easily be selected, moved and scaled etc. The Shortcut key for this operation is G.
Grouping vectors is particularly useful for machining purposes, where different vectors will be used for a single toolpath operation. Clicking any member of the group will select the entire group.
Draw Ellipse
Ellipse / ovals can be created interactively with the cursor and Quick Keys or by entering the exact coordinates for the center point, height and width with typed input.
Note
Pressing the Space-bar re-opens the last vector creation form you used. This is very useful when using other forms in between each shape you create.
Interactive - Cursor
The quickest and simplest way to draw an ellipse is:
- Click and drag the left mouse button in the 2D View to begin drawing the ellipse from its corner.
- While holding the left mouse button, drag to the required size.
- Releasing the left mouse button.
- Holding Alt and dragging creates an ellipse from the middle point.
- Holding Ctrl and dragging creates a circle.
Quick Keys
Instead of releasing the left mouse button when you have dragged your shape to the required size, you can also type exact values during the dragging process and set properties precisely.
- Left-click and drag out your shape in the 2D View.
- With the left mouse button still pressed, enter a quick key sequence detailed below.
- Release the left mouse button.
Default
By default, two values separated by a comma, will be used to set width and height of your ellipse. One value will create a circle with the given diameter. While you are dragging out the ellipse, type Width Value , Height Value Enter or Diameter , Enter to create an ellipse with the specified dimensions.
Specifying Further Properties
By using specific letter keys after your value, you can also indicate precisely which property it relates to.
- Value X - Creates an ellipse at current dragged height but with set width
- Value Y - Creates and ellipse at current dragged width but set height
- Value W Value H - Creates an ellipse with set width and height
Examples
- 1 x Current dragged height with width (X) of 1
- 1 y Current dragged width and height (Y) of 1.
Exact Size
Accurate ellipses can also be drawn by entering the required XY origin point with the Width and Height of the oval. Click to create the ellipse.
Editing an Ellipse
To edit an existing ellipse:
- Select the ellipse to modify and open the Draw Ellipse form.
- The selected shape is displayed as a dotted magenta line.
- Edit the Width and Height values.
- Click to update the ellipse.
To modify another ellipse without closing the form hold a Shift key down and select the next ellipse.
Object Selection Tools
Once vectors have been created within Aspire for ALPHACAM or have been imported from other design software packages you may want to make changes to them. These changes may be to prepare for machining or for use as construction vectors for making 3D shapes using the Modeling Tools. There are a number of functions for editing vectors which will be covered in this section of the manual. All the icons under the Edit Vectors section of the Drawing Tab will be referenced along with the icons under the Align Objects section of the menu.
Editing Modes
From the 2D view a vector can be selected and then three different editing modes allow different dynamic edits to be made to the vector(s) depending on which option is selected from the Edit Vectors section.
The three editing modes are:
By default the software is normally in the Vector Selection mode.
Create Rounding Toolpath
This gadget is used to simplify the task of creating toolpaths to machine a rough blank to a finished diameter for users with a rotary axis / indexer. It supports rounding from either round or square stock and creates the toolpaths directly from the gadget. The gadget is designed to be used in a rotary job
As with all Vectric gadgets, the first part of the form gives an overview of the gadgets purpose.
The start of the form also makes a VERY important point about where the Z origin should be set when the toolpaths are output via a wrapping post-processor. This has to be configured during job setup.
You have the choice of specifying if the tool is being zeroed on the center of the cylinder or the surface. When you are rounding a blank, you cannot set the Z on the surface of the cylinder, as the surface it is referring to is the surface of the finished blank. We would strongly recommend for consistency and accuracy that you always choose 'Center of Cylinder' when outputting wrapped toolpaths as this should always remain constant irrespective of irregularities in the diameter of the piece you are machining or errors in getting your blank centered in your chuck.
A useful tip for doing this, is to accurately measure the distance between the center of your chuck and a convenient point such as the top of the chuck or part of your rotary axis mounting bracket. Write down this z-offset somewhere, and zero future tools at this point and enter your z-offset to get the position of the rotary axis center
The Create Rounding Toolpath form is divided into 4 logical sections.
Blank Size and Shape
The gadget supports creating a toolpath to machine either a square blank or a round one. In this section you specify the shape of your initial blank and its dimensions. The diagrams show which dimensions are being specified.
Machining Method
The gadget offers a choice of three types of machining and for all types you can enter an allowance that will be left on the final shape if required. The Radial and Raster options can be used with either square or round blanks, the Optimized Raster can only be used for square blanks.
Radial (around cylinder)
This option creates a toolpath which rotates the blank around its axis 360° before stepping over to the next pass by the tool stepover distance and rotating the blank back again.
Raster (along cylinder)
This option machines along the length of the cylinder before incrementing the rotary axis round by an amount equal to the tool stepover and then returning the tool back along the cylinder axis. For many machines where the rotary axis is often slower than the X or Y axis, this strategy may allow shorter machining times.
Optimized Raster (along cylinder)
If you are machining a square blank into a round shape, the previous options generate a large number of wasted toolpath moves, because for much of the machining process they are machining 'fresh air'. The 'Optimized Raster' strategy only creates the toolpaths where there is actually material on the blank and hence is much more efficient for square stock.
After choosing your machining method, the next section on the form allows you to pick the tool you will be machining with. The tool is selected from the standard Vectric tool database and will control the stepover, step down and feed rates for the toolpath. It is important to note that after choosing the tool you will not be able to edit the parameters, so you must set up the tool with the correct parameters in the tool database to begin with. This section also allows you to specify a name for the toolpath which will be created.
The values in the final section of the form are picked up automatically and are presented for reference only.
After filling in all the values (all values will be remembered as the default values to use the next time the gadget is run), press the OK button and the toolpath will be generated within the program.
Crop Bitmap
Select the image you would like to crop. Then using shift + left click select the closed vectors you would like to use to crop the image. You may select multiple vectors but the image must be selected first. Click the crop bitmap button to clear the image outside of the vector. If multiple vectors are used for the cropping then the crop tool leaves only the area of the image that lies inside the selected contours.

Document Variables
Document Variables provide a mechanism for defining values that can be used in Aspire for ALPHACAM's Document Variables. They can either be created in the Document Variables dialog which is accessible under the Edit menu, or created from any Calculation Edit Box which supports variables by right clicking and selecting Insert New Document Variable from the Popup Menu.
Naming Document Variables
New Document Variable names must begin with a letter and then may consist of letter, number and underscore characters. Once created, they may be edited in the table beneath the New Variable section of the Document Variables Dialog.
Variables can be exported to a text file and imported into another job. When importing, any existing variable values with the same name will be replaced.
Deleting Document Variables
Variables may be deleted if they're not being used in any toolpath calculations but only when there are no toolpath creation forms open.
Using Document Variables
Once created a Document Variable may be used in any Calculation Edit Box by enclosing its name within a pair of curly braces as illustrated in the figure below.
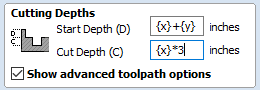
Right clicking in a Calculation Edit Box provides a Popup Menu that provides shortcuts for creating new Variables and inserting existing variables into the Edit Box.
Once a Document Variable has been created from the Popup Menu it will be inserted into the Edit Box.
Accessing Document Variables
Declared Document Variables can be easily accessed from a calculation edit box. Right-click on the calculation edit box and you will be presented with a menu showing the document variables available currently, as well as an option to quickly insert a new document variable.
Set Size
Selected items in the 2D View can be accurately scaled or resized using this option.
Anchor
The anchor position determines the point on your selected object's bounding box that will be resized to the dimensions entered.
Link XY
Checking ✓ this option will always scale the height and width in proportion. Leaving the Link option unchecked allows non-proportional scaling
Auto Scale Z
This option sets a specific mode of scaling for 3D Components. When it's checked, ✓ scaling a model component in X or Y will result in it also scaling proportionately in Z, as such if you increase its size in X and/or Y then its Z Height will also increase and conversely when you reduce its X and/or Y size it will shrink in height. When it is unchecked then the Z Height of your Components will remain constant regardless of any X and/or Y scaling done either within this form or dynamically using the mouse in the 2D or 3D View.
Interactive Sizing
The default mode is to enable selected items to be scaled interactively by clicking twice with the mouse.
The process is:
- Select the vectors
- Click a second time to activate the interactive options - handles on the selection box
- Click and drag on the white handles
The keyboard shortcut T opens the Scale form in interactive mode
Scale Model Height
This tool applies a global scaling to your final composite model. This allows you to accurately fit a design within the available material or to manage the depth of cuts required, without having to individually adjust the depth of each of the contributing Components.
Scale Both Sides
This option can only be selected when working within a 2 Sided Setup. Checking ✓ this option enables you to scale both sides of the model. If this is unchecked then you are only scaling the model of the side you are currently working on.
Scale Height
This slider will allow the user to increase and decrease the height of the model as a percentage based on its original height (when the Scale tool was selected).
Set Exact Height...
Clicking button lets the user define a specific value (in the current working units) for the height of the model, rather than use the proportional slider. If you are working in a two sided environment you have the option scale both sides. Checking ✓ this option enables you to scale both sides of the model. If this is unchecked then you are only scaling the model of the side you are currently working on.
Apply/OK
Exits the dialog keeping the changes made to the Model.
Close/Cancel
Exits the dialog discarding the changes made to the Model.
Interface Overview
- The Main Menu Bar (the Drop Down Menus) along the top of the screen (File, Edit, Model, Toolpaths, View, Gadgets, Help) provides access to most of the commands available in the software, grouped by function. Click on any of the choices to show a Drop-Down list of the available commands.
- The Design Panel is on the left side of the screen. This is where the design tabs can be accessed and the icons within the tabs to create a design.
- The Toolpath Tab is on the right side of the screen. The Top section of the toolpaths tab houses all of the icons to create, edit and preview toolpaths. The bottom half shows you toolpaths that you have already created.
- The 2D Design window is where the design is drawn, edited and selected ready for machining. Designs can be imported or created directly in the software. This occupies the same area as the 3D View and the display can be toggled between the two using F2 and F3 or the tabs at the top of the window.
- The 3D View is where the composite model, toolpaths and the toolpath preview are displayed.
- If you wish to see the 2D and 3D views simultaneously, or you wish to switch your focus to the Toolpaths tab at a later stage of your design process, you can use the interface layout buttons (accessible in the 2D View Control section on the Drawing Tab) to toggle between the different preset interface layouts.
Managing the Interface
The tool pages have Auto-Hide / Show behavior which allows them to automatically close when not being used, thus maximizing your working screen area.
The software includes two default layouts, one for designing and one for machining, which can automatically and conveniently set the appropriate auto-hide behavior for each of the tools pages. Toggle layout buttons on each of the tools pages allow you to switch the interface as your focus naturally shifts from the design stage to the toolpathing stage of your project.
Accessing Auto-hidden tabs
If a tools page is auto-hidden (because it is currently unpinned, see pinning and unpinning tools pages, below), then it will only appear as a tab at the side of your screen. Move your mouse over these tabs to show the page temporarily. Once you have selected a tool from the page, it will automatically hide itself again.
Pinning and unpinning tools pages
The auto-hide behavior of each tools page can be controlled using the push-pin icons at the top right of the title area of each page.
Default layout for Design and Toolpaths
Aspire has two default tool page layouts that are designed to assist the usual workflow of design, followed by toolpath creation.
In all three of the tools tabs there are 'Switch Layout' buttons. In the Drawing and Modeling tabs, these buttons will shift the interface's focus to toolpath tasks by 'pinning-out' the Toolpaths tools tab, and 'unpinning' the Drawing and Modeling tools tabs. In the toolpaths tab, the button reverses the layout - unpinning the toolpaths page, and pinning-out the Drawing and Modeling pages.You can toggle between these two modes using the F11 and F12 shortcut keys.
Draw Curve
This tool creates a smooth, flowing, continuous curve through clicked points.
Form
Draw Curve does not require an associated form, just use the mouse cursor directly within the 2D View.
Controls
- Click in the 2D View to begin drawing at the clicked point.
- Move the mouse pointer within the 2D View and click the left button to insert as many points as you require. A curve will be created that smoothly joins your points.
- Click the right mouse button or press Esc to finish drawing your curve and close the tool.
- Alternatively, press Space Bar to finish drawing one curve, but keep the tool active so that you can immediately begin drawing another curve.
Left Clicking
Left clicking when the mouse pointer is close to the first point on the curve will snap the curve closed.
Extending Contours
An existing open contour can be extended by holding down the Ctrl key and then clicking on either its start or end point.
CTRL clicking on the start point of a contour will cause the contour to be reversed before extending.
Mirror
Selected vectors/bitmaps/component grayscale previews can be mirrored to a new orientation.
Selected objects can also be mirrored about axes of symmetry relative to the bounding box of the selection, using the standard options on the Mirror Form.
- Select the object or objects to mirror.
- Click on the Mirror icon to open the Mirror Form.
- Select the Create a mirrored copy option to leave the selection and create a new set of objects.
- Click the button to accept the changes.
Use Rotated Bounds
This option is available only when a single object is selected. When it's checked, it will flip the object around its local rotated bounds as shown in the Selection Tool. If the object isn't rotated, it will just operate normally.
Shortcuts
The following shortcuts can be:
- H - Mirror Horizontally
- Ctrl + H - Create mirror. Copy Horizontally
- Shift + H - Mirror horizontally around center of material
- Ctrl + Shift + H - Create mirror copy horizontally around center of material.
- V - Mirror vertically
- Ctrl + V - Create mirror. Copy Vertically
- Shift + V - Mirror vertically around center of material
- Ctrl + Shift + V - Create mirror copy vertically around center of material.
Layer Management
Vectors, Bitmaps and Component Grayscale's can be assigned to different layers.
All the objects assigned to a layer can then be simultaneously selected, labeled, colored, temporarily hidden or even locked (to prevent accidental editing) using the Layer Management tools. Even for relatively simple designs, organizing the elements of your artwork onto layers can make managing your project much easier.
The Layers Tab
To get a complete overview of the current layer structure of your artwork while you are working, or to carry out more extensive organization of the layers, you can also use the Layers tab. The Layer List is identical in both the Layer Control and the Layers tab, but the latter can control layer ordering and be left visible, pinned or even undocked, while you continue to work on the artwork itself
List Item Command and Icons
Each layer in the list has five elements:
Status Icon

The leftmost icon indicates whether the layer is currently visible or hidden. Click on this icon to toggle the visibility of the layer.
The presence of a padlock shows that the layer is locked and cannot be accidentally edited.
Right-click the layer in the list and select the Unlock command to alter this.
Layer Colour

The color swatch can be used to color all the vectors on a layer. Click on the swatch icon Layer Color Icon and select a pre-set color from the color selector dialog, or choose to create an entirely custom color.
Layer Content

The layer content icon will be grayed-out as an additional indicator that the layer is not currently visible. Layer Empty Content Icon a blank white sheet indicates that the layer does not currently contain any objects or vector geometry. If you import files from 3rd party CAD drawing packages via DXF or DWG format it is common for the file to include empty layers. This icon allows you to identify these empty layers and delete them.
Layer Name
To change the name of a layer, you can double click on this part of the layer item in the list to trigger in-situ editing. This works in the same way as file renaming in Windows Explorer. Alternatively you can right-click or use the layer's Pop-Up Menu icon to select the Rename command.
Pop-up Menu

Click the pop-up menu icon Pop-up Menu Icon for access to Activate, Lock, Insert, Delete and Merge layers as well as further ways to choose which layers to show and hide.
Select All on a Layer
Double-clicking on a layer in the Layers List will select all the objects on that layer. Alternatively you can choose the Select Layer Vectors command from the layer's pop-up menu.
Layer Ordering Arrows

Adjacent to the Layers List heading label are two arrow buttons. These move the selected layer up or down in the Layers List. This can be important to set the drawing order of objects that might otherwise obscure one another (specifically Bitmaps and 2D Component Previews). Objects on the top layers in the list are always drawn before objects in the lower layers and will, therefore, be 'underneath' them in the 2D View. You can use the Layer Ordering Arrows to resolve this issue.
Add New Layer
New Layers can be added using the Add New Layer button. Alternatively a new layer can be created directly from the 2D View by right-clicking an object and selecting either the Copy to Layer ► New Layer... or Move to Layer ► New Layer...
Layer Name
It is always preferable to take the opportunity at this stage to give your new layer a meaningful name relating to its content or purpose. Later on this name will make it easier for you to manage your layers as your design becomes more complicated
Drawing Color
All the vectors on this layer will be colored according to this setting. This can be a very useful way of distinguishing between the vectors that are on different layers, directly in the 2D View.
New Layer is Visible
With this option checked, ✓ the new layer will automatically be visible as soon as it is created.
New Layer is Active
With this option checked, ✓ the new layer will automatically become the active layer and any subsequent vector creation or manipulation will occur on this new layer.
Insert New Layer
An even quicker way to add new layers is via the Insert Layer command from a layer's right-click Pop-Up Menu. This command will create a new layer above the selected layer which will be visible, unlocked and colored black. After creation the new layer item's name is ready to be immediately edited by typing a new name in.
Moving Objects to Layers
Objects on any layer can be moved onto another layer by right-clicking the object in the 2D View and selecting Move to Layer from the pop-up menu. It is also possible to place a copy of selected object to another layer by selecting Copy to Layer from the pop-up menu.
Gadgets
Gadgets are small programs that add additional functionality to Cut2D Pro, VCarve Pro and Aspire. They can be used to add new features to the software or automate common sequences of tasks. Examples include adding the ability to cut dovetail style joints with a standard end mill and applying toolpath templates to every sheet in a nested job followed by automatically post-processing and saving the files for your machine tool.
Install New Gadget... | Opens a standard Open File Dialog that allows you to chose a downloaded gadget you want to install. |
Gadget Shortcuts | Opens Gadget Shortcuts dialog. |
Installing Gadgets
You can expand your Gadgets library by downloading and installing more from the Gadgets website.
These Gadgets will install into your public documents folder (Public Documents/Vectric/Aspire for ALPHACAM/Gadgets). If you wish to delete any of these Gadgets, simply navigate to the location above and delete the folder.
Each Gadget has specific requirements in order for it to run, it is recommended that you read the instructions in full before use. Some Gadgets require that you select vectors before running the Gadget, others may need to be run before a job in the software is created. When there is a requirement that has not been met before running, you will receive an error message, stating which requirement has not been met.
Note
It is important to point out that the gadgets are NOT as polished as functionality which has been integrated into the main program. The gadget concept is intended to allow Vectric to produce simple add-ons which address minority requirements without cluttering up the main interface. As the Gadget library grows over time, we do not expect users to install every gadget, but only those that may be relevant to tasks they actually perform.
Running Gadgets
Installed Gadgets are accessible from the main Gadget menu, which is built dynamically each time Aspire for ALPHACAM starts up.
Alternatively Gagdets can be assigned shortcuts.
Gadget Shortcuts
Shortcut can be set to run a chosen gadget from the list of gadgets. To set the gadget shortcuts select the Gadget Shortcuts button from the Gadgets menu.
You may then assign one of the predefined shortcut keys to run a chosen gadget. The available shortcut keys are Ctrl and a function key.
Preinstalled Gadgets
A number of Gadgets are included as part of the default installation of Aspire for ALPHACAM. These are all available from the Gadgets menu:
Wrapping Sub-menu:
Note
We ship some gadgets which help perform common tasks for people with rotary axis. If a user has no interest in rotary machining, they can delete the 'wrapping' gadgets from their gadgets folder and those options will no longer be available from the Gadgets menu.
Developing Gadgets
Gadgets can also be created by our users using the LUA scripting language, we provide an SDK and tutorials on the gadgets website.
Please Note
This will require knowledge of programming.
The SDK and the Tutorials are provided as is, Vectric cannot provide support on the development of user Gadgets.
Gadgets have their own section on the Vectric Forum, you can get news on the latest releases from Vectric and fellow users.
Offset Model
I am only for
The Offset model tool creates a 3D offset of the composite model.
To use the tool, specify the distance that you want to offset the model.
Click on the button to see the results of the offsetting.
Click to proceed or click to exit the form.
The Clip Z values to the Zero Plane option will ensure that the final result will always be positive. When used on models with areas that end up lower than the zero plane these parts of the model will be removed leaving only the positive values. This can be helpful when you have a flat plane as part of the model to avoid it being effectively lowered by the offset amount.
Using this function you can offset with either positive or negative values.



Note
Clicking the Preview button repeatedly will apply your chosen offset multiple times. Click the Cancel button to remove all effects of the previews.
Draw Polygon
Polygons (e.g. Triangles, Pentagons, Hexagons etc.) can be created interactively with the cursor and Quick Keys or by entering the number of sides, exact coordinates and radius using typed input.
Interactive Creation
The quickest and easiest way to draw a polygon is by using the mouse in the 2D View.
- Click and hold the left mouse button to indicate the center point.
- Drag the mouse while holding down the left mouse to required radius.
- Release the left mouse button to complete the shape.
Note
Holding ALT and dragging creates a polygon from the middle point.
Quick Keys
Instead of releasing the left mouse button when you have dragged your shape to the required size, you can also type exact values during the dragging process and set properties precisely.
- Left-click and drag out your shape in the 2D View.
- With the left mouse button still pressed, enter a quick key sequence detailed below.
- Release the left mouse button.
Default
By default, entering a single values will be used to set the radius of your polygon. While you are dragging out the polygon, type Radius Value Enter to create a polygon with the precisely specified radius.
Example
- 2 . 5 Enter - Creates a polygon with a radius of 2.5. All other settings as per the form
Specifying Further Properties
By using specific letter keys after your value, you can also indicate precisely which property it relates to.
- Value D - Creates a polygon with the diameter specified, with all other properties as per the form.
- Value S Value R - Create a polygon with the specified number of sides (S) and the outer radius (R)
- Value S Value D - Creates a polygon with the specified number of sides (S) and the outer diameter (D)
Examples
- 1 R - Outer radius 1, number of sides as per form
- 1 D - Outer diameter 1, number of sides as per form
- 8 S 1 R - An 8 sided polygon with outer radius R of 1
- 6 S 2 . 5 D - A 6 sided polyon with an outer diameter of 2.5
Exact Size
Polygons can also be drawn by entering the required XY origin , selecting either Radius or Diameter and entering the required size.
Click to update the circle
Editing Existing Polygons
To edit an existing polygon select the polygon, edit the parameters and click to update the circle.
Keyhole Toolpath
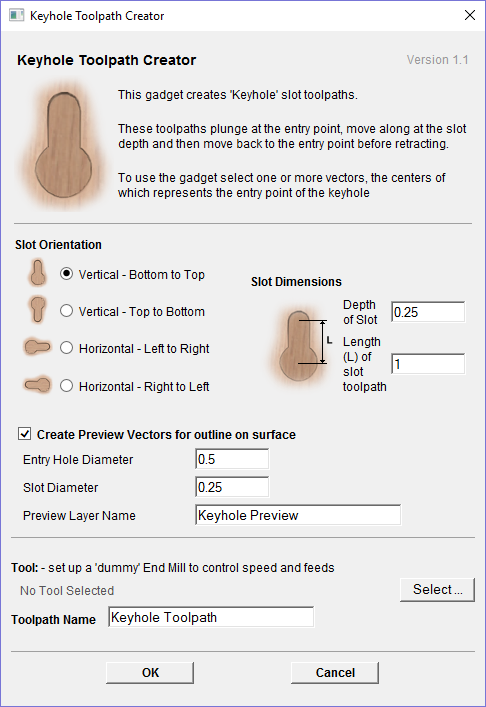
This gadget simplifies the process of creating 'keyhole' toolpaths which are cut into the back of a sign or plaque to allow easy hanging on a wall. These slots are cut using a 'keyhole' cutter as shown on the left. The toolpath for these slots needs to plunge into the material at the mounting screw entry point to a depth that will ensure that the wide part of the cutter is below the material surface. The tool then moves along the 'slot', once it reaches the end of the slot, the tool retraces its path back along the slot to retract at the original plunge point.
Like all Vectric Gadgets, the top of the form gives brief instructions on how it should be used. For this gadget, you need to select one or more circular vectors in your design to indicate where you want the entry points for the keyhole slots to be before the Gadget is run. If you start the gadget without selecting one or more vectors to indicate these positions, the following warning will be displayed:
Once the form is displayed you can enter the parameters for your keyhole toolpath.
The data to be entered falls into three separate categories.
Slot Parameters
In this section of the form you specify the direction the slots will be machined and also the depth and the length for the slots.
Preview Drawing
To help with visualisation of the slot, the gadget can draw a vector outline of how the slot will appear on the surface of your job. This drawing is optional and if you un-check the Create Preview Vectors for outline on surface check box you do not need to fill in the parameters in this section. If you do want previews drawn, you can specify the entry hole diameter which will be created by your keyhole cutter and also the diameter of the slot the tool will create on the surface. You can also specify the name of the layer the vectors will be created on.
Toolpath Parameters
The final section of the form is used to specify a tool which the feed and plunge rates are picked up from, and also a name for the toolpath which will be created. As keyhole cutters are not supported natively by the program, just set up an end-mill with the required feed rates to use.
After entering all your parameters and pressing , the gadget will create a toolpath within the program to machine your slots and also the vector preview if you enabled this option. The screen shot below shows the preview vectors in the 2D view along with the toolpath in the 3D view.
Right Mouse Click Menu
Clicking the ►RIGHT hand mouse button in different places in Aspire for ALPHACAM will display a menu with choices which depend on the area of the software being clicked on and/or the object or selection that the mouse cursor is positioned over. This page details some of these areas and the menus that you will see when RIGHT mouse clicking.
2D View
This menu is displayed when you Right mouse click in 2D View either in the white background of the part or over a selected vector. Most of these options repeat functions and icons described elsewhere in this manual, you should refer to the appropriate section to view how these work.
Layer and Side Operations
The Copy to Layer, Move to Layer, Move to Sheet, Copy to other Side, and Move to other Side options are unique to this Right click menu.
- Copy to Layer allows you to copy an object onto an existing Layer or to create a New one to copy it onto.
- Move to Layer gives you the same choices but moves the original object rather than making a copy.
- Move to Sheet can only be used if you have generated additional Sheets through the Nesting process, in that case it allows you to move objects from one Sheet to a different one from the list available.
- Copy to Other Side copies the selected objects onto the other side in a two-sided job. It will be transformed so that they match up when looking through the material.
- Move to Other Side moves the selection similarly to the Copy operation.
Span Editing Menu
If the current selection mode is set to Node Editing, one of two different menus will appear when the user clicks the RIGHT mouse button depending on whether the cursor is currently over a vector Node or a Span of a selected vector in the 2D View. These menus have functions in them that correspond specifically to this selection and position. The menu shown here will appear when the cursor is over a Span of a vector in Node editing mode. You can see a variety of choices: to convert the span to a Line, Bezier (curve) or Arc, Insert a Point, Cut the Vector at that point, Delete the Span, or Insert a Midpoint. Keep Bezier Tangency, which will fix the start and end directions of Bezier curves when they are being dragged directly, can be toggled on or off. From this menu you can also Reverse the direction of the selected vectors, Close any selected open vectors, Join two selected open vectors or Exit node editing mode. Many of these have corresponding Shortcut keys (shown to the right of the command in the menu) which can be selected from the keyboard when the mouse is in position (over a node-edit vector span) instead of Right Clicking the mouse button to access the menu.
Node Editing Menu
This menu will appear when the cursor is over a Node of a vector in Node editing mode. You can see a variety of choices: Delete the Point, Smooth it, Insert a point at a virtual midpoint, Cut the vector at that point, change the point to be the Start Point of the vector or extend the vector using the Polyline tool. Horizontal or vertical mirror mode for node editing can be toggled on or off. From this menu you can also close any selected open vectors, Join two selected open vectors, Exit node editing mode or lastly see and edit the exact XY co-ordinate position of the node by selecting Properties. Many of these have corresponding Shortcut keys (shown to the right of the command in the menu) which can be selected from the keyboard when the mouse is in position (over a node-edit vector node) instead of Right Clicking the mouse button to access the menu.
Bitmap Properties Dialog
When a Bitmap or Component Grayscale is the selected item in the 2D View and the RIGHT Mouse menu is activated then there will be an additional option in the pop-up menu called Object Properties. This will open the dialog shown below which can be used to fade the Bitmap or Grayscale object strengthen or fade the detail in it when it is not selected. This can be helpful to make it easier to see features perhaps to help you manually trace vectors over it or to fade them so its easier to see vectors that overlap the object.
Level Menu
When a Level in the Component Tree is selected and you RIGHT mouse click on it then the menu shown below will appear.
The first section allows you to make alterations to the selected level where you can change how the level combines with levels below it, you can choose to show or hide the level's visibility (and consequently the Components on it). Using the Select components option will select all the components within the level.
The next section contains the level effects which apply an effect to the level without affecting the individual components.
- The Clipping effect will dynamically clip the combined components on the level to the closed vectors which were selected when the effect was checked on.
- Mirror Mode allows you to mirror the combined components on the level in various ways.
- Wrapping is available for rotary jobs only and will allow components outside the job area that would otherwise be truncated to wrap around to the other side.
The next section allows you to insert new levels, delete the level and rename the selected level.
The final section of the menu allows you to export the complete contents of the level as a .3dClip file - when re-imported this would come into Aspire as a group.
Component Menu
This menu appears when a Component is selected in the Component Tree and you RIGHT mouse click on it:
The first option allows you to select the way the component combines with the other objects on its Level. You then have the option to position the components grayscale in the 2D View, by moving that to the Front or the Back. You then have the options to Copy and duplicate a component along with the option to Export the selected component as a .3dClip file. If you have more that one component selected you have the option to Group/Ungroup the components. You can delete and rename a component. There is also the option to show components, where you can choose to Show This, Show Only This, Show All But This and Show All. You can Hide a component, where an extra menu allows you to Hide This or Hide All. You can open the properties form for the selected component and the last option allows you to move the component to a new or existing Level within the Component Tree.
Component Grayscale Menu
When a Component Grayscale is the selected item and Object Properties is selected it opens the Bitmap Properties slider, allowing you to change the fading of the grayscale component. Two other options are also available on the Right mouse click menu for a selected Component Grayscale. Move to Front and Move to Back. Clicking Move to Front will make the selected Grayscale appear over all the other Grayscales on the same layer so you can see the selected one more easily. Move to Back will send the selected one behind all the others on the same layer so that it is easier to see all the other Grayscales in the part.
3D View Menu - Selected Component
When a component(s) is selected in the 3D view you can RIGHT mouse click and make changes to that selected component(s). You can check the combine mode of a component. You can Unselect a single component or Unselect All depending on how many components you have currently selected. You can hide and delete a component. You can open up the properties form for that component and you have the option to move the selected component(s) to an existing or new Level.
If you choose New Level you will be presented with the box below, where you simply add in the name for the new level and choose a combine mode from the dropdown menu.
3D View Menu - Non-Selected Components
When you RIGHT click on a component without selecting it first the menu will display the names of the components that are positioned at the point your cursor is within the job space. Selecting the name of the component will select it and open up the Properties form for that selected component.
Clipart Menu
When you RIGHT click on a piece of clipart in the clipart tab you have the option to import it to a new or existing level in your job. This will position the object in the center of the workspace and add it to the top of the list of Components on the selected Level or if you choose New Level will allow you to enter a name and Combine Mode.
Toolpath List Menu
When you RIGHT click on a toolpath name within the Toolpath List there are various options you are presented with to alter this toolpath. You can show a toolpath where you have the option to
- Show This,
- Show Only This,
- Show All But This
- Show All With This Tool
- Show All.
This toggles the visibility of the Toolpaths according to your choice. The next option allows you to Hide This or Hide All your toolpaths.
You can Edit, Rename or Duplicate the selected toolpath. Selecting Recalculate All will work through the toolpath list recalculating each toolpath with any updated geometry selections.
The last option allows you to delete one or more toolpaths, where you can Delete This, Delete All Invisible, Delete All Visible and Delete All.
Offset Vectors
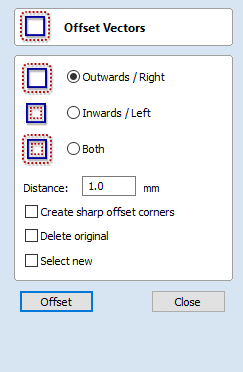
Selected vectors (open or closed) can be offset either inwards or outwards to create new vector shapes that might be useful for edge patterns or borders etc. To offset a vector shape, use the following steps:
- Select the vectors to offset
- Select the required direction - Outwards / Right or Inwards / Left
- Enter the Distance
- Click the button
Options
The offsetting options are slightly different in their behavior depending on whether the vector to be offset is open or closed. See below for more information.
Create sharp offset corners
Will retain any sharp corners in a design.
Offsetting Open Vectors
When offsetting open shapes, the options are either to the Right or Left side of the selection. The direction of open vector(s) is very important as this is used to decide the right and left side of the selection. Selecting Node Edit mode (pressing N on the keyboard) will display a Green node at the start of the vector. Looking along the vector(s) from the green node indicates the direction and the image below shows offsets to the left and right of an open vector.
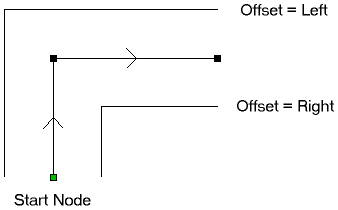
Advanced Modelling of 3D Rotary Projects
Modelling 3D spiral features
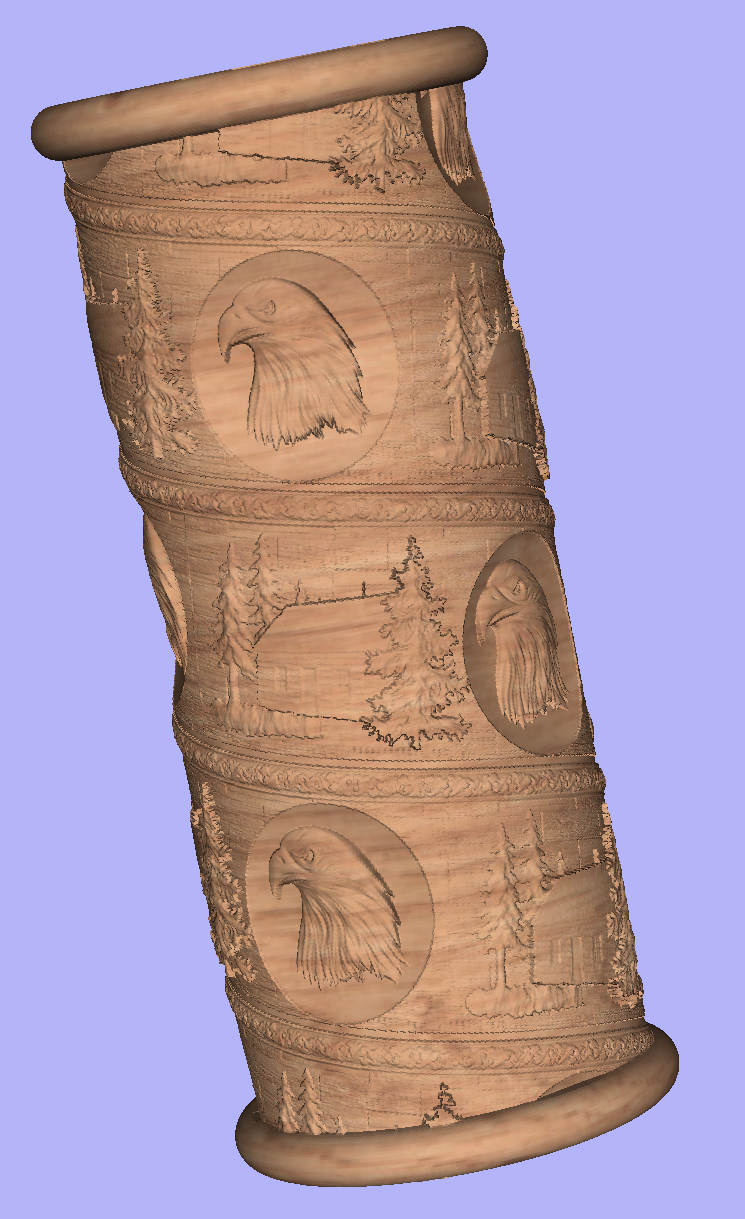

In this section we will show how to use level-wrapping feature to wrap a design in spiral manner around a column.
The workflow for creating spiral toolpaths has been presented in Simple rotary modelling using 2D toolpaths chapter. The basic idea involved creating a line at a proper angle to the rotation axis, that exceeded the 2D boundaries. When 2D toolpath is created based on such a line, it will be wrapped around material cylinder, creating a spiral.
This guide will build on that basic idea. The task is to create a horizontal strip with desired pattern and then wrap it like a ribbon around the cylinder.
To help with that task, it is important to create some helpful vectors first. We need to create lines, that will become boundaries of our strip. In this example the strip was being wrapped four times around full length of material. This example assumes that rotation axis is parallel to X axis.
To start, select Draw Line/Polyline tool and draw a horizontal line at the bottom of the job from left to right. If it is desired for the spiral pattern to only fill part of the cylinder length, this horizontal line should be drawn only in th desired location. While the drawing tool is still active, type 90 into Angle box and type y * 4 into Length box and pressing =. We used y * 4 formula so the strip will wrap 4 times. Then press Add button to add a vertical segment.
Now, start a new line that connects the horizontal and vertical lines, forming a triangle. Once this line is created, horizontal and vertical lines can be removed.
The line that we just created will form a bottom of the strip. Now copy this line and place line so its bottom left end coincides with top left corner of 2D job. This line will form a top of the strip. Then make another copy and place it in the middle. This middle line will be used later to position our design within strip. All three lines have been shown below.
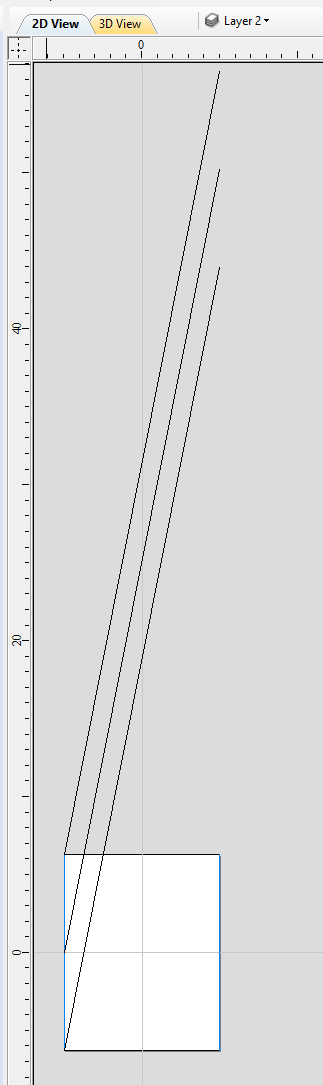
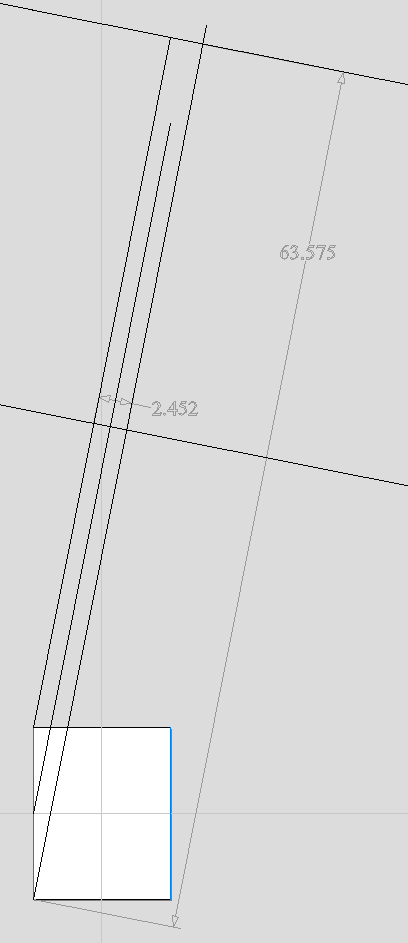
Next step is to find out the required length and width of the strip. We will need a few extra vectors to accomplish that.
Let's copy one of the created three lines and rotate by 90 degrees, to get a line that is perpendicular to the strip. Then place it in such way so it crosses the strip. This will help us measure the width.
Then copy the perpendicular line and place it so it touches the top line. Then extend the bottom line, until it crosses the perpendicular line we just added. This will help us measure the length of the strip.
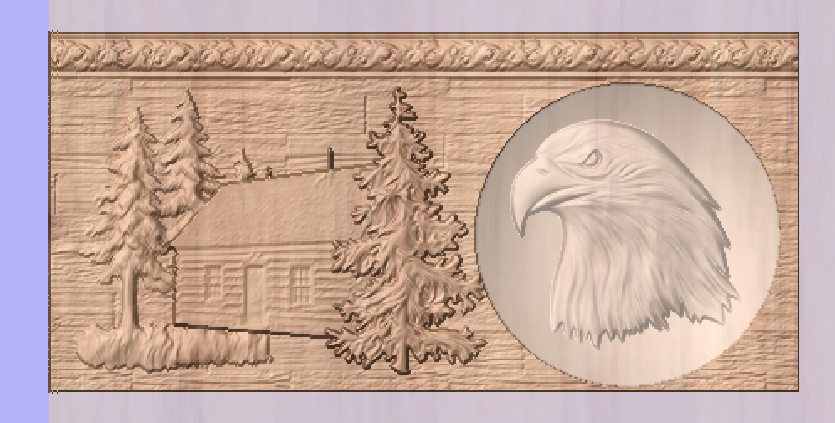

Easiest way to achieve that, is to create a textured component. To do that, select the design in the component tree and activate the Create Texture Area tool. This example used the default settings of the tool. The tool will create a new component that will fill the whole 2D job boundaries. The component itself will be filled with the design in tiled manner. Now use Set Size tool to resize textured component to match the strip size.
Now the component have to be rotated and moved to fit between the lines be have drawn at the beginning. This process can be made easier by utilizing Copy Along Vectors tool. To proceed, activate the tool and select the textured component first, then select the middle line in the strip while holding Shift. Make sure that Align objects to curveoption is selected and use Number of copies option. Since our strip has already have a correct size, we only need one copy. However the tool would place the middle of our component at the beginning of the line only. If enter 3 as the number of copies, then the tool will place two copies of component at each end and in the middle. Afterwards copies at the ends can be simply deleted. The picture below shows the strip in the 3D view after being correctly positioned.


As can be seen, the strip disappears as soon as it leaves the material boundaries. In order to make it wrap around, we need to create a new level in the component tree and move the texture component into it. Then right click on the newly created level and right click. From the pop-up menu select wrapping. After that wrapping will occur.
Note:
Wrapping can be enabled on any level in component tree and combined with mirror mode. If the level wraps on itself, then intersecting areas will be merged regardless of level's combine mode. If it is desired to create e.g. a woven pattern, then place left-hand spiralled component and right-hand spiralled components in different separate levels, both with wrapping enabled.
The last step is to make column endings. For that purpose third level was created, with Combine Mode set to Merge. This way the spiral pattern will be 'hidden' at the ends. A circular 3D tab clipart was placed at each end, and stretch vertically to match the job boundaries.
Modelling twisted shapes
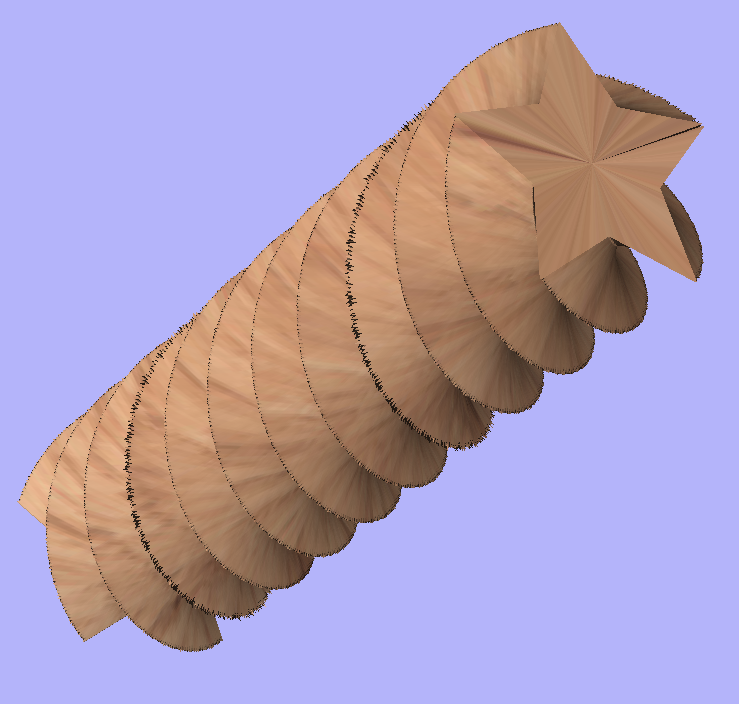
This section will show how to create twisted shapes, using combination of level-wrapping and Vector Unwrapper tool.
In this example a new rotary job was created, with diameter of 6 inches and length of 20 inches, rotating around X axis. To start, we need a cross-section vector. In this example a 5-armed star was used. To create a star, we can use Draw Star tool. This example used Outer Radius of 3 inches, to match the radius of the material.
The next step is to unwrap the cross section. In the case of star however, the center is not the same as center of star's bounding box. To find the real center, one can draw line from two of the star corners. Then open Vector Unwrapper and select the star. Then drag rotation center and snap it to the intersection of the lines, as can be seen below.
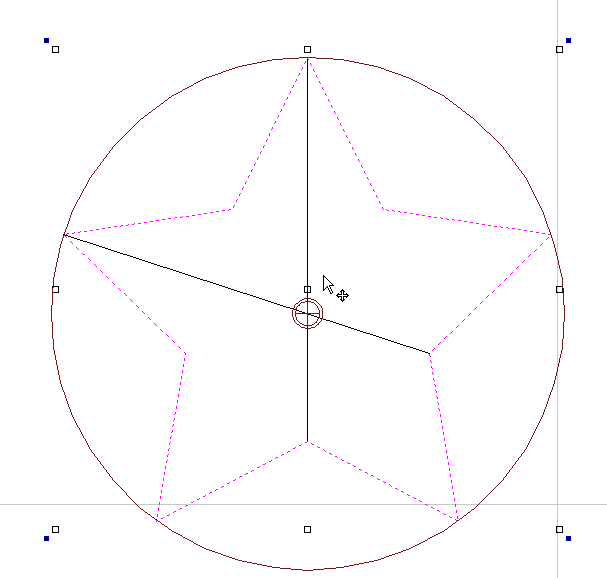
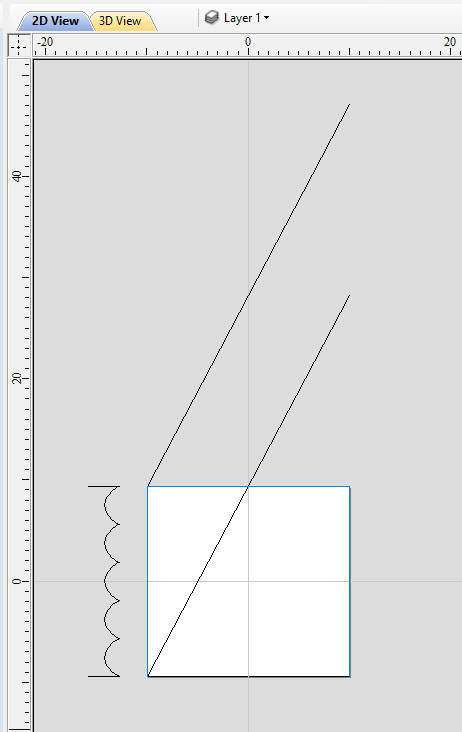
Once the star is unwrapped, we need to create rails, that will make spiral when wrapped. To do that, select Draw Line/Polyline tool and draw a horizontal line at the bottom of the job from left to right. While the drawing tool is still active, type 90 into Angle box and type y * 2 into Length box and pressing =. We used y * 2 formula so the star will make 2 revolutions Then press Add button to add a vertical segment. Finally, start a new line that connects the horizontal and vertical lines, forming a triangle. Once this line is created, horizontal and vertical lines can be removed.
Next step is to copy the line and place it so its bottom left end coincides with top left corner of 2D job.
Once the the rails are ready, one could use a Two Rails Sweep tool. However, since rails exceeds the 2D job boundaries, the created sweep will be cropped as soon as those boundaries are exceeded.
To overcome that, select both rails, open Draw Rectangle tool and press Create. This will create a bounding box containing the rails. Now, write done the size of the box and save current project. Then create a new single-sided project with the slightly bigger than the bounding box. Use Import Vectors option from the main menu and select previously selected file. Now select the rails and press F9 to center them.
Now use Two Rail Sweep tool. When component is ready, save the file.
Now re-open the original rotary project. Use Import Component and select single-sided project created in the step above. Move the component to the desired location. Then, create new level, move the component there and enable wrapping.
Using single-sided modelling tools
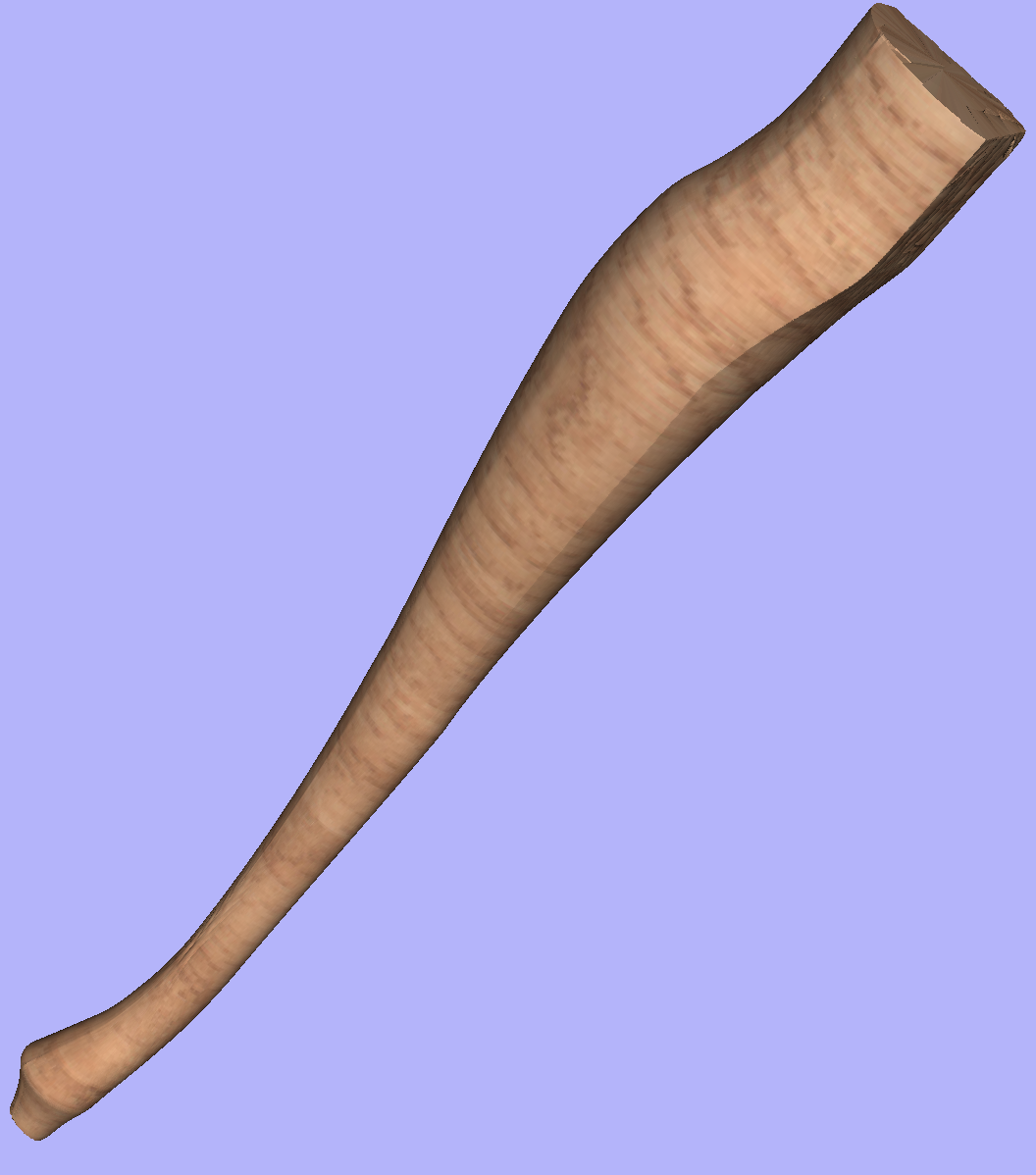
This section will present how to use single-sided modelling techniques in rotary projects.
Users familiar with modelling techniques used in single-sided projects may find them more convenient for modelling certain shapes. This example uses two vectors, representing side cross section of the table leg and a few of half cross sections for different parts of the table leg. Those vectors are presented below.
One can simply treat side cross section as rails and use Two Rail Sweep tool, placing half cross sections at appropriate locations. This way half of the leg can be modelled very quickly, with the result that can be seen below (using flat 3D view).

In order to use the created model in rotary project, we need to export and then import it back. Although it is possible to do this with two sessions of Aspire, it can also be done within a single session with rotary project. To export the leg model, make sure no other components are visible (including the automatically added zero plane) and open Export Model tool while holding down Shift. Pressing Shift allows to open the export tool in single-sided, rather than rotary mode.
Since half of the leg was modelled, Close with inverted front option was used. The resulting STL mesh can be seen below.
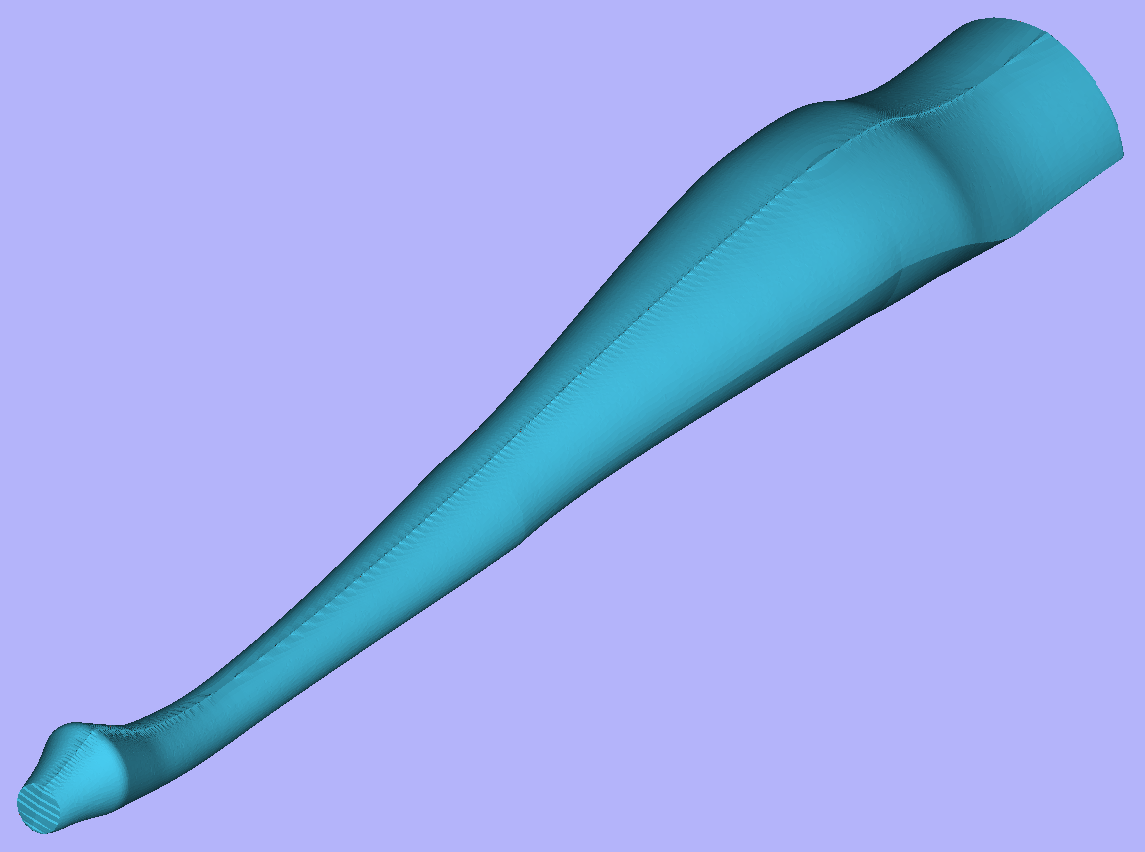
Once component is exported, it can be re-imported as Full 3D model. The model wil have a seam, in the place were two halfs were merged. This can be removed using smoothing function of Sculpting tool.
Two Rail Sweep
Two Rail Sweep uses a combination of vectors to define a swept 3D Component. The shape is based on two drive rails which can be open or closed vectors and multiple cross sections which are positioned on the drive rails and have to be created using open vectors.
Drive Rail Selection
The first stage of using this tool is to select the vectors which will represent the Drive Rails. From the 2D View use the mouse to select two open or closed vectors then click the button.
In the 2D view your rail vectors will now be colored red (first selected vector) and green (second selected vectors) and show a square green start node indicating the start point of each rail and arrow markers along its length to show the direction the shape will be swept.
The start point and direction may not be what you intended. To change the direction, right-click with the cursor on the drive rail you want to edit and select from the context sensitive menu, you will now see the arrows on the drive rail change direction.
You can also change the order the rails were selected by clicking on this will swap so the red rail becomes green and green becomes red, doing this will cause the cross-sections to hang in the opposite direction. On a closed vector you can change the start point by placing the cursor over an existing node in the drive-rail vector, right-clicking and selecting or you can right-click anywhere on the vector and select Insert Start Point to create a new node which will become the start point.
The button on the form can be used at any time to empty your current selection. This will delete your current shape and deselect all the drive rails and cross section vectors. This can be used if you do not want to create a Component before you exit the form or if you want to select new vectors in the 2D view to use as the drive rail for your shape.
Cross Section Selection
After you have chosen your drive rails the next step is to select one or more cross-section vectors to sweep along those vectors to form a 3D shape. In order for vectors to be used as valid cross-section shapes, they must be open.
Select a vector that you wish to use as a cross-section in the 2D View by left clicking on it with the mouse.
If you are using just a single cross section then you just need to make sure it is selected and then can proceed with the other settings in the form and calculate your shape. If you want to edit cross section positions or add more than one cross section then you will need to attach them to the drive rails.
Select a vector that you wish to use as a cross-section in the 2D View by left clicking on it with the mouse. Now click on the drive rail to attach the cross-section to that vector.
As you move the mouse over a selected drive rail it will indicate with a check mark ✓ that it is a valid place to add the cross section. Once a cross-section has been successfully attached to your drive rail, the 2D view will show a preview using line markers to indicate how the cross section will be positioned when it is extruded.
Two Cross-Sections are always created when you attach the first cross-section to the drive rail - one across the start nodes of each vector and one across the ends. The intermediate lines along the entire length of the rails indicate how the shape will flow between the defined cross sections. You can click the button to create your 3D swept shape.
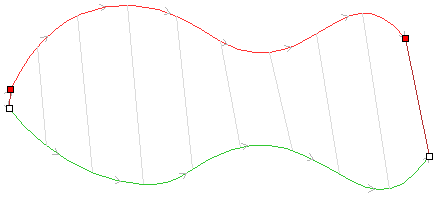
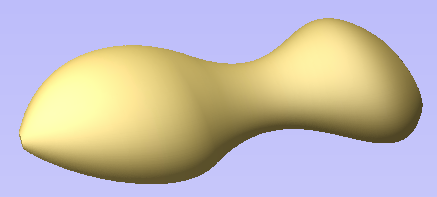
Using multiple cross-sections
It is possible to extrude between multiple cross section vectors along a drive rail blending from one vector shape to another.
Adding Cross-Sections
To add a new Cross-Section to an existing extrusion, simply select an open vector in the 2D View that you wish to use as a cross-section. With the vector selected, click on the point along the rail to which you wish it to be attached. A new Cross-Section will be inserted at this point and automatically attached to the second rail. On applying the change, the resulting 3D sweep will blend between all the defined Cross-Sections along the rail.
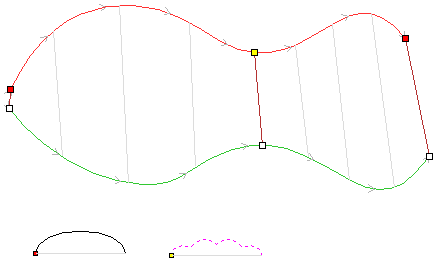
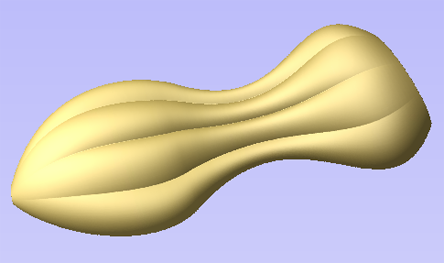
Note
To help differentiate which cross section is being used at each location the software will indicate a colored node at one end of each cross section and place the same colored node on the preview position. This node also indicates the direction the cross section is being 'hung' across the rails. The same cross section vector can be used in multiple locations along the drive rail.
Connecting Rail Nodes
By default, Aspire sweeps the cross-section along the drive rails connecting points at the same proportional distance along each rail's length. So, for example, the positions halfway or three-quarters of the way along each drive rail will be connected by the cross section in the resulting 3D shape.
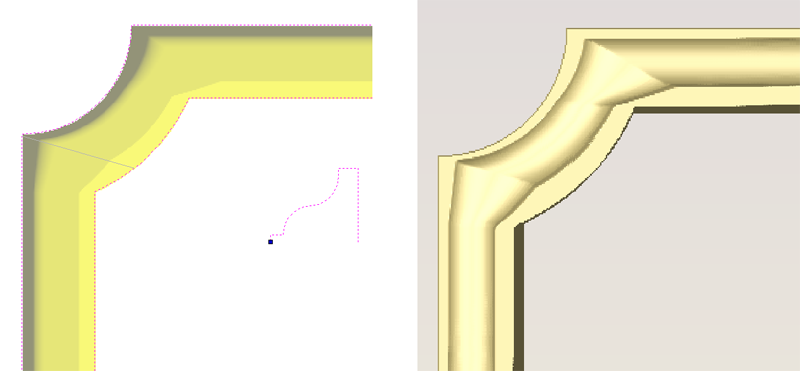
As the images above show, when the matching proportional positions along each rail do not match the appropriate features of the shape it can produce undesirable results. In this example the corners of the frame design are at different proportional positions along each rail and so the two-rail sweep does not connect the corners. Instead the cross-section appears stretched around the frame, as it is used to connect other points that do match in their proportional distance along each rail.
To resolve this, the software allows you to force the connection of pairs of points along the drive rails. This can either be done manually by inserting and re-positioning the cross-sections across the corners (see sections below for more information on this), or if both the drive rails have the same number of nodes it can be done automatically after you have added the first cross section by right-clicking on the first cross section preview position and selecting Add To All Rail Nodes. This will add that same cross section to every pair of nodes on each drive rail. When the cross section positions are set up correctly then Aspire will sweep the shape between each cross section location and create clean corners as shown in the images below.
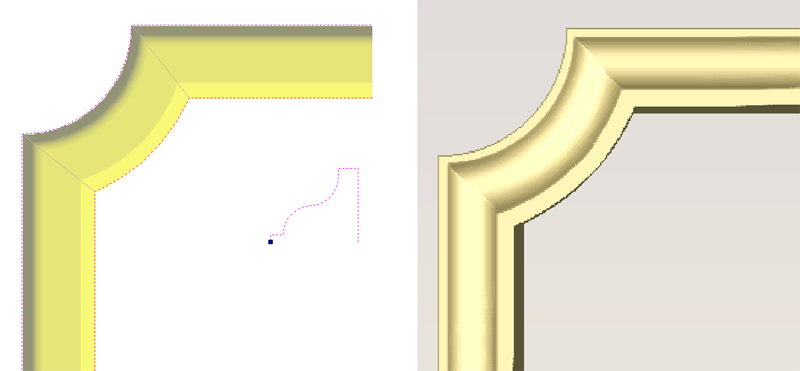
Removing Cross-Sections
To remove a Cross-Section, position the cursor over the cross section and press the RIGHT button on the mouse. Select the option to Delete Cross Section from the menu.
You can remove all the Cross-Sections on the drive rails by positioning the mouse arrow over a part of the curve that does not contain a cross section. This will bring up a different context sensitive menu and you can select the options to Remove All Cross Sections.
Altering Existing Cross-Sections
Existing cross-sections can be re-positioned on the drive rail. To do this click on the nodes at either end of the cross section preview in the 2D View (the ones on the rails), hold the mouse down and drag the node to a new position on the curve, let go of the mouse button to release that end of the cross section in its new position. You should make sure you do not drag a cross section past another existing cross section on the shape. If you need to move cross sections out of their current order then you should remove the existing cross section and insert the same shape at the new position so the shape can be created correctly. Any of your current cross-sections can be replaced by selecting a different open vector, moving the mouse over the end node of the cross section you want to change and clicking on it. The node color indicated on the cross section preview position on the curve will change to indicate which vector is now being used at that point in the shape.
Controlling the Swept Shape
There are check boxes in the form that allow you to Scale cross sections with width, Sweep between spans, and Fill center of inner closed vector rails. The Smooth option under the right-click menu allows you to control different aspects of the shape you create with the selected set of vectors.
Scale cross sections with width
As the cross sections are extruded along the rails the user can either choose to retain the exact shape and height of the cross sections or for a more natural look the Scale cross sections with width option can be checked ✓. This will alter the height of the cross section in proportion to the distance between the rails. This means that as the rails get further apart the shape gets higher and as they get closer together the shape gets lower. The image below left shows the result if this option is un-checked and below right with it checked ✓.
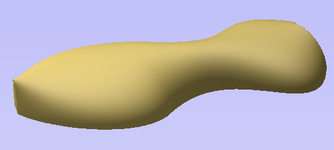
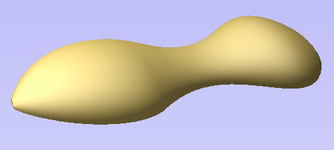
Sweep between spans
This option only becomes active if all selected cross section vectors have the same number of spans and nodes. When checked ✓ it will ensure that as the shape is extruded that it goes from a particular node/span in one cross section to the same node/span on the next cross section. In certain shapes this can give the user more control over the way the shape flows.
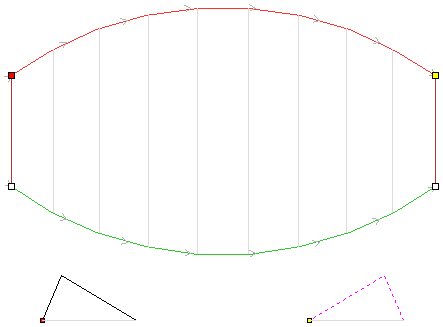
Fill center of inner closed vector rails
If you are sweeping two closed vectors to form a border or boundary shape, you can have Aspire automatically find the height that the cross-section forms on the inner boundary and then fill the shape to this height. To activate this check ✓ the Fill center of inner closed vector rails option in the form. This tool is perfect for sweep decorative bases, plaques or stands. Below left you can see a shape created with this option off and on the right an option with it activated.
Smooth transition through the Cross Sections
As the swept shape passes through each cross section the default is for it to flow smoothly through the profile. This can be edited by right-clicking over the end node of the cross-section and unchecking the Smooth option.
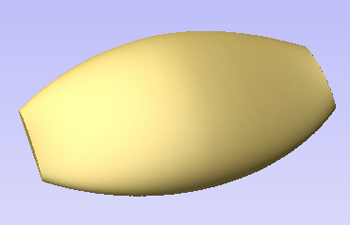
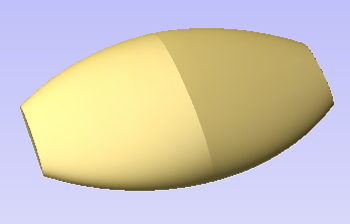
Scale to Exact Height
Checking ✓ this option scales the shape calculated so its maximum height is the value entered in the Height area of the form.
Common Modeling Options
All of the main modeling tools in the software use a common set of commands to assign a name and combine mode to the component being created along with options to apply the settings in the form, reset the shape, start creating a new component and close to exit the function.
Combine with other components...
This section includes options to allow you to name your Component and control the way it will be combined with other objects in the Component Tree.

Reset
Clicking the button will remove the current shape, doing this before you Close the form will ensure that a component is not created from the current selection. Clicking this does retain the current set of selected vectors or Components.
Apply
Clicking the button will create a shape based on the settings you have chosen. You can continue making edits to the component by choosing different parameters within the form and hitting Apply to update it.
Start New Component
Clicking the button will save the state of the component that has been created, deselect all components/vectors and start the creation process again on a new component. The values and options within the form will be retained in this case until you Close it.
Close
Clicking the button will close the form returning to the Modeling Tab icons and the updated Component Tree, reflecting any changes that you have made. If you wanted to remove the shape you just created then you can hit the Undo icon or use the keyboard shortcut to undo, CTRL+Z.
Join / Close Vector with a Smooth Curve
Join with a Curve finds the closest end points on 2 selected, open vectors and joins them together with a smooth curve.
Aspire for ALPHACAM has two smooth joining methods:
- A smoother method (new for V9.5)
- A more symmetrical shallower join method
Copy Along Vectors
This tool automatically creates repeating patterns of objects by placing copies of them along the length of one or more selected vectors. The tool allows any existing object to be used but it also has an option specifically for the creation of circles, which is a common design element for patterns of this sort.
Copy Object
Any shape vector or group of vectors can be copied along a curve or curves. The first vector or group of vectors selected is the object that gets copied multiple times along the curves.
Copy Circles
Enter the diameter of the required circles
Distance between copies
This is the distance along the selected curve between each pasted vector. The Force even spacing option ensures that objects are pasted at the end points on the curve(s). If this option is not selected the pasted objects will be placed at the specified distance and may not match the exact length of the curve.
Number of copies
Selecting a specific number of copies automatically sets the specified number of copies along the entire length with an even spacing between them
Align Objects to curve
With this option selected the pasted objects are automatically aligned 'normal' or perpendicular to the curve they are being copied onto. If this is not selected, the copied objects stay in the orientation of the original.
Create Copies on new layer
This option creates the multiple copies on a new layer making it much easier to select and organize the resulting vectors for machining purposes etc.
Reverse Direction
If your copies appear upside down, this option will perform the copy operation in the opposite direction along the selected vectors and the resulting copied shapes will be created the other way up.
Vector Selector
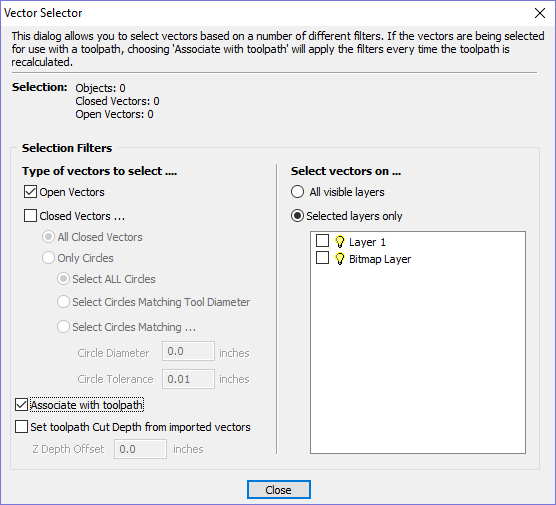
This tool allows you to easily select vectors which meet a set of criteria, such as open, closed, circular and also matching constraints based on layers. The dialog can be accessed from the Edit ► Vector Selector menu item, or from the button on each toolpath form. When the command is executed the dialog shown is displayed.
The dialog is used to configure a set of 'filters' that determine which vectors will be selected. A filter is enabled by clicking on its check box, or selecting a 'radio button' option, the current selection will be updated with all the objects in the file which match the current filter options.
Generally you will start at the top of the dialog and work downwards, specifying more and more explicit filters to determine the required selection exactly.
The simplest option is just to use the form to Select Closed Vectors in the job or Select Open vectors (you can specify both, in which case all vectors will be selected as long as they are on a visible layer).
The most common way to use the Vector Selector is to select all the vectors on a given layer as shown in the screenshot of the dialog below.
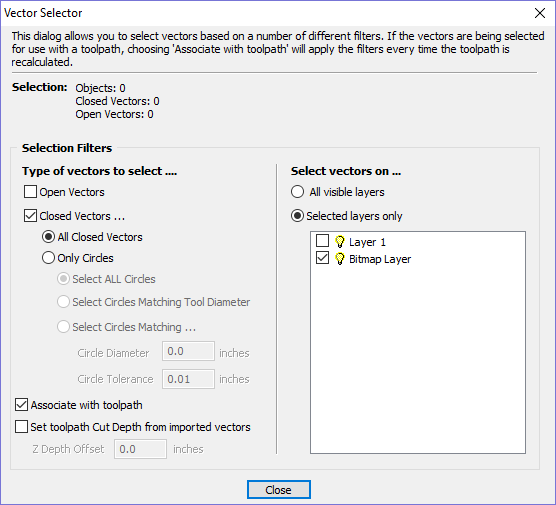
Note
When opened from Edit ►Vector Selector, the options Associate with toolpath and Set toolpath Cut Depth from imported vectors are not available. These options are only usable when applying the vector selector from a toolpath form.
Selection
The Selection: section at the top of the dialog is continuously updated to show the results of the current filter and the 2D view is also updated to show what is currently selected. The Objects: entry shows the total number of objects selected, if these objects include Text or Groups, this number may be less than the total of Closed and Open vectors displayed on the following line. For instance, a block of text is one object but will usually consist of many closed vectors. If a group contains both open and closed vectors, it will be selected as matching both Open and Closed filters.
Geometry Filters
The Geometry Filters section is used to specify constraints on the type of vectors to select. You can choose to select open vectors and/or closed vectors. Instead of selecting All Closed Vectors, the dialog can be used to select Only Circles and can even be used to specify an exact diameter and tolerance for the circles to be selected. This can be very useful for selecting vectors for drilling toolpaths, particularly if the vectors have not already been sorted into layers.
Layer Filter
The Layer Filter section allows you to pick one or more visible layers on which to select vectors which match the geometry filter. Alternatively, the All visible layers option disables the filtering by layer and selects all vectors which match the geometry filter regardless of the layer they are on, as long as that layer is visible.
Advanced Toolpath Templates
By associating a template with the result of a Vector Selector filter, we can make a template to automatically select the vectors it is intended to machine. A simple case would be to create a template which consisted of a Pocketing toolpath set up to machine all closed vectors on a layer called Pocket. After loading this template into a new job and choosing Toolpaths ► Recalculate All Toolpaths , the toolpath would be recalculated automatically selecting all closed vectors on the layer called Pocket.
The advanced templates are created by selecting the vectors for a toolpath using the Selector... button on the toolpath form. When a toolpath form is first opened, the Vector Selection: section on the form will show that vectors are being selected manually as shown below...
Pressing the Selector... button will display the Vector Selector form as shown previously. After making your geometry selection and before you close the form, select the Associate with toolpath option on the form as shown below.
After the Vector Selector form closes, the Toolpath form will indicate that Vector Selection is now 'Automatic' as shown below...
Note
Calculate the toolpath to apply the changes you have made.
When you re-calculate or edit a toolpath that has the Vector Selection mode set to automatic, the vectors which match the filter when the toolpath is re-calculated or edited will be selected. To cancel the Automatic vector selection mode, you can just select the vectors to machine normally with the mouse, or use the Selector... button to bring up the Vector Selectordialog again (the settings are remembered) and uncheck the Associate with toolpath option.
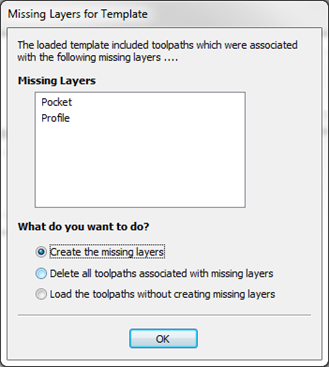
If toolpaths with the Vector Selection mode set to Automatic are saved as templates, these setting are saved with the template. When the template is re-opened and the toolpaths recalculated, they will automatically select all vectors which match the filters specified with the Vector Selector for that toolpath.
If you load a toolpath template which has toolpaths associated with layers which don't exist in the current file, the Missing Layers for Template dialog will be displayed. It lists all the missing layers and offers you the choice of having them created automatically, deleting toolpaths associated with missing layers or just loading the toolpaths as is.
Choosing to allow the dialog to automatically create the missing layers allows a toolpath template to be used to create 'standard' layers for machining operations and load the toolpaths ready to be calculated. All you then need to do is move vectors to the appropriate layers and recalculate all the toolpaths.
Choosing the Delete all toolpaths associated with missing layers option allows you to create a single template with many toolpaths and have the ones which aren't appropriate to the current job automatically deleted.
Options Dialog
Note
Many of the choices in this dialog will not take effect until the software has been exited and restarted.
Window Layout
Save Tab Layout | Save the layout and the 'pinned' state of the command and toolpath fly out tabs. |
Save Dialog Layout | Save the size, position and visibility for dialogs such as the Layer control and Toolpath Control dialogs. |
Save View Layout | Save the layout of the 2D and 3D view windows. |
Display Splash Screen | Display the program Splash Screen, while the program is loading. |
Top Side Ruler Color | The colour of the ruler on the top side in a two-sided project. |
Bottom Side Ruler Color | The colour of the ruler on the bottom side in a two-sided project. |
3D View Settings
Shaded Background Style | Allows to choose between Solid, Gradient and Image background styles. |
Background Color | Change the background color used for the 3D view. Used with Solid and Gradient background styles. |
Gradient Background Color | Change the bottom (lightest) color used for the 3D view. Used with Gradient background style. |
Draw Origin | Draw the origin arrows by default on startup. |
Draw Material Block | Draws Material Block boundaries by default on startup. |
Use Color Shaded View | Draw shaded model in 3D view by default on startup. |
Print 3D View Shaded Background | Include the shaded background when printing. |
Animate Camera Moves | Switch on/off animation in the 3D View when selecting View positon from the Iso View, Down X, Down Y or Down Z icons. |
Image File Path | Path to the image to be used as background. Used with Image background style. |
Toolpath Settings
Show Toolpath Operations with Preview | When the toolpath Preview form is visible, keep the 'Toolpath Operations' section visible (requires more screen space). |
Auto Open 3D view | Automatically swap to 3D view after calculating a toolpath. |
2D Solid Preview Color | Color used to draw the solid 2D toolpath preview with. |
Create 2D Previews | Create 2D previews of toolpaths in 2D view. |
Select Sheet When Edit Toolpaths | If a toolpath is associated with a sheet, select sheet when edit toolpath. |
Toolpath Geometry Fixing Timeout | Number of seconds the program will spend trying to fix problems with geometry when calculating toolpaths. |
Drop Tool | When projecting a toolpath onto the model, drop the tool on surface rather than project. If this is set, the toolpath will follow the surface of the model better, but could be slower to calculate. |
2D Toolpath Tolerance | Tolerance to apply to 2D toolpaths after calculating to reduce file size. |
3D Toolpath Tolerance | Tolerance to apply to 3D toolpaths after calculating to reduce file size. |
VCarve Toolpath Tolerance | Tolerance to apply to VCarve toolpaths after calculating to reduce file size. Note We strongly recommend that the Toolpath Tolerance should be left at their default settings unless different values are recommended by your machine tool manufacturer. If you do have a machine which struggles with the default settings, try doubling the values and cutting a test-piece to assess the tradeoff between machining times, file size and final machined quality. We have done some limited testing and on a sample complex 3D model, increasing the '3D Toolpath Tolerance' to 0.001 inches gave a 40% decrease in file size and no noticeable difference in quality on the test machine and job. In the test case there was no measurable difference in machining time on the CNC machine the test was carried out on. |
Maximum Toolpath Undo Stack Size (MB) | Maximum size in MB of Toolpath data undo stack for storing toolpath delete state. |
Append duplicated toolpath | When duplicating a toolpath, this determines whether it places the new toolpath next to the original or append it to the end of the list. |
Use new raster | Generate raster toolpaths that are more consistent in regards to machining direction, even for complex shapes. |
V-Carve Vector Intersection Check | This option determines whether or not to check for vector intersections when calculating a V-Carve toolpath and what to do when they are detected. |
General Settings
Use Graphics tablet | Switch on support for graphics tablet drivers, if installed - for use with the sculpting tool. |
Process User Files | Enable/disable processing of files in the 'Vectric Files' folder in your common user document folder. |
Recent File List Size | This sets the maximum number of items that will be displayed in the Recently opened files... list in left hand side bar of the interface when there is no file currently loaded. The list will not increase in size until the software has been re-started and more files have been opened and/or saved. |
Show the clipart Subfolder Contents | If set to Yes then this will show the contents within the selected Folder in the Clip Art browser along with up to 3 sub-folders if they exist and contain appropriate file types. If set to No it will only display the contents of the selected folder, not sub-folders. |
Always open local documentation | Force open the local copy of the documentation when accessed through the Help menu. Aspire for ALPHACAM automatically opens the local documentation if you have no internet connection or if the server is taking too long to respond. |
Smooth Join Vectors | Produce a smoother join between 2 vectors. This is option is there mainly to support older behavior. |
Default to last used text anchor position | Control the default location of the anchor when creating a text object. This is to either default it to the last set location, or always default to a specific location. |
File Dialog Default | This option controls the default directory that is opened when opening or saving files. The default Global options will open the last used folder as per the Operating Systems default behavior. If you choose Operation, the software will remember the last used folder for that particular operation. We divide operations in broad categories, such as, vector import / export, model import / export, toolpaths, tools, etc... If you choose Job, we will always default to your saved job's location. |
Create Shape
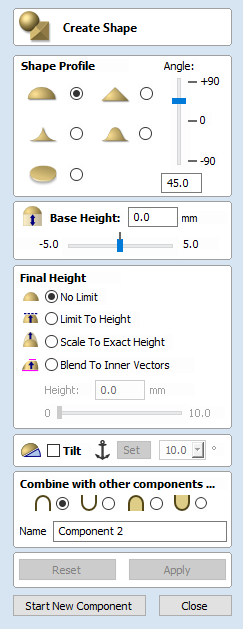
The Create Shape tool allows the user to create Components based on one or more closed vectors. The vectors can be selected either before the icon is clicked or after the form is open. The user works through the form specifying the profile and strength of the shape and modifying options to govern its height. There is also an option to Tilt the shape on an angle. Once any of the parameters have been defined the shape can be previewed by hitting .
This shape can be easily changed by altering the parameters in the form and hitting the button to update the preview. Once you are happy with the shape created then you have two choices, to (which will save your current component and start a new one) or the form.
Changing values with the sliders on the form will immediately update the 3D view when you release the slider. If you make changes to the edit fields such as Angle or Base height, pressing the 'Space' bar on your keyboard after you have finished entering your value will apply the changes and update the 3D preview or you can hit the button again.
If you select another vector, then the current shape will be discarded, so remember to hit if you want to keep a copy of it.
Shape Profile
There are five different shape types:
Curved

Angle

The Angle setting will define the angle of the edge of the rounded or angled profile shape - the higher the angle, the steeper the shape. Angular shapes can have a maximum angle of 89°. The slider bar to the right can also be used to change this as well as typing a specific angle into the form.
Concave

S-Shaped

Flat

Base Height
Specifies the height of a flat 'base plane' added below the profile you have chosen.
Final Height
No Limit
Checking ✓ this option lets the combination of the size and shape of the vector and the specified profile values govern the final height of the shape.
Limit to Height
Checking ✓ this option limits the height of the shape by flattening it off at the value entered in the Height area of the form which becomes active once this option is selected.
Scale to Exact Height
Checking ✓ this option limits the height of the shape by scaling the shape up or down while retaining its general specified profile. It is scaled to the height entered in the Height area of the form which becomes available once this option is selected. The slider can also be used to change the final height.
The Base Height value is not included or controlled by the Final Height setting and if specified will be added to this value to give the total height of the component being created.
Blend To Inner Vectors
This option applies the selected profile across the selected vectors. It blends to the profile from the outside of the vectors to the inner vectors

Tilt
When this option is checked ✓ the user can set a direction and angle to tilt the shape up at an angle in Z. The first part of this operation (once the option is checked ✓) is to press the button - then click two points in the 2D view.
The first click specifies the point which will remain at zero (the pivot point of the tilt).
The second click specifies the point that will be tilted upwards by the specified angle (the point that will be raised up).
The default angle (10°) can be edited by clicking the arrow next to the value and using the slider or by typing in a specific value and hitting the Space Bar on the keyboard to apply the angle.
Common Modeling Options
All of the main modeling tools in the software use a common set of commands to assign a name and combine mode to the component being created along with options to apply the settings in the form, reset the shape, start creating a new component and close to exit the function.
Combine with other components...
This section includes options to allow you to name your Component and control the way it will be combined with other objects in the Component Tree.

Reset
Clicking the button will remove the current shape, doing this before you Close the form will ensure that a component is not created from the current selection. Clicking this does retain the current set of selected vectors or Components.
Apply
Clicking the button will create a shape based on the settings you have chosen. You can continue making edits to the component by choosing different parameters within the form and hitting Apply to update it.
Start New Component
Clicking the button will save the state of the component that has been created, deselect all components/vectors and start the creation process again on a new component. The values and options within the form will be retained in this case until you Close it.
Close
Clicking the button will close the form returning to the Modeling Tab icons and the updated Component Tree, reflecting any changes that you have made. If you wanted to remove the shape you just created then you can hit the Undo icon or use the keyboard shortcut to undo, CTRL+Z.
View Toolbar

Above the view window is a handy toolbar that allows easier access to common tools. With the ability to create a double sided project you have easy access to switch between the Top and Bottom Sides of your project. The Layers Drop down bar has now moved from the drawing tab to the View Toolbar, making it accessible at all times. The other icons displayed in order of left to right are as follows
Snapping Toggle Options
 | Snap to geometry |
 | Smart Snapping |
 | Snap to Grid |
View Controls
 | Toggle Pan / Twiddle View |
 | Zoom to box |
 | Zoom to drawing |
 | Zoom to selection |
Toolpath Drawing Toggle
 | Toggle 2D Toolpath Drawing |
 | Toggle solid 2D Toolpath Drawing |
3D Drawing
 | Toggle drawing of material block |
Tile 2D & 3D View Windows
 | Stack 2D and 3D View windows vertically |
 | Stack 2D and 3D View windows horizontally |
Two-Sided Machining

When you are working on a two-sided job additional icons will appear on the View Toolbar. On the left you will see an icon indicating whether the job you are working on will be flipped horizontally or vertically. This is important because the software will automatically mirror your toolpaths and geometry around different axes depending on this setting. To maintain the correct alignment of your toolpaths you must physically turn the material on your CNC machine in the same direction as you have specified during the design process.
 | Turn horizontally from left to right |
 | Turn vertically, end over end |
Note
This icon is just for you information and does not perform any operation; it is not clickable.
The next button indicates which side you are currently working on. It is a toggle button that can be clicked. Clicking this button swaps the active side of your job.
 | Top side is active, all operations will apply to the Top side. |
 | Bottom side is active, all operations will apply to the Bottom side. |
Note
The rulers that border the 2D View are colored to provide a handy visual indicator as to which side is currently active. An Orange background indicates that the Bottom side is currently active and any drawing or toolpaths are associated with the Bottom Side of your design.
The final additional tool for two-sided job is on the right hand side of the View Toolbar and it allows you to toggle the 3D composite relief to show either the currently active side or your model only, or both sides of your model as a single solid block.
 | Toggle Two-Sided View |
Rotary Machining

When you are working on a rotary job an additional icon will appear. This button allows you to toggle the 3D view between wrapped display mode and flat display mode.
 | Toggle Wrapped 3D view. |
Vector Boundary
The Vector Boundary form allows you to create boundaries around selected vectors.
Offset Boundary
When this is checked ✓ the created boundary is offset outwards by the distance specified.
Rubber Band Boundary
When this is checked ✓ the created boundary is the result of stretching a rubber band around the currently selected vectors.
The images below demonstrate the difference between the two types of boundary that the form creates. The picture on the left illustrates the standard offset output and the one on the right shows the result when Rubber band boundary option is checked ✓.
Export Model as an STL File
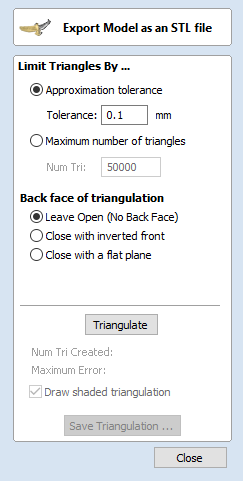
The STL file format is an industry standard for representing 3D models as meshes made up of a skin of triangles. It is a very robust way of exporting a version of your 3D composite model to external applications or even Rapid Prototype (RP) machines. Models can also be exported as an OBJ file, which includes the component colors and is primarily used for ray-traced rendering of your model.
Limit Triangles By...
In general, triangle meshes are not able to hold as much detail as Aspire's 3D Components. As a result, you must choose which strategy Aspire will use to reduce the detail in your STL file.
Note
When exporting the rotary model, currently there is no control over the number of triangles and the mesh will be exported at the highest quality. That means that the generated file will have a considerable size.
Approximate tolerance
Using this option the quality of the mesh is defined by how closely you allow the software to approximate the model. The smaller the number the better the detail and smoothness of the model but the larger the memory size of the file will be.
Maximum number of triangles
Using this option the quality of the mesh is limited by how many triangles you specify here, the larger the number the better the detail and smoothness but the larger the memory size of the file will be.
Back face of triangulation
The Composite model does not have a defined back face, because it is generally unnecessary for conventional 3-axis CNC machining. When converting your composite model to a 3D mesh, however, it can be useful to form a closed mesh by creating a back face automatically.
Leave Open (No Back Face)
This creates a mesh with an open back. This creates a shell with the 3D shape on its face and an open back side.
Note
When exporting the rotary model this option will result in a mesh without caps at the ends.
Close with inverted front
This creates a mesh with a copy of the front of the model on the back. This is used when a solid 2 sided model is needed for output. An example of this might be a 2 sided fish.
Note
When exporting the rotary model this option is not available.
Close with a flat plane
This creates a mesh that has its back sealed off with a flat plane. This type of closed model may be required by Rapid Prototyping (3D Printing Software) to allow the part to be prepared for the production process.
Note
When exporting the rotary model this option is not available.
Close with other side (two-sided jobs only)
In the case of two-sided jobs, this option can be selected. It will triangulate both sides of a job and produce a single closed mesh.
Note
When exporting the rotary model this option is not available.
Close sides
This option is only available for rotary jobs. When it is selected the created mesh will have caps on the ends.
Triangulate
When the options for the mesh have been selected then clicking will actually calculate the mesh and display the result in the 3D View. If this does not look correct (such as not being detailed enough) then the options can be changed and this button clicked again to re-calculate the mesh.
Num Tri Created
Once a mesh has been created, this field reports how many triangles it comprises. The more triangles are used, the larger the file size and the more difficulty external applications may have in manipulating them.
Maximum Error
This field indicates the worst deviation of a mesh triangle from the original 3D model.
Draw shaded triangulation
The triangle mesh can be viewed in wireframe or shaded modes using this option.
Save Triangulation...
Once the mesh looks correct, then clicking this button enables it to be saved onto your computer as an STL format file by default. The file save dialog also allows the selection of Wavefront (*.obj) and POV-Ray Scene (*.POV) as an alternative triangle mesh format using the Save as type option.
Note
When saving an obj file, an additional material (*.mtl) file and texture image file (*.jpg) will also be created - all three files will be required when opening the obj file in a 3rd party modelling or rendering package.
Emboss Component
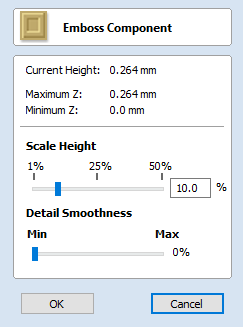
Embossing a component can be used in some cases to reduce the height of a model while preserving important surface detail as an alternative to the standard method for scaling a components height using the Shape Height option on the Component Properties form. A component must be selected before the tool can be used.
The images below show the same model, both results are scaled to ten percent of their original heights. The image below left was created using the standard Shape Height scaling from the Component Properties form and the image below right using the Emboss function.

Scale Height
Use the Scale Height slider to adjust the final height of the component.
Detail Smoothness
Since the results of the initial detail scaling can be noisy the Detail Smoothness slider can be interactively adjusted to improve the visual quality of the result. In general, the greater the Scale Height the more Detail Smoothing needs to be applied.
Remarks
The Emboss tool is a very powerful feature but will not provide ideal results on every type of 3D model. Although it's possible to use the Emboss tool on models created in Aspire for ALPHACAM and other low-relief imported designs (such as the clipart), it's important to understand its intended use is with data from imported, full 3D (high relief) models and typically the best results will be obtained with this type of data.
Model
| Create Component ► |
| Create Component From... ► |
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Export as Grayscale Bitmap |
| Export as 3D Clipart: Exports the selected model as a .3DClip file. |
 | |
 | |
 | Reset Inside Selected Vectors: Deletes everything in the Working Model contained inside the selected vector(s) |
 | Reset Outside Selected Vectors: Deletes everything in the Working Model contained outside the selected vector(s) |
 | Split Selected Component: Split the currently selected component using a vector. |
 | Create Vector Boundary Around Selected Components: Creates a new vector that matches the edge of the selected component. |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 |
Create Component
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | Add Zero Plane: Creates a component that is the size of your job setup with a height of Zero. |
Create Component From...
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Create Component from Toolpath Preview |
Export As Grayscale Bitmap
This is export option will save the Composite Model (Working Model + visible Components) as a raster based image file (.bmp/.jpg/.gif format). This is mainly intended for users of Laser engraving equipment and CarveWright/CompuCarve machines. It could also be used to export the 3D as a grayscale for use with graphics programs.
When the image is exported the highest areas in the model will be white and the lowest will be black, all the other depths in between will be assigned graduated levels of gray depending on their relative position between the top and bottom of the part.


To use this function you must have either visible Components or something in the Working Model.
Create Component from Toolpath Preview
This will take the current Toolpath Preview and create a Component model from it. There are two main applications for this feature:
- It can be useful for helping to identify areas which have not been machined so a smaller tool can be used to carve them with more detail.
- It can be used to create model Components where some of the shape has been created using the tool shape such as fluted veins on a leaf or a texture toolpath]. This second application would be particularly beneficial for customers who plan to save a grayscale image of the 3D model (for Laser or CarveWright) rather than running the actual toolpaths from the software.
Once this is selected the current Toolpath Preview will be converted into a Component. This is then added to the Component List and will be called Toolpath Preview.
If the part has been cut-out and the Delete Waste Material option has been used then just the parts left on the screen will become the Component. If the part is not fully cut-out or the waste material has not been deleted then the whole Toolpath Preview block will become the Component, including what may be scrap material. It is possible to avoid this even without deleting the waste by using the Shift key - see below for more information.
By holding down either the Ctrl or Shift key, there are two options that can be activated when the Create Component from Toolpath Preview feature is selected.
If you press the Shift key when you create the Component, the areas of the Toolpath Preview over transparent areas in the composite model will be discarded. This will give you a Component that represents the Toolpath Preview but deletes anything that is not within the area of the 3D model the toolpaths were created on in the first place.
If you press the Ctrl key, the Component created will represent the difference between the composite model and the Toolpath Preview. The model this creates will look odd as it will just represent the material that was left by the radius of the tool on the finish cut. This can be useful if you want to machine those areas with a smaller tool as this model may then be used to create the vectors to limit the toolpath for that operation, minimizing the time to create a more detailed finish.
The images below show the 3 options available. Below left is the standard Component created from a machined model which includes the waste block. The middle option shows the option when the Shift key is pressed which discards the Preview model outside of the original area of the machined part. Finally the right hand image shows the Component which is created when holding the Ctrl key down which is the different between the original part and the Middle image.



IMPORTANT NOTE
Although this option can be selected at any time, it only makes sense to use this feature while the Toolpath Preview is active in the 3D View, this will ensure that the Component represents what can actually be seen. The Toolpath Preview can be accessed using the icon in the Toolpath Operations menu (shown below highlighted with a red box), this will also appear automatically after the calculation of any toolpath.
Baking Components
In general, the most useful feature of individual Components is that they can be manipulated entirely independently of each other to build up simpler design elements into a sophisticated 3D model. There are some editing functions that require the individual element to be consolidated into a single object. For example you may wish to smooth one shape into another using the sculpting tools or bend a group of Components around a curve using the distortion tool. In Aspire, consolidating a selection of Components into a single, new object is a process called 'Baking'. Once baked, the selected Components will become a single Component object and you will no longer be able to access the individual elements.
Aspire for ALPHACAM will prompt you when you have a group or Component selection that requires baking before a particular modeling tool or operation can proceed. Alternatively, you can use the Bake command to perform this operation yourself. By manually baking-in existing fade, tilt or distortion, for example, you are then free to apply further dynamic properties 'on top of' the previously applied ones. In addition, consolidating multiple Components towards the end of the design process allows your computer to recover system resources and may give it a welcome performance boost - particularly if you have been modeling using a large number of high resolution or complex Components.
Copy
If you hold the Ctrl key down when you hit the Baking icon it will retain a copy of the original Components and create a new baked Component instead of replacing the original selection.
Fluting Toolpath
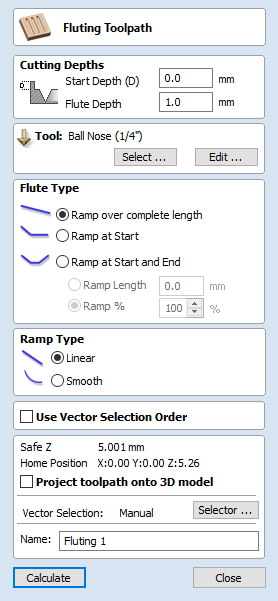
Fluting Toolpaths machine along vectors while varying the depth of the tool, creating extremely efficient machined decorative patterns.
This toolpath is similar to the option to Profile On a selected vector. The difference is the toolpath at the end of each vector can be ramped to taper the cut. This can be used for cutting standard woodworking Flutes or can be used for artistic engraving and marking effects with other types of artwork. In this section the options on the form will be covered along with some examples of the use for different applications.
Selecting Vectors
When the Fluting Toolpath form is open, the selected vectors will have their start points indicated in the 2D View by solid square green nodes, this is important as it will determine which end the ramps are added depending on what options are chosen on the form. An image of this is shown below where all the start points are to the left end of the selected vectors.
If you need to move the start points, go into node editing mode (press N on the keyboard or select the node editing icon in the Edit Vectors section on the left tab).

Select the vector you want to change the start point Move the cursor over the end you want to be the new start point Press P on the keyboard or Right Click and select Make Start Point from the pop-up menu. Exit node edit mode (press N again) Reselect all the vectors you want to flute
Cutting Depths
Start Depth (D)
This specifies the depth at which the Fluting toolpath is calculated. When cutting directly into the surface of a job the Start Depth will usually be 0. If machining into the bottom of an existing pocket or stepped region, the depth of the pocket/step that you are starting from must be entered.
Flute Depth
This is the depth of the Fluting toolpath relative to the Start Depth; the total depth will be the combination of the Start and Flute Depth.
Tool
Clicking the button opens the Tool Database from which the required tool can be selected. See the section on the Tool Database for more information on this. Clicking the button opens the Edit Tool form which allows the cutting parameters for the selected tool to be modified, without changing the master information in the database. Hovering the mouse cursor over the tool name will display a tool tip indicating where in the Tool Database the tool was selected from.
Flute Type
Ramp over complete length
Checking ✓ this option means the tool will ramp over the whole length of the toolpath. At the start of the selected vector/s it will be at the Start Depth and at the end of the selected vector/s it will have cut down to the Fluting Depth.
Ramp at Start
Checking ✓ this option means the tool will ramp down only at the start of the vectors to the Fluting Depth. The distance of this ramp can be specified using the Ramp Length or Ramp % options.
Ramp at Start and End
Checking ✓ this option means the tool will ramp down at the start of the vectors then will ramp up again at the end of the vectors. The distance of these ramps can be specified using the Ramp Length or Ramp % options.
Ramp Length
Checking ✓ this option means that the length of the ramp can be set to an exact distance entered into the box. The ramp distance is measured from the start and the end of the vector/s depending what Flute Type you have selected. If the distance entered is greater than the possible length of the ramp then the maximum length will be used, this would be the same as choosing Ramp over complete length. When you choose Ramp at Start it is possible to specify a ramp length which is up to the length of the vector/s. When Ramp at Start and End is checked, ✓ the maximum length possible would be half way along the vector/s as after that it would start to ramp up again.
Ramp %
Checking ✓ this option means that the length of the ramp can be specified as a percentage of the maximum possible ramp length (controlled by the length of the selected vector/s and chosen Flute Type). When you use this with Ramp at Start selected then 100% would be the whole length of the selected vector/s, the ramp length would be a percentage of this distance for each one. When you use this with Ramp at Start and End then 100% would be the half length of any of the selected vector/s. The ramp length would be a percentage of this half-length. In this situation using a 50% value would give you a Ramp from the start which was ¼ of the vector length and a ramp from the end which was also ¼ of the vector length.
Ramp Type
Linear
Selecting the Linear type will create a ramp which is a diagonal line (following the vector) from the Start Depth to the Flute Depth. Below you can see a Linear Ramp Type shown from the side. This ramp is set to only ramp from the start and to go 50% of the flute length.
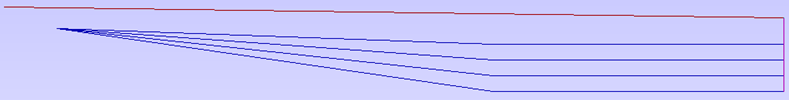
Smooth
Selecting the Smooth type will create a curved ramp (following the vector) from the Start Depth to the Flute Depth; this will smoothly transition from the ramp into the full depth of cut. You can see an example of this shown in the image below.
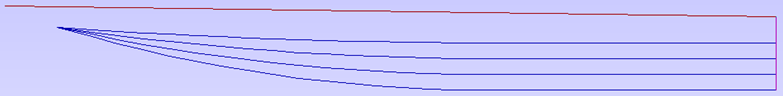
Wrapped Fluting Layout
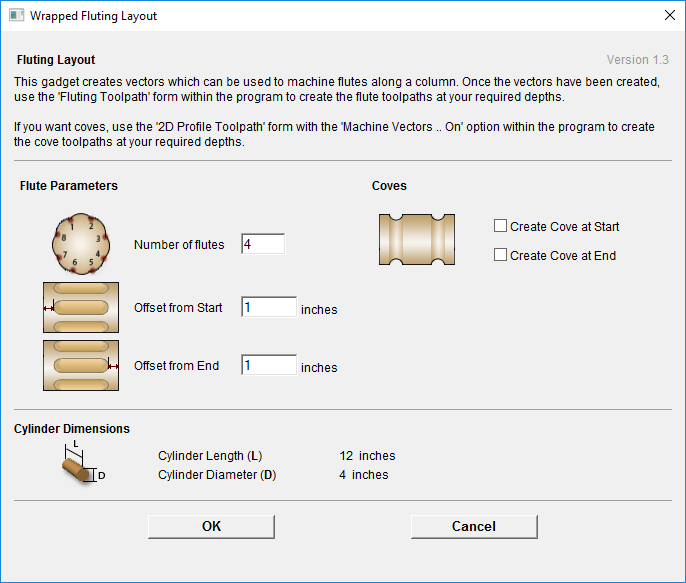
This gadget is used to simplify the task of creating toolpaths to machine flutes and coves on a rotary work piece. The gadget is designed to be used in a rotary job
This gadget does NOT create toolpaths directly. It lays out vectors in the 2D view which can then have toolpaths created using either the Profile or Fluting toolpaths within the main program. The top part of the form allows the user to specify how many flutes to create and how far from the start and end of the work piece the flute should start and end. Flutes are laid out evenly spaced based on the circumference of the cylinder. If the user chooses to create coves at either or both ends, extra vectors will be created which can be machined with the Profile toolpath and the Machine Vectors On option to create the coves.
The bottom section of the form contains details about the cylinder dimensions and is presented for reference only.
After the gadget has run the vectors required for machining will be visible in the 2D view. If you have a 3D form for your rotary piece, you can use the Project toolpath onto 3D model option on the toolpath forms to have your fluting toolpaths follow the work piece surface.
Fit Curves To Vectors
This function allows the user to fit arc, Bezier curves or straight lines to selected vectors. The newly created vectors will be approximated based on a user defined tolerance. Using this function can aid with smoothness for some toolpath options and also help to simplify data for modeling purposes.
Fitting Type
Circular Arcs
Checking ✓ this option means the selected vectors will be approximated using arcs:
Bezier Curves
Checking ✓ this option means the selected vectors will be approximated using Bezier curves.
Straight Lines
Checking ✓ this option means the selected vectors will be approximated using straight lines.

Tolerance
The value which is set in the Tolerance area determines how closely the original vectors will be approximated. The newly created, Arcs, Beziers or Lines will be generated within a distance of the original vector which is plus or minus the specified Tolerance value. The smaller the value the closer to the original the new data will be but it will also mean more data points will be used. A larger Tolerance will not be as accurate to the original but will have less data points.
Keep Sharp Corners
Checking ✓ this option will make the Curve Fitting routine keep sharp corners which have a difference greater than the Max Angle value specified. Any corners where the difference in angle is less than this value will be modified within the specified tolerance.

Replace selected vectors
Checking ✓ this option will delete the current vectors and replace them with the new curve fitted vectors. Un-checking it will keep the original vectors as is and in addition create new curve fitted vectors. The new vectors will always be created on the currently selected Layer.
General Workflow
Aspire for ALPHACAM has been developed to allow the production of decorative and artistic dimensional carved parts. As well as drawing and modeling tools, it includes both 2D and 3D machining, along with 3D V-Carving / 3D Engraving to allow a huge variety of jobs to be produced as quickly and easily as possible.
Workflow Logic
- Layout 2D Design:
- Import Vectors
- Draw Vectors
- Import Bitmaps
- Create 3D Components:
- Create shapes from 2D design vectors
- Create (texture) shapes driectly from bitmaps
- Import 3D Clipart and models from other CAD systems
- Manipulate 3D components to create the 3D composite model using the component tree:
- Change location, depth, size, angle etc.
- Group and change relationship to other components
- Create 2D, 2.5D or 3D toolpath:
- Create or edit vector boundaries for toolpaths
- Specify tool details for each strategy
- Preview Final Part:
- Visualize the part as it will actually look.
- Create proof images for customer.
- Check estimate for cutting time
- Save the CNC Code: Save the final cut file to send to the CNC machine
Design
Aspire for ALPHACAM includes drawing and editing tools that allow designs to be created and modified. Functions for vector creation and editing are very easy to use and multiple design elements can also be drawn or imported, scaled, positioned and interactively edited to make a new design. Text can also be created using any TrueType or OpenType fonts installed on your computer, or the single stroke engraving fonts supplied with the software.
Model
Once the 2D design is ready, 3D components can be created from 2D Vector drawings. This will probably involve adding and changing 2D artwork a bit as the 3D design evolves, so Aspire for ALPHACAM's interface makes the drawing and modeling tools easily accessible.
In addition, existing 3D models can be imported to be incorporated into a design, these could be files previously created in Aspire for ALPHACAM, 3D Clipart that has been purchased and downloaded or models from other CAD design systems in a supported format.
Toolpath
A comprehensive set of 2D, V-Carving, Engraving and 3D toolpath strategies provide you with efficient ways to use your tooling to carve the finished part. This process is usually relatively independent of drawing or modeling (although toolpaths are often created directly from some artwork or 3D composite models). Aspire for ALPHACAM provides simple interface buttons to toggle screen layout to assist the shift in focus from design to toolpathing.
Output
Finally you can use Aspire for ALPHACAM's large selection of post-processors to save toolpaths in precisely the format that your particular CNC machine tool requires.
Vector Texture
Repeating texture patterns can be created using the Create Vector Texture tool. These vectors can be machined in a variety of ways to create attractive textures.
To use the tool click the icon on the drawing tab. If required, select any contours that you wish the pattern to be created within. By using the sliders and edit boxes on the form the style of the created pattern can be varied. Click Preview to see a preview your created texture as you adjust the form's parameters. When you are happy with the preview, click OK to create the pattern.
Angle
The lines in the texture are created at an angle. This value can be set to any value between -90 degrees and 90 degree.
Line Spacing
The line spacing controls the distance between the contours created by the tool. Use the edit box labeled Max. Spacing to enter a maximum value of line spacing. The slider underneath the edit box controls the degree of variation in the line spacing. If the slider is to the far left then this mean variation is at a minimum and so the lines are evenly spaced. If the slider is to the far right the variation is highest and so the distance between created contours varies between zero and the maximum spacing specified.


Wave Parameters
Within this section of the form the created pattern can be made to behave in a wave-like fashion. This wave is controlled by two parameters: the amplitude and wavelength.
Wavelength
The wavelength describes the length over which the contours shape repeats itself. A bigger wavelength gives a long wave while a small wavelength gives a short wave.

Amplitude
The amplitude describes the height of the wave. Larger amplitude means a taller wave and smaller amplitude means a shallow wave.

Noise
The noise slider controls the degree of randomness applied to the above values and can be used to create less regular patterns.



Vector Layer
To create the vectors on a new layer make sure the check box labeled Place Vectors on Layer is checked ✓ and enter the layer name into the edit box labeled Name.
Job Setup Form
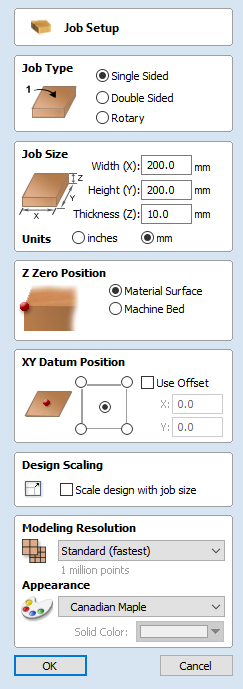
The Job Setup form is displayed whenever a new job is being created, or when the size and position of an existing job is edited. It allows to create following types of job:
Job Setup - Rotary
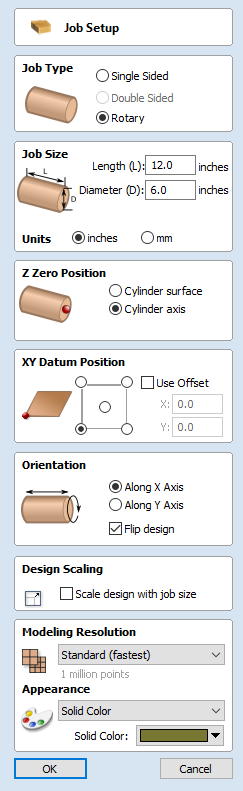
The Job Setup form is displayed whenever a new job is being created, or when the size and position of an existing job is edited.
In most cases a new job represents the size of the material the job will be machined into or at least an area of a larger piece of material which will contain the part which is going to be cut. Clicking OK creates a new empty job, which is drawn as a gray rectangle in the 2D View. Dotted horizontal and vertical Grey lines are drawn in the 2D design window to show where the X0 and Y0 point is positioned.
Job Size
Length
Length of the material
Diameter
Diameter of the material
Units
Whether the job units are measured in mm or inches
Z Zero Position
Indicates whether the tip of the tool is set off the rotation axis (as shown in the diagram) or off the surface of material for Z = 0.0. For the best accuracy using Cylinder Axis option is recommended
XY Datum Position
This datum can be set at any corner, or the middle of the job. This represents the location, relative to your design, that will match the machine tool when it is positioned at X0, Y0. While this form is open, a red square is drawn in the 2d view to highlight the datum's position.
Use Offset
This option allows the datum position to be set to a value other than X0, Y0.
Orientation
This option selects along which axis the material block will rotate.
- Selecting Along X Axis means that X coordinates represent movement along the cylinder, whereas Y coordinates represent the angle around the cylinder.
- Selecting Along Y Axis means that Y coordinates represent movement along the cylinder, whereas X coordinates represent the angle around the cylinder.
Flip Design
When this option is enabled, the design will be flipped when the orientation is changed
Design Scaling
When editing the Job Size parameters of an existing job, this option determines whether any drawings you have already created will be scaled proportionally to match the new job dimensions. If you wish to preserve the existing size of your drawings, even after the job size has changed, leave this option unchecked. With this option checked, your drawings will be re-sized to remain in the same proportion and relative position within your new material extents when you click
Modeling Resolution
This sets the resolution/quality for the 3D model. When working with 3D models a lot of calculation and memory may be required for certain operations. Setting the Resolution allows you to choose the best balance of quality and speed for the part you are working on. The better the resolution quality chosen, the slower the computer will perform.
As this is completely dependent on the particular part you are working on and your computer hardware performance, it is difficult in a document like this to recommend what the setting should be. Generally speaking, the Standard (fastest) setting will be acceptable for the majority of parts that Aspire users make. If the part you are making is going to be relatively large (over 18 inches) but still has small details, you may want to choose a higher Resolution such as High (3 x slower) and for very large parts (over 48 inches) with small details then the Highest (7 x slower) setting may be appropriate.
The reason that the detail of your part needs to be taken into account is that if you were making a part with one large item in it (e.g. a fish) then the standard resolution would be OK but if it was a part with many detailed items in it (e.g. a school of fish) then the High or Highest setting would be better. As previously stated these are extremely general guidelines as on slower/older computers operations with the highest setting may take a long time to calculate.
As the Resolution is applied across your whole work area it is important to set the size of your part to just be big enough to contain the part you plan to carve. It would not be advisable to set your material to be the size of your machine - e.g. 96 x 48 if the part you plan to cut is only 12 x 12 as this would make the resolution in the 12 x 12 area very low.
Import 3D Model into Single or Two Sided Job
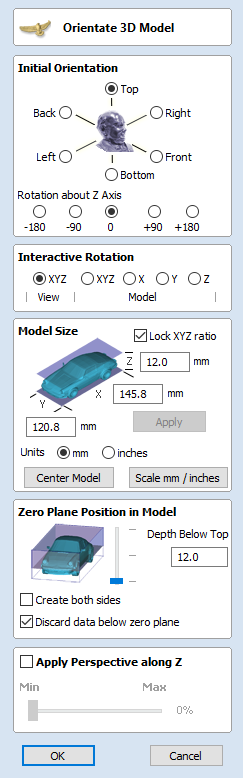
Initial Orientation
Choose one of the 6 options to determine the most suitable direction on the model that defines the top surface (upper Z) that you want to use when it's converted into a Component.
You can also use the five options for Rotation about Z Axis to modify the position of the part being imported at this stage.
Interactive Rotation
The default choice XYZ-View allows you to left-click in the 3D View with the mouse to rotate your view so you can examine the part from different angles. Using this will not change the orientation of the part for import. If you select one of the other four options above the word Model then this will adjust the actual positional orientation of the imported part. Choosing the XYZ option will allow rotation around all three axes simultaneously, X, Y or Z will only allow rotation around the specified axis. This is also done using the left-click in the 3D View with the mouse.
Model Size
Lock XYZ ratio
Un-checking this option allows the model to be distorted from its original shape. This means independent X, Y and Z sizes can be entered. Leaving it checked ✓ fixes the ratio so it cannot be distorted. Instead it will automatically scale the other axes as you enter new values for X, Y or Z.
Apply
Applies the values you have entered for the X, Y or Z dimensions.
Many mesh files do not inherently have the units that they were made in embedde in the files, so the software is not able to tell if the files are supposed to be inches or metric, they will just have a particular value. Therefore it is quite common to need to scale the part from inch to metric or vice versa. If you import your model and you wish to work in inches and the file seems very large or if you work in Metric and the file seems very small then you will probably need to use the Scale mm/inches option. The next two items on the form cover this need.
Units
Choose the unit of measurement (mm or inches) that you are working in, within the part the file is being imported into.
Changing the units will result in resizing the model. For example, if you had 5x5 mm dimensions, they would become 5x5 inches so the model becomes a lot larger.
Scale mm/inches
Scales the X, Y and Z values up or down depending which Unit option is selected. If mm is selected then the software assumes you want to scale the values up so multiplies the current values by 25.4, if inches is selected it assumes you want to scale the values down and divided them by 25.4.
Zero Plane Position In Model
This slider bar determines where the 3D model will be cut-off when converting to a Component. You can move this up and down with the mouse or use the Middle or Bottom buttons to locate the plane in the correct position.
Note
Anything in the original model which is an undercut (goes underneath another part of the 3D model) will be discarded and a vertical wall will be created down to the plane from the silhouette (looking down Z axis) edge of the model.
Discard data below zero plane
Checking ✓ this will remove any data below the original Zero level within the imported 3D model. If the model is effectively a negative model such as a dished or recessed design with a flat plane then you should uncheck this option to make sure you retain the 3D data below the plane.
Create both sides
If you are working in a 2 sided setup you can check ✓ this option and two components will be created - one looking down the Z axis from above to the zero plane and one looking up from below. Each side of the model will go onto a side. This will provide you with the geometry that can be edited to cut the original imported 3D part as a 2-sided job.
If you were importing a model that contains a non-convex surface for instance a bowl you can import the entire model on each side by sliding the slicing plane all the way to the bottom.
Center Model
The button which will move the center of the model's bounding box to datum position (XYZ zero). This is particularly useful if you intend to unwrap a model for rotary machining. This may change the Zero Plane position in the model.
Apply Perspective along Z
Checking ✓ this will enable you to apply a perspective distortion to the model along the Z axis by using the slider. Points on the model closest to the observer will become further apart as the distortion strength is increased - this makes the model appear as if it is coming out of the screen.
OK
Creates a 3D Component based on the settings in the form, the Component will have the same name as the imported file. If you selected 'Create both sides' you will have two components with the name of the imported file followed by the suffixes -Top and Bottom.
Cancel
Cancels the Import function and returns to the standard Modeling Tab icons.
Wrapped Spiral Layout
This gadget is used to simplify the task of creating toolpaths to machine spirals (rope or barley twist) on a rotary work piece. The gadget is designed to be used in a rotary job
This gadget does NOT create toolpaths directly. It lays out vectors in the 2D view which can then have toolpaths created using Profile toolpath within the main program. The top part of the form allows the user to specify how many strands to create and how far from the start and end of the work piece the strands should start and end. Strand ends are laid out evenly spaced based on the circumference of the cylinder. The spacing between strands during spiralling can be controlled using either Spiral Pitch or Spacing between strands option. It is also possible to choose between right and left hand twists.
If the user chooses to create coves at either or both ends, extra vectors will be created which can be machined with the Profile toolpath to create the coves.
For machining both spirals and coves, Machine Vectors On option should be used.
The bottom section of the form contains details about the cylinder dimensions and is presented for reference only.
After the gadget has run it will display message saying how many revolutions will each strand made and the vectors required for machining will be visible in the 2D view. Please note that the vectors will be extending beyond the 2D boundaries of the job. That is expected and thanks to wrapping feature will end up producing spirals. Please refer to Spiral toolpaths
Create Component from Visible Model
The Create Component from Visible Model feature allows you to quickly create a single component which is a copy of the model shown in the 3D View (the Composite Model). The new model created is placed on the active level.
It is common when working with lots of components to find that a number of levels have been used. If, as a final step, you want to edit the models using a tool like the sculpting (which requires the components to be baked together) then they all must be on the same level, however placing the models on the same level may change the appearance of the composite model. In this case we can use the Create Component from Visible Model tool. This resulting component may then be sculpted without any of the previous modelling information being lost.
Consider the following example of a lioness we are modelling, and all of its current levels.
If we want to sculpt this model we must first bake it, but we currently can't bake it because the components lie on different levels. Also, baking them together will mean we lose all our structure that we have carefully built up losing the potential to edit the individual parts. So instead we use the Create Component from Visible Model tool. This creates a copy of what is visible. We can then bake this new component, and we can now sculpt without losing our structure
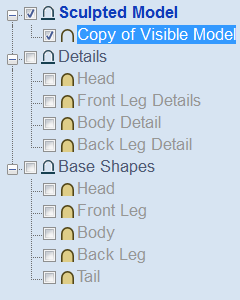
Create Zero Plane
Creates a component that is the size of your job setup with a height of Zero.
Create Texture Area
The Create Texture Area tool assists in the creation of components with a repeating pattern or texture. It requires a single component and optionally one or more closed boundary vectors which define the region in which the tiling should take place.
The Create Texture Area form is accessed from the modelling tab.
The first step is to select the component you wish to be tiled. If you want to restrict the tiling to a region then you should also select one or more closed vectors which will represent the boundary when the texture is created. If no boundary vector is selected then the tiling will fill the entire job space.
The Create Texture Area form contains options to adjust the spacing, overlap, positioning and symmetry of the texture which are discussed below. When you click the Apply button then the software will create a Component based on the settings in the form and any vector you may have selected for the boundary.
At this moment the original selected Component will be made invisible to avoid confusion with what you can see in the 3D View.
Once you click then this will effective fix the basic outline or silhouette of your Texture Area either based on the selected vector or the job area. It is possible to edit the size, position and rotation of this but if you wanted to change to a different border shape then you would need to start again with a new selection.


By default the form has Transform Object selected at the top. In this mode you can click on the Texture Area Component and use the drag-handles to move, scale or rotate it. Note that this will not change the size of your Tile (original seed Component). To change the size of the Tile you would use the Edit Textured Area Component option which is covered further down in this document.
Note
Create Texture Area effectively fits a box around the original object in order to apply the settings from the form, it can be useful to keep this in mind while editing the values. It's simpler to only edit one value at a time to keep track of what is happening as the Texture Area is built.
Spacing
The spacing edit box or sliders can be used to control the degree of spacing between the tiles in a pattern component. You can adjust the spacing between the components horizontally and/or vertically. The amount of horizontal spacing is given in terms of a percentage of the width of the tile component. The amount of vertical spacing is given in terms of a percentage of the height of it. To control the amount of spacing, use the two sliders in the box marked Spacing. Drag and release the slider to set the percentage, or alternatively type an exact amount into the edit box above and either hit or press the Space bar on the keyboard to update the result. You can enter both positive and negative values. Positive spacing values open gaps between the objects in the texture and negative spacing has the opposite effect making the tiles overlap one another as shown below.

Translation : X/Y Shift
The X/Y shift option can be used to move all the tiles in alternate rows horizontally or alternate columns vertically by the specified amount. As with the spacing, the X/Y shift is given as a percentage of the size of the component in the appropriate dimension and can be adjusted using either the sliders or the edit boxes. For example entering a shift value of 50% horizontally (X) would move the second row over by half the width of the object, the third row would be as the first, then the fourth shifted, this shift would also be applied to every other row after that within the Textured Area. Similarly entering a value of 50% for the vertical shift (Y) will move every other column up by half the height of the object.


Reflection
The reflection tool consists of four buttons. Each button represents one tile in a mini-group of four, starting from the lower left copy which is represented by the original Tile. Each button has 4 states of reflection, each time the button is clicked, the icon representing the button will change to show the current state. Click to update the Texture Area Component with your new choice.




Editing an Existing Texture Area
When you have created a pattern you can edit the size of the individual Tile component you are creating a pattern from by selecting the Edit Textured Area Component option at the top of the form. Within the 2D View this will then put an orange transform box around the lower left component in the pattern. You can alter the size of this by left clicking on one of the handles and dragging it to size, when you let go this will update the pattern to fit the new size within the Texture Area boundary. You can also move the location of this Tile by clicking the center node and dragging it with the mouse to a new location. This again will change the layout of the pattern.
Note
It is not currently possible to scale or move the Tile using drag handles in the 3D View.
A Texture Area component will remember that it is in a special state and not a standard component. This means that they can be further edited using the Texture Area form even after Closing and re-entering the function. To edit an existing Texture Area component, select it and then open the Create Texture Area tool. Alternatively, open the Create Texture Area tool and then select the existing component. This will then let you continue to make changes to it using the form.
Resizing
Texture Area components do not behave like standard components when they are scaled in X or Y. When a Texture Area component is resized, then this resizes the boundary in which the tiling takes place so the size of the individual Tiles will not change, just the area that they are covering will be updated.
Common Modeling Options
All of the main modeling tools in the software use a common set of commands to assign a name and combine mode to the component being created along with options to apply the settings in the form, reset the shape, start creating a new component and close to exit the function.
Combine with other components...
This section includes options to allow you to name your Component and control the way it will be combined with other objects in the Component Tree.

Reset
Clicking the button will remove the current shape, doing this before you Close the form will ensure that a component is not created from the current selection. Clicking this does retain the current set of selected vectors or Components.
Apply
Clicking the button will create a shape based on the settings you have chosen. You can continue making edits to the component by choosing different parameters within the form and hitting Apply to update it.
Start New Component
Clicking the button will save the state of the component that has been created, deselect all components/vectors and start the creation process again on a new component. The values and options within the form will be retained in this case until you Close it.
Close
Clicking the button will close the form returning to the Modeling Tab icons and the updated Component Tree, reflecting any changes that you have made. If you wanted to remove the shape you just created then you can hit the Undo icon or use the keyboard shortcut to undo, CTRL+Z.
Trim Objects
The trim tool allows you to trim all the objects inside a given boundary. It is much more efficient than manually trimming all the contours with the trimming scissors, and allows the trimming of closed contours, open contours and components.
To use:
- Select objects you wish to be trimmed
- Select the object you wish to trim against (hold shift to add to selection)
- Choose to clear inside or outside
If the Clear outside boundary option is selected then all the objects that intersect this boundary are clipped, and the area outside is removed. If the Clear inside boundary option is selected, then the parts of the selected objects which lie inside the boundary are removed.
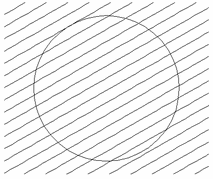
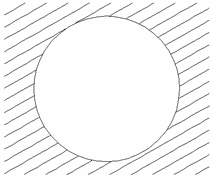
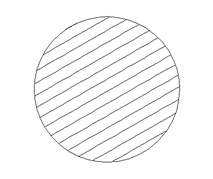
If you want to use multiple vectors for the trimming boundary, they must be grouped for trimming. To group a collection of vectors select the vectors, right click and choose Group Objects from the drop down menu, alternatively select all the vectors and press the G key.
Refit Curves After Clipping
In order to clip curves the trim tool will convert them to curves consisting of many small lines. If this option is selected then after clipping has happened the vectors will be converted to curves.
PDF Export
The PDF Export form allows vectors within your drawings to be exported into PDF format.
Vector(s)
Export All
Selecting this option will export all of the vectors contained on the specified sheets and layers.
Export Selected Only
Selecting this option will export only the vectors which are currently selected and on the specified sheets and layers.
Sheets
The sheets you wish to be exported to PDF can be selected from within this section. Clicking will deselect all of the sheets and clicking will cause all of the sheets to become selected. You can also manually select/deselect individual sheets by clicking on the check box to the left of the sheet name.
Note
Each sheet will be saved as a separate page within the PDF file.
Layers
The layers you wish to be exported to PDF can be selected from within this section. All the visible layers with content on them will show up in this list.
When All visible layers is chosen all of the vector layers will be selected. Only vectors on the layers selected will be exported into the PDF file. When Selected layers only is chosen individual layers can be manually selected/deselected by clicking on the check box to the left of the layer name.
Options
Export Job Bounds - If this option is selected a vector representing the boundary of the job will also be output to the PDF file.
Clicking will prompt you to choose a filename and location for your file and save your drawing in PDF format at that location.
Rotate
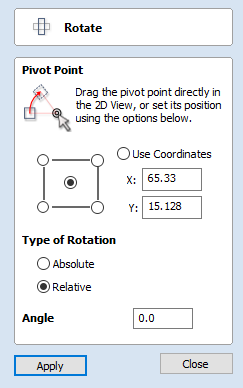
For precise control of the rotation, or to use a point other than the selection's center as the rotation center, you can open the rotation form from the Drawing Tab.
Selected items in the 2D View can be rotated to a new orientation using this tool. The rotation options form can be activated from the tool icon on the Drawing Tab. Alternatively you can use the interactive transform mode (where the form is not required) directly from the 2D View.
With this form open the additional Pivot Point handle is available (two concentric circles initially positioned at the center of your selection) for you to click and drag in the 2D View. The Pivot Point (around which the selection will be rotated) responds to the currently enabled snapping options to help you to position it precisely on significant locations within your artwork. Hold down the Shift key to temporarily disable snapping while you drag the Pivot Point.
Pivot Point
On the form there are also six radio button options for snapping the rotation Pivot Point to the selection itself or to a precise position. The first five options allow you to snap to the corners and center of your selection.
Use Coordinates
The X and Y edit boxes allows you to precisely specify the position of the Pivot Point. This is also the option that will be selected by default if you drag the pivot point using your mouse directly in the 2D View.
Type of Rotation and Angle
This controls what the angle value does.
- Relative will simply rotate the object by the given angle. For example, you can enter a small angle, and then rotate multiple times to nudge the object a little bit at a time. A positive angle results in a counter clockwise rotation. A negative angle results in a clockwise rotation.
- Absolute will set the rotation of the object to the given angle. For example, setting a zero angle here will reset the rotation of the object back to its original orientation (as long as the rotation hasn't been baked).
Keep in mind that when rotating an object, it's rotation is maintained so that you can restore the rotation or scale along its original axes later on if required.
Interactive Rotation
Generally the most convenient way to rotate an object in the 2D View is to use interactive transform. This mode is initiated by clicking the selected object twice with the cursor. The process is:
- Select the object by clicking on it in the 2D View (or multiply select objects using box selection or by shift-clicking on them).
- Click the selection a second time to activate the interactive options rotation handles on the selection box.
- Click and drag on the blue handles (solid squares) at the far corners of the selection to rotate it.
Note
Holding down an Alt key when dragging to rotate the object snaps to angular rotation steps of 15° increments.
Open a File
This option opens the File Open dialog window, allowing Aspire files (CRV) and importable 2D vector files to be selected and opened.
Draw Circle
Circles can be created interactively with the cursor and Quick Keys or by entering the exact coordinates and diameter / radius with typed input.
Note
Pressing the Space-bar re-opens the last vector creation form you used. This is very useful when using other forms in between each shape you create.
Interactive
Cursor
The default mode and the procedure for drawing circle is:
Click and drag the Left mouse to indicate the center point followed by releasing the button at the required radius / diameter (depends on what is set on the form).
Note
Holding Alt and dragging creates a circle from the middlepoint.
As the cursor is dragged across the screen the radius is dynamically updated. The increments will depend upon your snap radius and the job size.
Quick Keys
The radius or diameter can be specified while dragging out a circle:
Type the value while dragging followed, by D if it's a diameter, or R if it's a radius:
Example:
1 2 R Gives a radius of 12
Exact Size
Circles can also be drawn by entering the required XY origin, selecting either Radius or Diameter and entering the required size on the form.
Click Create to update the circle.
Edit
Open the Draw Circle form and select the circle to modify.
The selected circle is displayed as a dotted magenta line. Edit the Center Point and Radius or Diameter
Click to update the circle
To modify another circle without closing the form hold a Shift key down and select the next circle.
Close the form
To finish drawing with the tool, you can :
Click Close on the form
- Press the key Esc
- Click the Right mouse button in the 2D View
Create Fillets
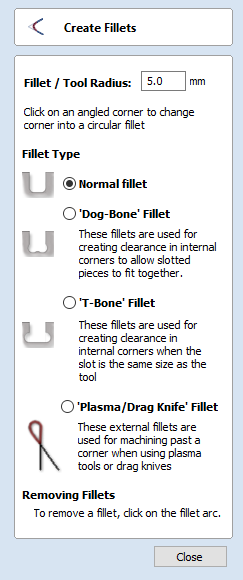
Fillets or radiuses can be added interactively at points where any two spans on a contour meet.
Creating Fillets
To use the filleting tool we select the icon from the drawing tab. Choose a radius for the fillet and the type of fillet you would like to use.
When the mouse cursor is near a node that can be filletted, the mouse cursor changes to show a check-mark ✓:
Fillet Type
Normal Fillet
This creates a standard corner fillet based on the Radius defined, typically this would be used for design purposes and not for editing a slot for fitting purposes. Below left the image shows the vector before filleting the two inside radii, on the right is the filleted version
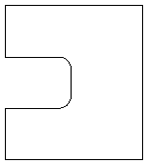
Dog-Bone Fillet
This creates a circular cut-out style of fillet, the circles will be placed so the upper right part of the circle touches the original sharp corner and are created with the Radius specified. This option should not be used if the slot width and the tool are similar in size. Below left is the vector showing the slot before filleting, on the right is the filleted version using the 'Dog-Bone' option.

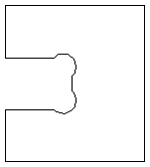
T-Bone Fillet
This creates a circular cut-out style of fillet, the circles will be created with the Radius specified. This option should be used if the slot width and the tool are similar in size so the slot can grow out to the side to ensure there is space for them to fit. Below left is the vector showing the slot before filleting, on the right is the filleted version using the 'T-Bone' option.

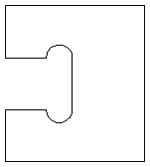
The placement of the fillet is an interactive process; you can choose which side of the 'corner' the T-bone filet is placed. If you click on a 'corner' the fillet will be placed automatically on the longest side. By clicking to the side of the corner you want the fillet placed you can choose which side the fillet is placed on.
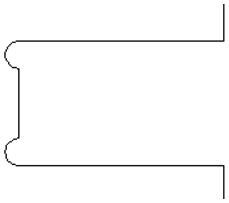
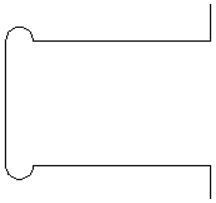
Removing Fillets
Fillets can be removed in the same way that we add fillets: move the cursor over the fillet that you wish to remove.
If this fillet can be removed then the cursor shows a cross to indicate that it is possible to remove a fillet:
Clicking removes the fillet:
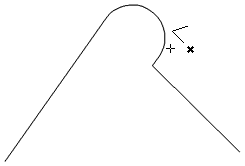
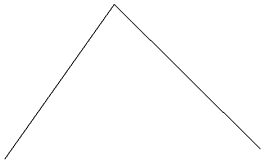
When removing fillets the software does not store what kind of geometry the fillet was created from. It always defaults to using straight lines to return the fillet to a sharp corner. As such if the fillet is across multiple spans or is derived from arcs or Bezier curves then it will not go back to its original state and instead it will remove the radius and extend two straight lines to create the new corner.
Extend Vectors
This tool allows you to extend two vector lines to their common point of intersection.
With the Extend Vectors tool active, moving the mouse pointer over the ends of open vector shapes (without clicking) will highlight a dashed preview extension line from that shape. The line will change dynamically as you move the mouse over the end spans of different open shapes. Clicking with the left mouse button at this point will set it as the target line to extend and the magenta line will remain visible.
The mouse can now be moved over existing spans along the length of the preview extension line, or over the end of another shape to create a second, intersecting, preview extension line.
Clicking on any of the intersection points indicated by the mouse cursor will extend the initial shape to that point and complete the operation.

The tool can be closed at any time using the button on the form. Right-clicking in the 2D View will reset the tool so that it is ready to select another target line to extend.
Drag Knife Toolpath
This Gadget supports drag knife tooling in your CNC machine. It uses the selected vectors in the 2D View as the basis of a centerline profile-type toolpath that incorporates swivel moves at corners to ensure the drag knife blade remains properly aligned throughout the cut.
Warning
When machining please ensure you have the spindle switched off.
Blade Offset
The tip of a drag knife is offset by a small amount from the pivot center of the tool to allow it to swivel as it cuts. This value specifies the distance and will be provided by your tool manufacturer.
Tolerance angle
This value determines when a swivel move needs to be used on a corner. Changes in tool direction, or corners, with angles less than this value will not generate swivel moves.
Cut Depth
This value sets the final cut depth of the toolpath. It defaults to be the current material thickness.
Swivel Depth
The knife must remain in some contact with the material in order to swivel correctly, but a small retraction is generally used to lift the knife blade slightly to minimize marking the material during the swivel action. This value must, therefore, be less than the cut depth and appropriate for your tool and material.
Passes
This value determines the number of passes used to cut down to full depth. The depth of each cut will be specified cut depth divided by the number of passes.
Use Vector Start Points
If Use Vector Start Points is checked ✓ then the gadget will use the existing vector start points to begin cutting vectors. Please note that this gadget assumes that the blade starts parallel to the positive x-axis. If this is option not checked the gadget will attempt to find what it thinks are sensible start positions.
Feed and Plunge Rates
These are the rates that the machine will push the knife through the material during a cutting pass, and the rate of descent of the tool into the material at the beginning of a cutting pass. Please ensure that the values are appropriate for your machine tool and the material you are cutting.
Job Setup Sheet Editor
The Job Setup Sheet Editor is a gadget which enables you to personalise the existing Job Setup Sheet that you can generate from the Toolpaths Menu. You can access the gadget from the Gadgets Menu.
Change Logo
To change the logo from the default Vectric logo, press the button. This will open a dialog box enabling you to search your local computer for images to select. Images in landscape are better suited as they will be scaled down to W165 x H52 pixels. Images must either be JPG, PNG or GIF file format.
Title
To change the default title of “Job Setup Sheet”, enter the desired title in the edit box.
Color options
There are two options to change the color of the Header and Footer blocks, you can either: Point and click the mouse in the colored edit box, this will bring up the color selector, select a color and then click anywhere outside of the selector to accept this. Type a colors hex value directly into the edit box.
Add or Remove Setup Sheet Information
Each of the 5 sections of the Job Sheet can either be included or removed to display as much information as required. The image to the left, represents a default Job Sheet which includes the following 5 sections:
- Job Layout
- Job Notes
- Material Setup
- Toolpaths Summary
- Individual Toolpath Summaries
Restore to default sheet
Upon first successful run of this gadget, it will detect if you have already created a modified version of the Job Setup Sheet within the public gadgets directory, if so it will backup this Gadget so you could, if required restore it at a later date. If no modified gadget is found, it will backup the software default "Job Setup Sheet" so you have a copy if you want to revert back to the standard layout at a later date.
3D Toolpath Files
Files from Vectric's Cut3D, PhotoVCarve and Design and Make Machinist that include 3D toolpaths can be imported into Aspire for ALPHACAM using the main menu command: File ► Import ► PhotoVCarve, Machinist or Cut3D Toolpaths.
The 3D file must first be scaled to the required size before toolpaths are calculated, and then the complete file saved ready for importing into Aspire for ALPHACAM. These files can only be moved and positioned inside Aspire for ALPHACAM but cannot be scaled.
A Grayscale thumbnail of the 3D job is drawn in the 2D View with the X0 Y0 origin at the position it was set in Cut3D, PhotoVCarve or Design and Make Machinist. The associated toolpath(s) are also drawn in the 3D window and the names appear in the Toolpath list.
Positioning
To move the 3D design toolpaths open the 2D Window, click the Left mouse Twice on grayscale image (turns light Blue to indicate it's selected), then drag to the required position, or use the Move or Alignment tools for accurate positioning.
The toolpath(s) are automatically moved in the 3D window to the same XY position as the image.

Toolpaths for the example above have been calculated with the X0 Y0 in the middle of the 3D design. When imported into Cut2D the data is automatically positioned using the same coordinates, which places three quarters of the design off the job. In the second image the grayscale image has been moved to the middle of the job.
The 2D mirror and rotate drawing tools can also be used to edit the 3D data set.
3D toolpaths can also be copied using the Duplicate Toolpath command on the Toolpaths Tab making it very easy to use multiple elements from a single design on a job. The thumbnail preview is also copied for each toolpath, making it very easy to position additional copies of a 3D toolpath.
For example, a single design can be copied and mirrored to create Left and Right versions of a 3D design or to place multiple copies of a decorative design in the corners of a cabinet door panel as shown below.

Toolpaths for the 3D elements can be previewed along with the conventional Profile, Pocketing and Drilling toolpaths, and everything will be saved ready for machining.
A good example of where this functionality might be used in conjunction with PhotoVCarve is for making personalized picture frames that include the PhotoVCarve grooves plus descriptive engraved text and a decorative Profiled or Beveled border. As shown below:


Options
Imported toolpaths can also be edited to position them inside the material or to change the cutting parameters - speeds and feed rates can be changed.
Design and Make Machinist
When using a Design and Make Machinist file that includes multiple toolpaths, you must remember to edit the Start Depth for all of the imported 3D toolpaths.
Click the Edit toolpath icon or Double click on the toolpath name to open the edit form.
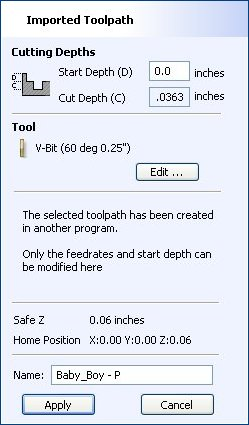
For example, after machining a half-inch deep pocket a PhotoVCarve design can then be edited to have a Start Depth = 0.5 inches and this will carve the photograph onto the base of the pocket surface.
Plate Production
This command is for designing and engraving multiple badges or nameplates using variables for positioning imported data from a text file list. The production plate functionality is typically used by engravers making badges from a database file supplied by a customer, but could also be useful for making nameplates for hotel rooms with consecutive numbering.
Procedure
Draw and Setup the Master Template
Create a New job and specify the Material Size to equal the Sheet size the badges will be cut from.
Layout the badge / plate at the required size and using the Text Tools add variables where imported data / text is required. Variables are defined using double exclamation marks ('!!') at the start and end of the variable name.

Calculate Toolpaths
Select and calculate the toolpaths for each of the elements on the design. For example, calculate an engraving toolpath for the text and logos and a separate Profile cut-out toolpath around the outer edge to cut out the design
Use the Plate Production Tool on the master template
With all of the vectors that make up the master template selected, click on the Plate production tool to open the Plate Production Dialog window.
The Plate Production Dialog
The left side of the Plate Production form is used to layout the plates / badges on the selected sheet of material, and shows the total number of plates that can be engraved / machined from each sheet of material.
Material Size
This is the material sheet size that the badges will be engraved onto. If the number and size of the badges requires additional sheets of material to be used the software automatically creates a separate layer for each sheet required.
Plate Size
This is the size of the selected Plate / Badge and is based on the bounding box of the selected vectors.
Sheet Margins
This specifies the border margin between the edge of the material sheet and the plates.
Independent margin spacing can be set for the Top, Bottom, Left and Right sides of the material
Equal Margins ensures the same space is added around all 4 sides of the plates.
Spacing
This is the horizontal and vertical spacing between each Plate / Badge.
Number of Plates
The number of plates that will fit on to the specified material sheet size is automatically calculated. This calculation takes the plate size and adds the Sheet Margins and Plate Spacing to determine the maximum number of plates that can be made from each sheet.
Toolpath Options
If toolpaths have been calculated for the master Template this option is available.
Checking ✓ this option automatically calculates toolpaths for all the plates / badges in the project.
Unchecking this option only creates the vectors for each plate / badge.
Import the Data to be Merged into the Template
The right-hand side of the Plate Production form is used to select the data that will be merged into the template, and how the data will be interpreted to create each plate / badge
Import the required text / data file using and select the appropriate format separator.
The data file is commonly created using a spread sheet such as Windows Excel. Use the option to Save As or Export to obtain the required file format that includes the correct Separator information.
Separator
The separator is the method used in the data file for dividing each set of information into columns. The most commonly used options are: Comma, Tab, Semicolon or a Space
First row is column names
It's very common for the first row of data in a file to simply show what each of the field names are, and this information is not used on the badge or plate. Checking the box First row is column names tells the software to start working with data from row 2
Assign the Variables to the data in the text file
All of the variables specified on the template - text with double exclamation marks '!!' on either side '!!' are automatically listed on the form. These variable names are each assigned to a data field (column of text) inside the data file.
Variable Assignment
Click to select a Variable Name then select the data field from the imported file that is required on each badge / plate i.e. the person's name
Repeat for each of the Variable Names listed on the form
Number Formatting
Variables can be assigned to Text from a data file - Names, Dept., etc. or to a Counter number that can be formatted and incremented using the Number Format options.
Calculate
Click to create all Badges and associated Toolpaths
If toolpaths have previously been calculated for the vectors in the Master Template, the option to automatically Create Toolpaths for each badge / plate is switched on in the bottom left corner of the form.
Close
Click to finish plate production and close the form
Multiple Sheets
Multiple Layers are automatically created if multiple sheets of material are required to engrave all of the badge data from the imported text file. Layer named Sheet 1 is displayed in the 2D view showing the badges on this sheet.
Each of the Sheets is on a different layer and can be set visible or invisible using the Layer Manager.
Multiple Toolpaths
When Toolpaths are automatically calculated, a separate toolpath for each operation on each sheet of material is calculated and named using the convention 'S1 - Name', where the Name is the name of the toolpath previously calculated for the template.
Dimensions
This tool allows you to add a variety of dimensioning annotations to your vector drawing.
Creating Dimensions
Unless otherwise noted below, dimensions are created by following these steps:
- Select the dimension type you wish to need: length; height; width; angle or the radius or diameter of an arc.
- In the 2D View, click with the left mouse button to set the points the dimension needs:
For an Angle Dimension, the first point is the centre-point. - Click where you need the arrow-tips to be.
- Click to set the location of the dimension-line.
- Click to set where the annotation text will appear.
Editing Existing Dimensions
To edit an existing dimension while the form is open, hold down aShiftkey while selecting it.
Dimension Types
The dimension tool supports a number of different dimension types.
Length Dimension
Use this to dimension a straight-line length in any orientation between two points.
The text preview box will snap to to the middle of the dimension line, unless a Shift key is held down while dragging.
Vertical / Horizontal Dimension
These two options also allow you to select any two points, but the resulting dimension will be locked to indicate a vertical or horizontal distance (respectively) between the two points.
The text preview box will snap to the middle of the dimension line, unless a Shift key is held down while dragging.
Angle Dimension
This option allows any arbitrary angle to be measured. The process is similar to creating a 3 point arc. First you must pick the center of an angle you wish to measure - typically a corner point. The next 2 points clicked will set the extents of the sweep you are measuring. The next Click will determine the dashed dimension line positioning and the final click will set the position of the text annotation.
- Angle Dimensions' arrow-heads will pop outside small angles if there is not room to draw them inside.
- Angles are extended with a dashed extension-line where required, allowing the dimension to be placed anywhere. The text snaps to the angle center and the leader-line angle snaps to horizontal, vertical or diagonal (disable snapping by holding down aShift key).
- Angle Dimensions use a separate Decimal Places value to the other dimensions (as you change dimension-type you may notice the Decimal Places value change).
- Angle dimensions can now have up to six decimal places.
Arc Dimension
With this option selected you will only be able to select arc spans with the first click of dimension tool (Bezier curve spans are not supported). The second click will set the position of the dimension annotation, which will show the radius (or diameter) of the selected arc span.
- To display the diameter of an arc dimension simply check ✓ the Show Diameter box.
- Arc Dimensions recognise when a circle has been selected and allow placement anywhere around the circle. Arcs will now be extended with a dashed extension-line where required, allowing the dimension to be placed anywhere. The text snaps to the arc/circle center and the leader-line angle snaps to horizontal, vertical or diagonal (disable snapping by holding down a Shift key).
Note
Circles or arcs that are polygonized (from an imported file or from the Curve fit vectors command using Straight lines) are not recognized and cannot be dimensioned with this tool
Font Selection and Settings
This section of the form allows the user to change the settings for the dimension annotation, such as the font to be used, the height of the text and how many decimal places are required. The Offset field determines the gap left between the dimension markers and the vectors that are being measured.
Use Custom Text
You can check ✓ Use Custom Text to insert your own custom text. The text is stored per dimension, so you change between calculated and custom text without losing a dimension's custom text. When the form is first opened it defaults to calculated text.
Place Dimensions on Layer
By default this option is checked ✓ and the dimensions will be placed on a mid-gray Dimensions Layer. You can edit the name of the layer in the Name edit field. If a layer of this name does not exist, it will be created automatically.
Note
Dimensions can be edited. Hold shift while selecting the dimension you wish to edit or use the Undo shortcut Ctrl+Z to undo previously created Dimensions while still in the Dimensioning tool.
Join/Close by Moving End Points
Join Moving End Points finds the closest end points on 2 selected, open vectors, calculates the mid-point between them and moves the end points to this position.
Cut Operation
The Cut tool removes the selected objects from a design in a similar way to pressing the Delete key, but the selected objects are copied to the clipboard and can be Pasted into either the current file or a new file if required. Only one item can be Cut or Copied at a time.
Vector Selection Mode
When the Vector Selection Tool is chosen, the selected vectors are shown as dotted magenta lines. Vectors need to be selected before any of the editing tools such as scaling and moving etc. can be used.
Vector selection methods
Multiple vectors can be selected in the following ways:
- Manual multiple selection:
Hold down the Shift key while clicking the Left mouse button on each vector required. Objects can be deselected by simply clicking on the object again with a Shift key pressed. - Moving the cursor from Left to Right selects only fully enclosed objects:
Click and drag the left mouse button moving from Left to Right selects all objects completely inside the selection rectangle. - Moving the cursor from Right to Left selects all objects inside or touching the selection rectangle:
Click and drag the left mouse button moving from Right to Left selects all objects inside the selection rectangle + any that the selection touches. - Pressing the keyboard keys Ctrl+A will select all vector objects in the design:
Selected vectors are displayed as dotted magenta lines.
Deselecting Vectors
Selections can be cancelled by:
- Left clicking on an area outside the selection
- Pressing the Esc key
- Pressing the Right mouse button and clicking Selection ► Unselect All from the pop-up menu.
You must click on the white drawing background to get this option in the pop-up menu.
Calculation Edit Boxes
Numerical edit boxes generally support simple calculations.
A sum can be entered directly into the edit box:
Having typed an equation, pressing the = key will perform the entered calculation and fill the edit box with the answer.
Special Calculation Characters
As well as the simple numerical calculations, such as 3+(4/5), several of Aspire for ALPHACAM's stored values can be accessed by using certain letters (which are not case-sensitive): When used, Aspire for ALPHACAM substitutes the character with the appropriate value in the calculation.
Character | Name | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
W or X | Material Width |
| Half of the material width |
H or Y | Material Height |
| Twice the height of the material |
T or Z | Material Thickness |
| 0.25 units less than the material thickness |
P | PI (3.141593) |
| Area of a 10 radius circle (π.r2) |
I | Imperial Conversion |
| Converts 25.4mm to inches |
M | Metric Conversion |
| Converts 2 inches to millimetres |
' | Feet |
| 34 inches (2 feet and 10 inches) |
Add Draft to Model
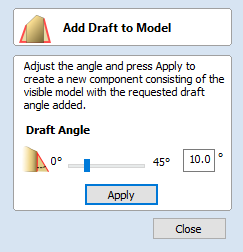
For some applications it can be useful to eliminate vertical walls on 3D models, especially if the machined part is intended to be used as the basis for a mold or vacuum forming tool.
The Add Draft tool will automatically add a minimum angle to any steep walls that exist in your model. The draft angle is specified by using the slider or entering a typed value in the form.
When the button is pressed, the tool creates a new 3D Component by baking the visible Components and applying the draft angle across all the walls of the composite model. Note that you do not select the Component/s to apply the draft angle to, just ensure that they are visible in the 3D view. The resulting Component will not have any wall angles that are steeper than the specified draft angle. Once complete, both the original Component/s and the new Component will be visible, although the original may be obscured by the new Component. The Component with the draft angle will be named appropriately indicating the amount of draft that was added. The images below show how a Component looks before and after adding 20° of draft.


Note
If you are creating a model within a two sided environment the draft will only be applied to the side you are currently working on. To apply a draft to both sides you will need to switch over to the opposite side and apply a draft to the model there.
Import a Component or 3D Model
This command opens the File Open dialog window, allowing existing Aspire for ALPHACAM files (CRV3D extension) and importable 3rd party 3D files to be selected and opened. If you select a 3rd party 3D model format, the Orientate Model form will open (see below) to allow you to manipulate the 3D model before it is converted into a Component.
CRV3D | 3D data from files previously created and saved in Aspire for ALPHACAM will be opened and a new single Component Created (from all the visible 3D Components in the file when it was saved). The new Component will have the same name as the file. This will be imported at the size and position the part was saved in the original file. |
3DCLIP | 3D Clipart files are exported from Aspire for ALPHACAM. This format maintains the component structure of clipart pieces at the time of saving, so will import all the components comprising the clipart piece. This will be imported at the size and position the part was saved in the original file. |
V3M | V3M is a proprietary file format developed by Vectric for Vector Art 3D and Design and Make. Files in this format can be purchased from www.vectorart3d.com and www.designandmake.com and when imported into Aspire for ALPHACAM will create a new Component with the same name as the file. This will be imported at the size and position the part was saved in the original file. |
STL | This is a standard format for complex 3D models, based on a triangular mesh. STL files can be exported from many 3D design software programs such as Rhino. These models can be completely 3 dimensional (i.e. have a front, back, etc.), this means that when this type of file is opened that it must first be sized and oriented before a Component can be created (Aspire for ALPHACAM only represents base-relief so cannot work with a completely 3D object). Once the file becomes a Component it will have the same name as the original STL file. This file type will need to be imported using the Orientate 3D ModelAspire for ALPHACAM. |
DXF | 3D DXF files from AutoCAD and many other CAD orientated modeling packages, these must be 3D meshes and not just wireframe data of the models vertices. This file type will need to be imported using the Orientate 3D ModelAspire for ALPHACAM. |
3DS | A native format from 3D Studio Max and many other animation orientated modeling packages. This file type will need to be imported using the Orientate 3D ModelAspire for ALPHACAM. |
OBJ | A native format from Wavefront and many other animation orientated modeling packages. This file type will need to be imported using the Orientate 3D ModelAspire for ALPHACAM. |
SKP | A native format from the SketchUp modeling package. This file type will need to be imported using the Orientate 3D ModelAspire for ALPHACAM. |
Note
If you wish to read data from a 3D digitizer or scanning device then STL is typically the best format that should be used to import the data. Many software packages that work with a scanner offer an STL export option, if not then a third party software program may be required to convert the data to an STL model.
Importing a 3D Model (STL, DXF, 3DS, OBJ, ...)
When one of these formats are chosen for 3D file Import, the imported model needs to be oriented and scaled before it can become a Component. A special import window is opened and a set of orientation/scaling tools enabled. Depending on the job type, import window will be different:
File Types
CRV3D | Files previously created and saved in Aspire for ALPHACAM will be opened and displayed in the 2D Design window and 3D View if they contain 3D data. All calculated toolpaths are stored/opened from the CRV3D file. |
CRV | Files previously created and saved in Aspire for ALPHACAM will be opened and displayed in the 2D Design window. All calculated toolpaths are stored/opened from the CRV file. |
DXF | Files from other CAD or graphics software packages such as AutoCAD will be opened in the original size and position. The Job Setup Form is automatically opened showing the maximum X and Y dimensions of the opened design. The actual size of the material can then be specified along with the required thickness and appropriate X0, Y0 and Z0 origins. |
EPS | Files from typical design software such as Corel Draw can be opened. The Job Setup form will automatically be opened so the required material size can be specified. By default the EPS file will be placed with the lower left corner of the design at X0, Y0. |
AI | Files from typical design software such as Adobe Illustrator and Corel Draw can be opened. The Job Setup form will automatically be opened so the required material size can be specified. The AI file will be placed with the lower left corner of the design at X0, Y0 |
Software such as the Adobe product range can be used to convert files from other design and word processing software into the industry standard PDF file format. The text and vector content of PDF files is extracted when imported into Aspire for ALPHACAM. When importing multiple page PDF documents each page is placed on a separate layer. | |
SKP | SketchUp files with a .SKP extension (see www.sketchup.com) can be imported as 2D data suitable for machining. |
Smooth Components
Often it is advantageous to apply a general smoothing effect over the whole of a component (rather than smooth a particular area with the Sculpting Tools). To use this tool, select the components you wish to smooth and then click the Apply smoothing filter to selected components icon on the Modeling tab. The form will appear and Aspire for ALPHACAM will take a few seconds to prepare the model for the smoothing operation. You will see a progress bar at the bottom of the screen while it is doing this.
One or more Components can be selected for Smoothing. If you select multiple shapes or a Component Group then the software will need to Bake your selection into a single Component, if applicable you should ensure you have a safe copy of your current Components before proceeding.
If you wish to smooth individual components one after another, potentially with different amounts of smoothing, you can do this by selecting one component, apply a suitable smooth filter value with the slider and then hit the Bake Current Smoothing button in the form and then proceed to selecting the next component you wish to smooth. When pick a new Component the software may take a few seconds to pick it and apply the smoothing filter to it at the default of 50% strength. If you do not click on the button before you select a new component then the effects of the smoothing will be lost on the previously selected component.
Note
Smoothing should be performed with both the 2D and 3D View visible (Tile Windows), so you can easily see the selected Component in the 2D View and also view the effects of the smoothing in real time on the 3D model in the 3D View.
Smoothing
This slider will allow the user to control the strength of the smoothing applied to the Component. By default 50% smoothing is applied, using the slider different levels of smoothing can be applied to the model. Find the strength which gives you the amount of smoothing you require. If the Max setting has not smoothed the model enough then hit the Bake Current Smoothing button which resets the smoothing slider to allow you to do further smoothing.
Preserve Transparency
Checking ✓ this option will keep the smoothing only on the current 3D areas of the selected shapes and not smooth the edges into the background. Un-checking this option will smooth all the edges of the modeled area into the background of the part, blurring the silhouette of the Component.
Bake Current Smoothing
The button bakes the current smoothing value into the Component and resets the form. This means you are able to perform multiple smoothing operations without leaving the function.
3D Design and Management
As well as creating toolpaths directly from 2D drawings, Aspire for ALPHACAM can produce extremely flexible 3D toolpaths. These toolpaths are created from 3D design elements called 3D Components that can be generated from models created in external 3D design packages, imported as 3D clipart or built entirely from within Aspire for ALPHACAM using 2D artwork as a source.
The 3D View
The 3D View can show you the current Composite Model (which is built from all of the currently visible 3D Components and Levels), the Toolpath Preview (a highly accurate 3D simulation of the resulting physical object that will result from your toolpaths called the Preview Material Block). Which of these is currently displayed will depend on whether or not you have a part which has 3D Components and Toolpaths or are just working on something that only includes 2D Data.
Whenever you have the Preview Toolpaths form open on the Toolpaths tab, the 3D View displays the Preview Material Block instead of the Composite Model. When this is closed if you are working on a part that only includes 2D data and 2D or 2.5D toolpaths it will continue to display the Preview Material Block. If your part contains any visible 3D Components then as soon as the Preview Toolpaths form is closed it will revert to showing the Composite Model in the 3D View and hide the simulation. In addition to these items, you can see line drawings of any calculated toolpaths in the 3D View. The visibility of these calculated toolpaths can be controlled from the Toolpath List on the Toolpaths tab using the check-boxes next to the toolpaths name. If working in a 2 Sided environment you can view both sides of a project in the 3D View using the Multi Sided View option.
The Composite Model
Aspire for ALPHACAMhas been designed to work in a way which enables the user to easily create even very complex projects. In any situation, the best approach to producing something complicated is to break it down into smaller pieces until a level of simplicity is reached that can be understood and managed. In Aspire for ALPHACAMthis is achieved by letting the user work with pieces of the design which are combined to make the finished part. In the terminology of the software these pieces are called Components. To help organize the Components they are assigned to Levels. Step by step, Components and Levels can be created and modified until you have all the elements you need. In the images below you can see an example of how this might work. On the left you can see the separate component for a model of a bunch of grapes and on the right you can see these positioned to make the complete part - we call this resulting combination the Composite Model.


There is no limit to how simple or complex a Component or the Components on a Level can be (this is the user's choice). In the example shown, you can see that a model of a whole bunch of grapes may be made up of smaller individual components but they could also be combined to exist as one single Component (the assembled bunch of grapes) that could then be used to lay-out a more complex part with multiple bunches of grapes. They could also be organized so all the grapes were on one Level and leaf and stem on another to provide a different way of managing and manipulating the shapes. Each user will find a level of using Components and Levels they are comfortable with which may be dependent on the particular job or level of proficiency with the modeling tools.
3D Components and Levels
In Aspire for ALPHACAM, the aim is to end up with a set of Components and Levels that when combined together will make the finished 3D part. One way to think of this is like building a 3D collage or assembly. As the design evolves, new Levels or shapes may need to be created or existing ones changed. The parts of the collage are managed with the Component Tree which will be covered in more detail later.
Creating and Editing Components
An existing Component can be copied, scaled and have other edits carried out on it as an object. The user can also change the way it relates to the other Components, for instance whether it sits on top or blends into an overlapping area of another Component. The shape, location and relation of these pieces determine the look of the final part. As the job progresses, the user will need to create brand new Components or edit existing ones by adding new shapes, combining them with others or sculpting them.
Components can be created and edited by:
- Use a modeling tool to create shapes from 2D vectors.
- Import a pre-created 3d model - either a model previously created in Aspire or from another source such as a clipart library or a different modeling package.
- Create a 'texture' Component from a bitmap image.
- Use the Split Components Tool to break an existing Component into multiple pieces.
All of these methods are covered in detail throughout the training material.
Dynamic Properties
As well as having its underlying 3D shape, each component also has a number of dynamic properties that can be freely modified without permanently changing its true shape. These include scaling of the Component's height, the ability to tilt it, or to apply a graduated fade across it.
These dynamic properties can always be reset or altered at any time during your modeling process, which makes them a particularly useful way of 'tweaking 'your components as you combine them together to form your final composite model.
Combine Modes
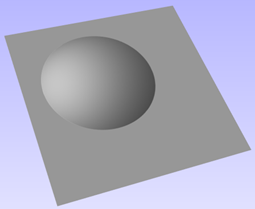
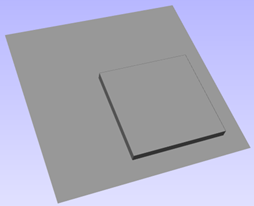
The Combine Mode is a very important concept when working with 3D shapes within Aspire. The options for combine mode are presented when creating new shapes and also when deciding how Components and Levels will interact in the Component List. Rather than cover this in every section where it is applicable, it is worth summarizing the options here so the general concept can be understood.
When you have more than one 3D shape, such as the Component pieces of the design or where you have an existing shape and are creating a new one, then you need to have a way to tell the software how the additional entities will interact with the first. This can be an abstract concept for users who are new to 3D but it is an important one to grasp as early as possible. In Aspire this is controlled by a choice called the Combine Mode.
There are four options for this: Add, Subtract, Merge High, Merge Low.
As modeling is an artistic and creative process, there is no general rule to describe when to use each one. As a guide though you can assume that if the second shape's area is completely within the originals one then you will probably be adding or subtracting and if the shapes only partly overlap that you will probably use Merge or, very occasionally, Low.
The four options and their specific effects are described on the following pages. To illustrate the different effects a combination of an overlapping beveled square and a dome will be used. You can see in the image top right how these are arranged in the 2D View and how they overlap. Then you can see each individual shape in the images below middle and right. These shapes will be used to demonstrate the different Combine Modes. In every case the Dome will be considered the primary shape and the square is the secondary shape which is being combined with the first. In addition to the dome/square example some images of 'real world' parts will also be included to help to understand how these can be used on actual projects.
As well as working on individual shapes, the Combine Modes are also assigned to Levels. These will govern how the combination of all the individual components on one Level interacts with the result of all the Components on the Level below it in the Component Tree
Note:
There is a 5th Combine Mode available from the right mouse click menu after a component has been created called Multiply. This combine mode has specialist applications which are dealt with in the appropriate tutorial videos. This option will literally multiply the heights of the Component or Levels being combined to create the new Composite 3D shape.
Add
When Add is selected, it takes the first shape and then just adds the height of the second shape directly on top of the first. Any areas which overlap will create a shape which is exactly the height of each shape at that point added together (see below)
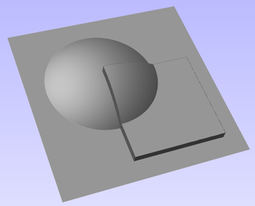

Typically the add option is mainly used when the shape being added sits completely within the original shape, this ensures that the uneven transition where the parts only partly overlap (as shown in the example) do not occur.
The example above shows the Maple Leaf and border extrusion Components being Added to the dome Component in the sign example from the Introduction to Modeling document.
Subtract
When Subtract is selected it takes the first shape and then removes the height of the second shape from the first. Any areas which overlap will be a combination of the original height/shape less the second shape. Areas where the shape goes into the background will become negative regions. You can see how this looks using the dome and square in the image below:
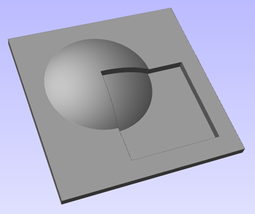
Typically subtract, like the add option, is mainly used when the shape being removed sits completely within the original shape, this ensures that the uneven transition where the parts only partly overlap (as shown in the example) do not occur.
The image shown above has some 'creases' to help define the muscles of the lioness. The shapes to create these recesses were created by using the Subtract option with the Create Shape tool on the vectors representing those recessed areas.
Merge
When the Merge option is selected any areas of the shapes which do not overlap remain the same. The areas that overlap will blend into each other so that the highest areas of each are left visible. This results in the look of one shape merging into the other and is in effect a Boolean union operation. You can see how this looks using the dome and square in the image below:
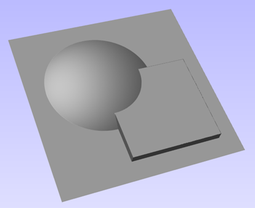
Typically the merge option is used when the shape being combined partly overlaps the original shape. This enables a reasonable transition to be made between them.
The image above shows 2 Herons, a rope border and banner Components. Each of these overlaps with the others and so they are set to Merge in this areas. Whatever is the higher of the two merged areas is what is prominent. In this case the rope is lower than everything and the Banner is higher than the Herons so the desired effect can be achieved.
Low
The Low option is only available when combining Components (not in the modeling tools). When this mode is selected, any areas which do not overlap are left as they were in the original two shapes. Any areas which overlap will create a new shape which is the lowest points taken from each shape, this is in effect a Boolean intersection operation. You can see how this looks using the dome and square in the image below:
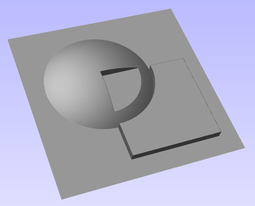
The Low option is used for recessing a shape into a raised shape. An example of this is shown in the image above.
The example shown on the right above uses the Low option to combine the flat topped 'button' component on the left with the curved top face component with the letter 'A' on the right. Combining both components with the merge low option gives the keyboard button with the curved top you see in the bottom row.
Level Mirror Modes
Right-clicking Levels in the component tree will open a pop-up menu offering commands and operations related to the clicked level and Mirror Modes can be set in this way. If a mirror mode is set on a Level, all the components it contains will be continually mirrored dynamically as they are moved, transformed or edited. The mirroring is non-destructive, that is it can be turned off or on at any time and does not alter the underlying components in any permanent way. Working inside a Mirror modes Level is a simple way of achieving a complicated symmetrical pattern by editing only one half (or quarter, see below) of the design.
The available Mirror Modes are broadly divided into two groups. The first group apply one plane of symmetry:
- Left to Right
- Right to Left
- Top to Bottom
- Bottom to Top

These modes allow you to work in one half of your job and the other half will be automatically and dynamically generated for you. For example, in Left to Right mode you would place your components in the left half of your job and a mirrored equivalent of each would be created in the other half of the job. This 'reflection' is updated dynamically as you work.
The other group offer two planes of symmetry (horizontal and vertical):
- Top Left Quadrant
- Top Right Quadrant
- Bottom Left Quadrant
- Bottom Right Quadrant
When using these modes your components should all be in the quadrant (quarter) of the job. Mirrored reflections horizontally and vertically will be created in the other quadrants of the job for you.
Multi Sided View

When working in a 2 Sided environment you can create components independently per side or using the Right click option you can copy or move a component to the opposite side. Selecting the option to work in 'Multi Sided View' allows you to view components you may have on the Top and Bottom side in the 3D View. In the Toolpath Preview form of a project that contains toolpaths for the Top and Bottom Sides the multi sided view presents the simulation of the toolpath preview on both sides also, if the multi sided view is not selected you can use the 'Preview all Sides' option in the Toolpath Preview form to display the Top and Bottom Toolpaths in the 3D view. 2 Sided Setup will be described in detail later in the relevant section of this manual.
Sculpting
The Sculpting function in Aspire for ALPHACAM is a very powerful way to edit (or create) 3D shapes. It allows the user to perform truly dynamic interactive editing of 3D Components. Once activated, the user chooses from a variety of tool options which determine how the model will be changed and then uses the mouse (or a pen tablet) to actually edit the 3D model. This is done in the 3D view and requires the user to click and move the mouse cursor in the area of the model they want to apply the tool. The best way to understand this tool is to actually try it and to watch the Tutorial Videos that are supplied with the software as it is very much a visual tool (which is what gives it its power).
One or more Components can be selected for Sculpting. If you select multiple shapes or a Component Group then the software will need to Bake your selection into a single Component, if applicable you should ensure you have a safe copy of your selection before proceeding.
In addition to components, you can also select bitmap. The bitmap will be overlaid on the sculpted model. This is useful when sculpting based on the photo.
Tool
One sculpting tool at a time can be selected by clicking the option from the form or using the shortcut keys (numbers 1-6 displayed next to each option):
Smooth
As the user moves the mouse back and forward over the 3D model the area under the red cursor will be smoothed out to average the high and low areas of the model.
Smudge
As the user moves the mouse from one place to another on the 3D model the material under the red cursor will be dragged, similar to smudging a piece of clay with your thumb. In Aspire for ALPHACAM it means that going from a high to low will pull the higher material into the lower and vice-versa.
Deposit
As the user moves the mouse over the 3D model the area under the red cursor will have material added to it to increase its height.
Remove
As the user moves the mouse over the 3D model the area under the red cursor will have material removed from it to decrease its height.
Undo Brush
As the user moves the mouse over any area of the 3D model that has already been sculpted then the area under the red cursor will be gradually returned to its original state. This can be used to undo some of the sculpting if you make a mistake.
Note
If you press the 'shift' key with the Undo Brush selected you can erase the section of the model under the cursor completely, this is a useful way to tidy up the edge of a shape or delete specific parts of a component.
Alternately you can use the Key combination Ctrl+Z to undo the last move that you made without using the Undo Brush.
Twiddle
Normally when in the 3D View you can twiddle (rotate) the direction of the view by left clicking and moving the mouse. In the Sculpting mode the left click is what activates the sculpting so cannot be used for twiddling the view. Selecting this option allows the user to twiddle the view as normal before returning to one of the other sculpting tools. A Short-Cut to this while in the sculpting is holding the Alt key while holding the left mouse button and moving the mouse.
Diameter
This slider will allow the user to control the size of the sculpting cursor (red circle). This value can also be changed while sculpting by rolling the 'wheel' on a roller mouse, pressing control while rolling the wheel will change the diameter in smaller increments.
Strength
This slider controls the strength of the tool that is currently selected. The higher the strength the more effect the tool will have as the cursor is moved over the model. The strength can also be adjusted by rolling the mouse wheel while pressing the Shift key if you have a roller mouse.
Smoothness
This slider controls how smoothly the selected tool will manipulate the model. A higher smoothness setting will create a more gentle transition while a lower smoothness setting will create a jagged and potentially distorted effect.
Preserve Transparency
This option is checked ✓ by default when you first go into the Sculpting. Leaving it checked ✓ will mask the sculpting so it is only applied within the existing boundary of the component. This stops the edges being blended into the background. It is called Preserve Transparency as the background is represented by a transparent (lighter colored) flat plane around the edge of the 3D component. Un-checking this option allows the user to sculpt the part into the modeling plane if the shape needs to be changed to go outside of its original edge or if the edges need smoothing into the background. Pressing the 0 key while sculpting is a shortcut to toggle this option.
Show Grayscale Background
Exposes the selected component without entirely hiding the other components: they are displayed as a grayscale image on the sculpting screen.
Mode
The sculpting mode defines how the tool is applied to the model in terms of the heights of the shape under the sculpting cursor. The Raise option is good for filling in holes and the Lower option is good for eliminating spikes in a model. A good example of need for this may be if the user was working with 3D digitized data which had been imported from a scanner (e.g. as an STL model).
Normal
Selecting this option means that the sculpting operation will average the high and low points under the cursor dragging them up or down as appropriate.
Raise
Selecting this option will maintain the highest points under the cursor when smoothing or smudging only allowing material to be added (based on the currently selected tool).
Lower
Selecting this option will maintain the lowest points under the cursor when smoothing or smudging only allowing material to be removed (based on the currently selected tool).
Overlay Image
If bitmap is selected when opening this tool, it will be overlaid on the sculpted model.
Overlay image opacity
Controls how translucent the overlaid image is.
Show overlay image
Allow to quickly toggle between overlaid image being visible or not. This allows the user to work with overlaid image hidden and only displayed periodically to guide the sculpting process.
This option can also be accessed by pressing the O key.
Presets
Selecting a preset from the drop down list will restore the sculpting tool settings previously stored within it. This is a quick way of switching between commonly used settings. Selecting <Add new preset...> from the list is an alternative way to create a new preset.
Add
Clicking the button will save the current sculpting tool settings in a preset. You will be prompted to enter a name for the preset. If a preset with the same name for the same tool type already exists then you will be asked if you would like to overwrite it.
Remove
Clicking the button will remove the preset currently displayed in the drop down list.
Changes
Sculpting is a very iterative process and frequently as the user progresses, they will want to either get rid of a recent change, or will want to save the changes they have made and continue sculpting. The options under Changes in the form allow the user to do this.
Keep
Clicking the button will internally save the sculpting changes made so far. This should be clicked if the user is happy with the sculpting so far and wants to keep it but also wants to continue to sculpt the model.
Discard
Clicking the button will discard all the changes made with the sculpting tools back to the stage that the Keep button was last clicked. If the Keep button has not been clicked within a particular sculpting session then all the changes will be discarded. In order to ensure that this is not accidentally selected a Warning will appear giving you the option to verify you want to discard your changes. This warning can be bypassed by holding down the Shift key while pressing Discard.
OK
Clicking will accept all the changes made to the model within the sculpting session and exit the form updating the Component Tree with the newly sculpted model.
Cancel
Clicking will exit the sculpting and discard ALL the changes you made within that sculpting session. The changes will be discarded even if you have previously hit Keep. If you wanted to keep most of your changes but discard just the ones you made since the last Keep then you should hit first then . In order to ensure that this is not accidentally selected a Warning will appear giving you the option to verify you want to exit and discard ALL your changes. This warning can be bypassed by holding down the Shift key while pressing .
Draw Line
This tool creates continuous straight lines through points clicked, entered coordinates, tangent between a point and an arc or tangent to two arcs.
Interactive - Cursor
The quickest and easiest way to draw a line is by clicking within the 2D View using the mouse.
- Click the left mouse button to indicate the start point of your line.
- Move the mouse pointer and click again to set the next point in your line.
- Repeat this process to add as many line segments as you require.
- Right-click or press Esc to finish your polyline and exit the form.
- Alternatively press the Space bar to complete this polyline but keep the form open and begin drawing another polyline.
- Press the Tab key to automatically close the vector.
- A smooth bezier span can be created by clicking and dragging to modify the curvature. The next span will then also be smoothed. If you want next line to be straight line then you can press S to disable the smoothing.
Creating Tangent Lines
The polyline tool can also be used create lines that are tangent to arcs in your existing drawing.
From A Point To An Arc
To create a line tangent from a point to an arc simply enter the initial point and then hover the cursor over the arc and press T.
From An Arc To A Point
To create a line tangent from an arc to a point click on the arc to insert a point and then hover the cursor over the next point position and press T

Note
You cannot create a tangent line to a bezier curve
From An Arc To Another Arc
To create a line tangent from one arc to another click on the arc to insert a point and then hover the cursor over the second arc and press T.

Note
Arcs are not trimmed as a result of creating a tangent line
Quick Keys
Instead of releasing the left mouse button when you have dragged your shape to the required size, you can also type exact values during the dragging process and set properties precisely.
- Left-click and drag out your shape in the 2D View.
- With the left mouse button still pressed, enter a quick key sequence detailed below.
- Release the left mouse button.
By default, entering a single value will be used to add a point at the specified distance along the line direction currently indicated by the mouse pointer position, relative to the preceding point. With polyline drawing underway, move the mouse pointer in the direction you wish to create a new line segment and type Length Value Enter to extend the line by the specified distance in that direction.
By default two values, separated by a comma, will create the next line point at the absolute X Y coordinate indicated by the two values, respectively. While drawing, type X Value, Y Value Enter to place the next point precisely at specified X and Y position
Examples
- 3 . 5 Enter - Adds the next point at a distance of 3.5 along the line direction indicated by current mouse direction
- 1 , 2 . 5 Enter - Adds the next point at the absolute position 1 in X and 2.5 in Y
Specifying Further Properties
By using specific letter keys after your values, you can also specify the line segment in terms of angle and length. Using the key sequence value A value L creates the next line segment at angle (A) degrees from the last point and with a length(L)
Examples
- 45 A 3 L - Creates a line segment at 45 degrees and length 3
Next Point
You can also use the form to enter values for each line segment as you go along. The segments can be defined using :
- The absolute X Y position of the next point
- The Angle and Length to the next point
The relative offset in X (dx) and Y (dy) to the next point.
Once you have entered the values you wish to use :
- Click the Add button to enter a new point.
- The Undo button deletes the last point entered and allows a new point to be added.
- The Finish button completes drawing the current line and leaves the form open to allow additional lines to be drawn.
Note
The X Y position use absolute coordinates. The Angle, Length and dx/dy positions are incremental from the current position.
Component Properties
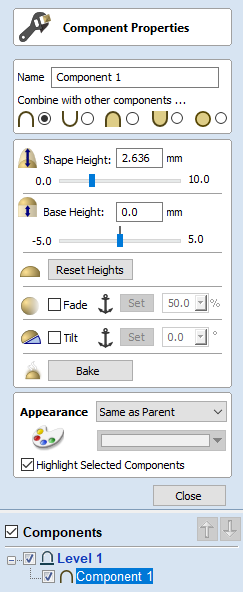
The Component Properties form allows you to adjust a number of dynamic properties for a selected Component or Level. Adjusting these properties does not make permanent changes to your Components and can be further edited or reset any time until the component is Baked, in which cases they will be made permanent in the Component shape and this form will be reset.
Note
You can only edit the Name, Combine Mode, Base Height and Appearance for the Properties of a Level.
Multiple Selections
If you have more than one component selected while using the Component Properties tool, Aspire for ALPHACAM will apply the changes to all the selected components. Some properties where this would be inappropriate (such as the component's name) are grayed-out when there is more than one component selected. These properties must be applied to components one at a time.
Combine with other components
The Combine Mode dictates how the components (or Level) are combined with the objects below them in the Component Tree. This is done by the software starting at the bottom of the list and working upwards. The first level and first component's combine mode determines only how it combines with the modeling plane. The second and subsequent components are combined with the result of everything below them based on their Combine Mode as detailed below. See Component Tree for more details.
Add

Adds the selected component/s to the result of all the previous components in the list.
Subtract

Subtracts the selected component/s from the result of all the previous components in the list.
Merge

Where they overlap, this Merges the selected component/s into the result of all the previous Components in the list keeping the highest part of the overlapping area. This means the higher part of each shape will be what remains in this area.
Low

Where they overlap, this Merges the selected component/s into the result of all the previous Components in the list keeping the lowest part of the overlapping area. This means the lower part of each shape will be what remains in this area.
Multiply

Where there is an overlap, this Multiplies the result of all the previous components in the list by the heights in this component.
Shape Height
Use the slider or type in a specific percentage to scale the height of the selected Component(s) up or down based on its current height (100%).
Enter a value in the Shape Height edit box directly, or use the slider to adjust the height of your component selection interactively. In either case, the 3D view of the component will update automatically as you adjust the value. The range of available heights on the slider is determined by your current material thickness setting. If these values appear to be inappropriate you can still enter any value you like into the associated edit box, or you can close the tool and select Edit ► Job Size and Position from the main menu. In the Job Setup page you can then correct the current setting for the material thickness before continuing.
Base Height
Enter a specific value into this box to raise the Component or Level up on a flat plane of the thickness you specify. This can be useful to help move an object up so it sits proud of another component it is Merging with. If you are not sure of the value you need, then enter an amount and hit the space bar to apply this. If this is not correct, type in another value and hit space again to apply the new value, look at the 3D View to judge the result - repeat until you get the value you need.
You can also apply a Base Height to a Level. Adding a base height to a level will add the same base height visually to the components in that Level, however the components themselves will have no base height added to them within their properties. This is useful to raise a set of objects on a Level above things that need to appear to be behind them (for example above a textured area).
Note
Level Base Heights are not included in Baking operations on the Components on those Levels but are a separate value that is added on after the objects on the Level have been combined. They are scaled proportionately though when the Scale z height of Model function is used to adjust the Z Height of the Composite Model (visible components).
Reset Heights
The button will remove the dynamically applied Shape and Base height settings from the selected component. To reset the Base Height back to zero using the slider control, double click the central line marker above the slider bar.
Fade
When this option is checked ✓ the user can fade the Z depth of the Component. The first part of this operation (once the option is checked ✓) is to select the button - then click two points in the 2D view. The first click specifies the point which will remain at the current height. The second click specifies the point that the Component will be faded down toward. The shape will fade down from the first point to the second by the percentage selected. Change the strength of the fade by clicking the down arrow next to the percentage value and using the slider to move this up and down or type in a specific value for the amount you would like to reduce the depth by. The fade will be applied linearly between the two selected points. This is a useful tool for giving the effect of a Component fading into the distance to help with overlapping areas of Components if you want to lower an area to give it the appearance of going behind another one.
Tilt
When this option is checked, ✓ the user can set a direction and angle to tilt the Component up in the Z axis. The first part of this operation (once the option is checked ✓) is to select the button - then click two points in the 2D view. The first click specifies the point which will not move (the pivot point of the tilt). The second click specifies the point that will be tilted upwards by the specified angle (the point that will be raised up). Change the tilt angle by clicking the down arrow next to the value, you can use the slider to alter this, or type in a specific value for the angle. This is an extremely useful function for raising a part of one Component above another one when they overlap, without having to raise the whole Component up using the Base Z Position option. In some cases this allows the overlapping areas to sit proud without having to create a deep raised wall around the whole edge of the Component.
Bake
Sometimes it's useful to apply a component's dynamic properties permanently, one example where this is useful is so that further dynamic changes can be applied 'on top' of previous ones. To do this, use the button.
Appearance
Aspire for ALPHACAM gives you a lot of control over the appearance of the 3D shaded image for visualization purposes, such as customer approval proofs or marketing material. Each component can be given an individual color or material.
Same as Parent
Use appearance of the objects parent. This is a level for components and the model in case of level. This will ultimately use the model's appearance, as specified in Job Setup.
Solid Color
This option allows to use a single color for shading the component.
Use Material
When this is selected the user can choose from the list of pre-defined material effects by clicking on the box immediately below the Appearance choice. These include many wood grains, metal effects, stone and plastic.
Additional materials can be added to the library. See Preview Toolpaths for more details.
Color from Children
This option is used for a Group of Components or Level and will allow the software to use the individual colors and materials assigned to the groups constituent Components to display in the shaded image even though it is a Group. If this option is not selected the Group/Level will be given its selected Color or Material.
Highlight Selected Component
When choosing a material or color to use for a particular component, the red selection highlighting of the component can prevent you from seeing your chosen material accurately in the 3D view. You can un-check this box to temporarily disable the red highlighting while you make your selections. This option will automatically be re-enabled on exiting the Component Properties page.
Close
The button will exit the Component Properties form and return to the standard set of modeling icons.
Node Editing Mode
The Node Editing tool can be selected from the Editing window or by pressing the Keyboard shortcut N to toggle between Selection and Node Editing modes.
When the Node Editing tool is active the cursor changes to a Black Arrow indicating that individual points (nodes) and their connecting spans can be edited. Nodes can be interactively moved by clicking and dragging the left mouse button on a node to select and move the node to a new position.
The shape of lines, arcs and Bezier (curve) spans can be edited by clicking and dragging on the nodes or control points to move them. Multiple nodes and control points can be selected and moved by using the multiple selection options such as the Shift key and dragging to make a selection.
The shape of individual spans can also be edited by dragging the span itself using the left mouse button.
Holding down the Ctrl key while dragging an arc or Bezier span will move the entire span rather than change its shape.
The start and end directions of Bezier curves can be fixed when being dragged directly, by toggling on Keep Bezier Tangency mode.
If you right click on nodes or spans a context sensitive popup menu will be displayed which allows you to insert or delete points and nodes, cut the vector, move the start point, etc.
Node editing vectors is a very powerful way to be able to make changes to the vectors in your part.
Useful Tip
Smart Snapping combined with Distance Snapping or Quick Keys can give more accuracy when dragging nodes.
Weld Vectors
Selected closed vectors that overlap can be merged together to create a new shape. These tools consider the closed vectors to be solid areas.
The following examples begin with these five vector shapes where the rectangle was selected last.
Welds overlapping vectors together to create a new shape which follows the outermost edge of all the selected shapes.

When welding text, the internal regions of characters are preserved.


Text On A Curve
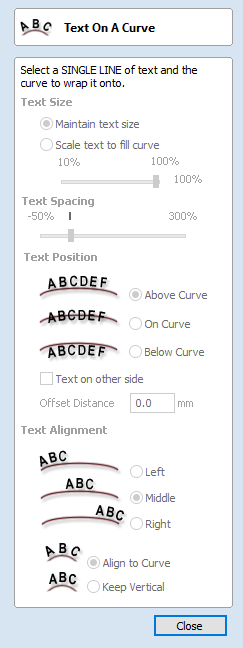
This tool requires the user to select a single line of text with the Draw Text tool and a single vector curve/line. It will take the text and fit it onto the selected vector to follow the curvature. Options within the tool allow position, space and location against the line to be edited.
To edit properties of text object that was already on a curve, just select the text object. To place it on another curve select both the text object and a vector.
It is also possible to use a closed vector to wrap the text around it.
Text Size
Maintain text Size
Will not change the size of the text block
Scale text to fill curve
Will increase the character size in order to fit along the entire length of the selected curve.
Text Spacing
The slider can be used to increase or decrease the word and character spacing. Each time the form is opened, or new text is selected, this control starts at the 100% mark. While this text is being edited the spacing scale can be increased or decreased from its original value.
Text Position
Above Curve
On Curve
Below Curve
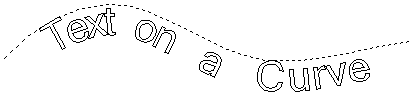
Text on other side

Offset Distance
Allows the text to be moved away from the curve by a specified distance.
Text Alignment
The 3 options allow the text fitted to the curve to be aligned to the left, middle or right hand side of the selected curve. Or, when using a closed vector curve, relative to the Start Node.
Note
Remember the Start node can be changed using the Node Editing Tools available from the Right mouse menu and selecting Reverse Direction.
Characters in the text string can also be aligned 'normal' to the drive curve or left in the original vertical position.
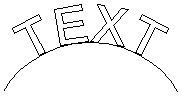

Position on the curve
The text's position on the curve can be adjusted interactively, by dragging the anchor point handle in 2D View.
Detaching from the curve
The text object that was wrapped on a curve can be detached from it.
To detach text right-click on the selected text object and select "Remove Text From The Curve" option.
Vector Validator
The Vector Validator is intended to help find issues with contours after file imports that are stopping tool-path creation such as overlapping contours or intersections. It also indicates zero-length spans.
The Vector Validator dialog can be opened with a selection to work on. If there is no selection, all visible vectors on the current Side of the current Sheet on visible layers will be validated. The selection can be changed while the form is open.
The text on the button changes to show whether all vectors or just the selection are going to be searched. While searching, the Search button becomes a Stop button.
To cancel a search, click the or button.
Issues found so far will be marked.
Marks
Examples of the marks described on the form are shown below:
If zero-length spans are found, the button is enabled. Clicking this will remove the zero-length spans and clear their markers
V-Carving Mode
When this option is checked, Vector Validator will perform its vector checks as it is executed and required for V-cutting.
For example,
- It will ignore intersections that may exist within the text, as this may be due to problems in the font. If you get intersections that involve text, you could try soldering it and run Vector Validator on the output.
Celtic Weave Creator
This Gadget dramatically simplifies the creation of complex 3D Celtic weave patterns using an interactive interface to produce all the vectors required by the Extrude and Weave tool.
Using the Gadget to create the 2D Artwork
Knot Grid
Simply define the size of the weave grid you require. Click to see your changes reflected in the Weave Preview Image.
Weave Preview Image
Click on the interactive weave image to cycle through the different crossing options at each intersection point. The 3 options are:
- Cut Vertical
- Cut Horizontal
- Cut Neither
You can reset the Weave Preview Image at any time using the button.
Cross Sections for Extrude
When you are happy with the layout of the weave pattern, choose which cross-section you would like and click to add it to your 2D View.
Click the button to convert the weave design you have created into vectors artwork in the 2D View. You can change the Weave Preview Image and click to update this artwork as often as you like.
Click once you are happy with your design. The Celtic Weave Creator form will close, but if you re-select the unedited weave pattern in the 2D View and re-open the Celtic Weave Creator gadget it will reflect you currently selected weave in the Weave Preview Image for further editing.
Creating the 3D Weave from the 2D Artwork
To complete the weave process, open the Extrude and Weave tool on the modeling tab. Select the main weave pattern vectors (but not the cross-section vector) and click on the button in the Drive Rails section at the top of the form. Now select the cross section vector and click anywhere on the weave rails vectors in the 2D View to apply the cross-section shape to it. Click to create the weave.
There are many more options available to use the weave vectors created by this Gadget. For a full description, please see the section on the Extrude and Weave tool.
Vector Unwrapper
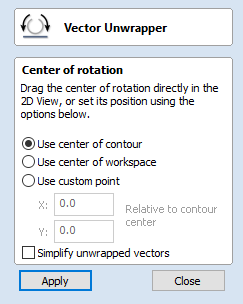
This tool converts one vector into another vector that can be used with the two-rail scanning tool to create rotational models from a desired cross-section.
To unroll the vector, follow these steps:
- Select the contour you want to unroll
- Use the options or the slide handle to select the center of unpacking
- Press Apply
The generated contour can now be used with the two-rail scanning tool to create rotary models.
Note
This tool is only available in rotary projects.

Center of Rotation
The center of rotation for the unwrapping changes the unwrapping of the contour so that when the resulting contour is used to create a rotary model, the center of rotation of the model is the chosen point.
Use center of contour
Sets the center of rotation to be the center of the bounding box of the selected contour
Use center of workspace
Sets the center of rotation to be the center of the workspace.
Use custom point
Sets the center of the job to be a specified point. The custom point can also be chosen by selecting the drag handle and dragging to the desired point.

Refine unwrapped vectors
Typically the resulting unwrapped contour will contain a large number of nodes. Selecting this option will result in an unwrapped contour with far fewer nodes.
Measure - Inspect
The Measure tool allows you to find important information about your model or drawings.
Measure Between 2 Points
With this option selected, you can click on two points in the 2D View and the form will report the measurements between the clicked locations
Distance
Straight line distance between the two points.
Angle
The angle (in degrees) of the line joining the two points, where horizontal is zero degrees and vertical is ninety degrees.
X Distance
The separation between the two clicked points in X only.
Y Distance
The separation between the two clicked points in Y only.
First Point
The precise X and Y coordinates of the position first clicked.
Cursor Position
The dynamically updated coordinates of the mouse cursor position.
Span / Contour Properties
This mode allows you to find precise information about the individual spans of a vector shape in 2D View. Use your mouse pointer to click on any part of the shape and the information relating to the entity you have clicked will be displayed on the form.
Type
The type of span you have clicked.
Possibilities include:
- Line
- Arc
- Bezier Curve
Length
The length of the clicked span.
Start Point and End Point
The precise coordinates of the node forming the start and end of the selected span.
Vector
Information relating to the whole vector, of which the selected span is part, is shown in this section.
Area
The total area of the selected vector
Perimeter
The total length of all the spans forming the perimeter of the shape
Num. Spans
The total number of spans in the shape.
Model Cross Section
The Model Cross Section option allows you to select two points on the 2D View and create a new vector that shows the corresponding cross-section of the underlying 3D model.
Creating a Rotary Job
XY Origin
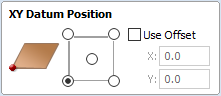
XY Drawing Origin - Here you can specify where the XY zero origin will be placed on your job. These options correspond to the same fields on the normal 'Job Setup' form within the program. Most people would use the default Bottom Left Corner, but for some jobs you may prefer to have the XY origin in the Center.
- In a job with horizontal orientation (Along X Axis), the X offset will correspond to the length of the cylinder, and the Y offset will be a point along its circumference.
- In a job with vertical orientation (Along Y Axis), it's the opposite. The Y offset will correspond to the length of the cylinder, and the X offset will be a point along its circumference.
Orientation
Cylinder Orientation Along - This section is used to tell the program how you have your rotary axis aligned on your machine. If you've already made your design, but just want to change the job for a different machine, then you could flip your design with the material so that all the vectors and components stay the same relative to the job.
Z Origin On - This section determines whether the Z Origin is set to the surface of the material or the base (center of cylinder). These settings can be over-ridden when the toolpath is actually saved, but we would strongly recommend the 'Cylinder Axis' is selected for rotary machining. The reasons for this are detailed in the note below.
Z Origin
You have the choice of specifying if the tool is being zeroed on the center of the cylinder or the surface. When you are rounding a blank, you cannot set the Z on the surface of the cylinder, as the surface it is referring to is the surface of the finished blank. We would strongly recommend for consistency and accuracy that you always choose 'Center of Cylinder' when outputting wrapped toolpaths as this should always remain constant irrespective of irregularities in the diameter of the piece you are machining or errors in getting your blank centered in your chuck.
Tip:
A useful tip for doing this is to accurately measure the distance between the center of your chuck and a convenient point such as the top of the chuck or part of your rotary axis mounting bracket. Write down this z-offset somewhere, and zero future tools at this point and enter your z-offset to get the position of the rotary axis center. Another reason for choosing 'Center of Cylinder' is that some controls will be able to work out the correct rotation speed for the rotary axis based on the distance from the center of rotation. If the Z value is relative to the surface, the control would need to know the diameter or radius of the cylinder at Z zero.
Vector Layout
As well as creating a job at a suitable size for wrapping toolpaths, when creating the job, it will create a number of vectors which can be very useful when creating your wrapped job.
The vectors are created on their own individual layers and by default these layers are switched off to avoid cluttering up your work area. To switch on the layers, display the 'Layer Control' dialog (Ctrl+ L is the shortcut to show / hide this). To show / hide the layer simply click on the check box next to the layer name.
2Rail Sweep Rails - This layer contains two straight line vectors which can be used to sweep a profile along if you are creating a shaped column.
Bounding Box - This layer contains a rectangular vector covering the entire job area. This vector is useful if you are going to machine the complete surface of the cylinder.
Choosing stock material
When setting-up rotary project, software assumes a perfect cylinder with an exact diameter. In practice the stock material may be uneven, or only blank with square profile may be available. In those cases blank needs to be machined into cylinder of desired size, before running toolpaths associated with the actual design.
Another consideration is length of the stock material. Typically, part of the blank will be placed within the chuck. It is also important that during machining, the cutting tool is always in safe distance from both chuck and tailstock. For those reasons, the blank has to be longer than the actual design. When setting-up the machine for cutting, one has to pay extra attention to ensure that origin is set accordingly to avoid the tool running into chuck or tailstock!
If the design was created without those considerations in mind, the blank size can always be adjusted in the Job Setupform.
The picture below presents an example of a rotary project layout. As explained above, the actual blank is longer than job defined in Aspire to allow for the chuck and sufficient gaps. The actual design is shorter than job defined in Aspire, to leave some space for tabs, that can be machined with the profile toolpath prior to removing the finished part from the chuck.
When machining 3D shapes with varying thicknesses like on the example shown below, it is a good idea to place the thicker end of the model on the side closest to the driving motor. This way torsional twisting will mostly affect the stronger end of the machined part and help to avoid bending or breaking of the part during machining.
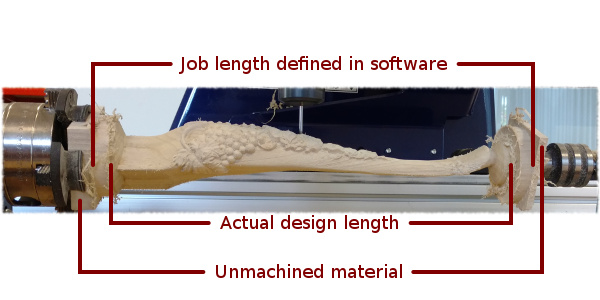
View
 | Zoom to Drawing | Use when you need to see the whole drawing and material as large as will fit in the 2D View window. |
F5 | Refresh 2D View | In situations where the complete vector geometry represents a very large job and the user zooms into a small region, the shape of arcs and curves may look faceted. This is only a display issue and will not impact on the quality of toolpaths. This command will rebuilds the display information to correct the graphics being drawn on the screen so curves are drawn smoothly again. |
| Guide Lines ► | For more details see the section on Rulers, Guidelines and Snapping. Opens the Guide Lines sub-menu. |
 | Draw Origin | XYZ origin arrows can be toggled on and off in the 3D View to show exactly where the X0, Y0 and Z0 origin is position is relative to the material. |
 | Draw Modeling Plane | This option controls the display of the semi-transparent 'modeling plane' which shows the position of the working model base plane. |
 | Draw Material Block | Toggles the drawing of a wireframe representation of the limits of the material block. This is useful for seeing how the 3D model will be positioned in the block of material it is being cut from. |
= | Multi Sided View | Allows you to view both sides in the 2D and 3D view when working in a multi sided environment. |
 | Auto-Wrapping View | Allows you to view wrapped toolpaths and models when in rotary job. |
 | Color Shaded View | Draws / Undraws the color shaded job in the 3D window. |
 | Use Shaded Background | Shows either the default gradient filled color background or a solid light blue color background. The solid color is very useful for saving images that need to be cropped out of the background in a graphics software package. |
 | Light follows viewer | The default light setting for the 3D window shines a light onto the job from the top left corner of the material bounding box. Checking ✓ this option can sometimes be used to help visualize the job more easily. |
 | Use Shadow Shading | Toggles the drawing of increased shadows in the 3D view. This can be useful for emphasizing details in models. This degree of shading can be increased or decreased using Ctrl + NumPad+ or Ctrl + NumPad- |
| Save Shaded Image | Saves a color shaded image of the 3D view as a BMP, JPG, PNG or GIF file. Note Saving the image without the color shaded background is often useful when the image will be used on its own in a brochure or on a web site etc. If you select PNG as the file type with the shaded background switched off the image will be saved with a transparent background. To switch the shading off, go to Edit ► Options ► Use Shaded Background and set Use Shaded Background to No. |
Page Down | Tile Windows Horizontal | Tiles the 2D and 3D View Horizontally, 2D View at the top and 3D at the bottom. |
Page Up | Tile Windows Vertical | Tiles the 2D and 3D View Vertically, 2D View on the left and 3D on the right. |
| Cascade Windows | Cascades the 2D and 3D View so they overlap. |
Guide Lines sub-menu
 | Guides Visible | Toggles the visibility of Guide Lines in the 2D view. |
| Delete All Guides | Deletes all the Guide Lines in the 2D view. |
| Lock All Existing Guides | Locks the position of all the Guide Lines in the 2D view. |
| Unlock All Existing Guides | Allows all the locked Guide Lines in the 2D view to be moved again. |
Ungroup Selection
Ungroup a set of Grouped vectors back to its individual vectors before it was grouped.
The Shortcut key for this operation is U.
Ungroup to the group's layer
By default, when grouped objects are ungrouped they revert to the layers on which they had previously been located before the grouping operation. However this is sometimes inconvenient. For example, when you have copied a group of vectors to a new layer, it is easier for subsequent editing if the copied vectors to remain on the new layer, even after ungrouping. An alternative right-click pop-up menu command has been added to make this process easier.
A shortcut key combination is also available to provide support for both of the ungroup operations. In summary, therefore, the group and ungroup shortcut options are as follows:
- GGroup the selected objects
- U Ungroup the selected objects to their original layers, sub-groups remain grouped.
- Ctrl + U Ungroup the selected objects to the group's layer, sub-groups remain grouped.
- Shift + U 'Deep' ungroup the selected objects to their original layers. Sub-groups are also ungrouped.
- Ctrl + Shift + U 'Deep' ungroup the selected objects to the group's layer. Sub-groups are also ungrouped.
Two-Sided Machining
Array Copy
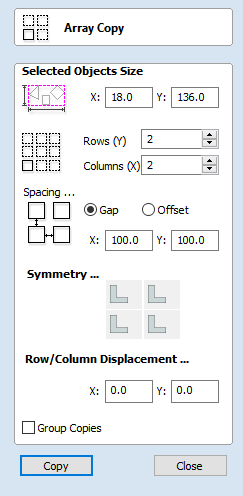
This tool will automatically create copies of the selected object and lay them out in a grid pattern. The grid size is determined from the number of row and columns requested and the spacing of the object copies can be set directly as a gap distance, or in terms of an offset distance between each copy's position.
Selected Objects Size
Reports the current size of the selection that you are intending to block copy. This is for information only, but the values can be selected, copied and pasted to use in other calculations.
Rows and Columns
These options specify how many rows and columns of the selected object to create. The total number of copies made will be X multiplied by Y.
Spacing...
There are two ways to specify the spacing between elements in array:
- Gap : The X and Y fields will be used to specify the gap between edges of each object copy.
- Offset : The X and Y fields are used to define the offset of the position of each object copy, relative to the preceding one.
Symmetry...
The symmetry area of the form gives you the ability to mirror and rotate objects. This allows for more advanced pattern making, by default the block symmetry form is set so there is no symmetry or rotation. To alter the pattern you can simply press the block symmetry buttons to create your desired pattern.
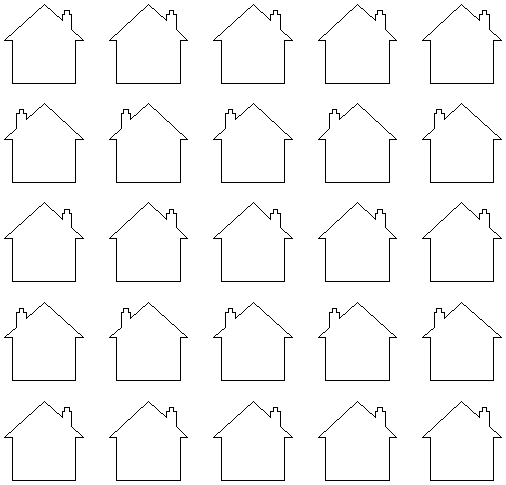
Row/Column displacement...
Entering values in the Row/Column displacement allows you to offset every other row or column by the value specified.
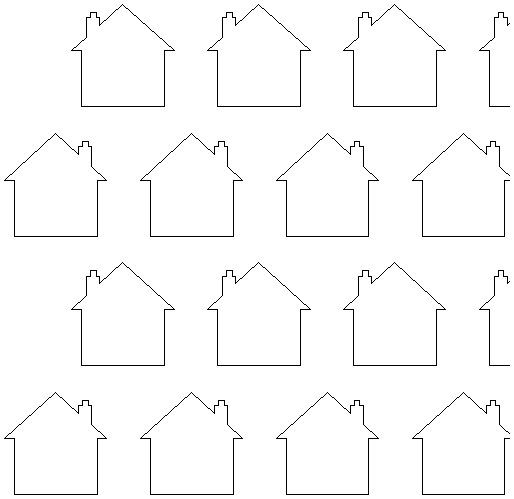
Group Copies
Having this option checked ✓ will group the objects that you have created in the form when you hit the button.
Copy Operation
The Copy tool copies selected objects to the clipboard, leaving the original in place and allows duplicates to be made and re-used in the design by pressing the Paste icon. Only one item can be Cut or Copied at a time.
File
 | New | Creates a New Aspire for ALPHACAM job. |
 | Open... | Opens an existing Aspire for ALPHACAM job |
| Close | Closes the current file but leaves the software running |
 | Save | Saves the current Aspire for ALPHACAM file over the last saved version of the file. Note This command will overwrite the old file with any changes made since the last save. If you are not sure of your changes then use the File ⇒ Save As... command instead option and give the file a new name. |
| Save As... | Opens the standard File Save dialog so you can save the current file with a new name. |
| Increment and Save | The Increment and save operation allows you to automatically number iterations of files you are working on. If you select this operation when editing a file which ends with an underscore, or a hyphen followed by a number, then the number will be increased by 1 and the file will be saved using this number. For example, MyFile_1.crv3d becomes MyFIle_2.crv3d MyFile-1.crv3d becomes MyFile-2.crv3d Note The increment and save option will keep incrementing until it finds a file that does not currently exist. It will not overwrite an existing file. |
| Opens the Print Setup box to Print your design | |
| Print Preview | Displays a Preview of the design to print |
| Print Setup | Opens the Print Setup box to Print your design |
| Import... ► | Import various entities into the job |
| Export... ► | Export vectors from the job |
| Open Application Data Folder... | Opens the Windows folder where files used by the software are stored. This is useful for adding to the default files installed initially. Application files include: Bitmap textures for creating custom materials. Gadget scripts for customized automation of the software. Postprocessors The Tool Database Default toolpath strategy settings Vector texture files. |
| Exit | Closes the job and exits the software. |
Import
 | Import Vectors... | Import Vector data. |
 | Import Bitmaps... | Import Bitmap data |
 | Import Component / 3D Model... | Import 3D Model or Component |
| Import PhotoVCarve or Cut3D Toolpaths... | Import a toolpath file created in another Vectric application, such as, Cut3D or PhotoVCarve. |
Export
Allows you to export selected Vectors as either an eps, dxf, ai, svg or pdf format vector file. If no vectors are selected, the all visible vectors will be exported.
- EPS
- DXF
- AI
- SVG
Note
When exporting in DXF format, the layer information relating to the exported vectors is preserved.
Printing and Print Preview
The contents of either the 2D or 3D view can be printed using the Print... command on the File menu. Simply select the view you wish to print (2D or 3D) and then click the Print... command. The standard Windows printer dialog allows you to select the printer and adjust its properties. When the OK button in this dialog is clicked, the view will be printed. To adjust the printer settings without printing, you can open the same dialog using the Print Setup... command on the File menu. When used in this way, the button on the dialog will store the settings without printing immediately.
Note
By default printing the 3D view does not print the shaded background; this behaviour can be changed using the Options dialog, which is opened using the Options command on the Edit menu.
The Print Preview... command on the File menu allows you to check the layout of your page before you print. If you are happy with the preview, use the button to begin printing the document directly from the Print Preview page.
Note
The printed view is always scaled to exactly fit the currently selected page size (including allowance for margins). Drawings are not, therefore, printed at actual size and are not printed across multiple pages.
Clearing or Splitting Components
The options to clear areas of a 3D Component, inside and outside of vectors or to slit a vector into multiple pieces are very useful modeling tools. There are many occasions where the standard modeling options may not allow you to create or control the exact shape that you need. Often you may need to create the general shape then crop (cookie cut) the resulting Component either to leave just the part of the shape you want or to make a hole in it. Many examples of this will be covered in the video tutorials supplied with the software.
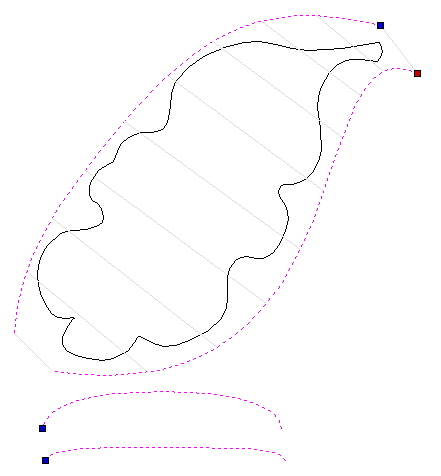
In the image above and left you can see the vectors selected for a 2 Rail Sweep to make a simple flowing shape. The result of this sweep is shown in the middle image. Our actual leaf edge vector can be seen in the left hand image after cropping the swept shape back to the leaf outline vector.
To use the cropping function you need to select the Component or Components you want to edit first and then select the object last that you want to use as the cropping region. If multiple Components, or a Component group, are selected for this tool, Aspire will prompt for you to bake the Components before continuing. See Baking Component for more information.
Clear Component Inside Selected Vectors
Removes the contents of the 3D model that is inside the currently selected object.
Clear Component Outside Selected Vectors
Removes the contents of the 3D model that is outside the area of the currently selected object.
Split Component
This tool allows you to split the selected Component into two independent Components. To use this tool, you must select the Component you wish to split and a single vector to indicate the split boundary then click on the icon.
You can use either an open or closed vector to define the split boundary. A closed vector can be envisaged as a 'cookie cutter'. The resulting two Components will be as if the cookie cutter vector was pushed through the selected Component to split it.
If an open vector is used to define the split boundary, Aspire will extrapolate from the ends of the selected vector to the edge of the modeling area to create the two resulting split Components.
The names of the resulting Components are automatically appended with '- A' and '- B' in the Component tree.
If multiple Components, or a Component group, are selected for this tool, Aspire will prompt for you to bake the Components before continuing. See Baking Components for more information.
View Controls
Your project is represented using 2D and 3D workspaces, each viewed via independent windows; the 2D View and 3D View, respectively. This division usefully maps to the typical workflow in which you will initially focus on the 2D design and layout of your project before moving to the 3D stage of modeling, toolpathing and previewing your finished part.
You can switch between the views using the tabs at the top of each window. In addition the shortcut-keys F2 and F3 will toggle the display between the two windows.
It is sometimes useful to see both the 2D and 3D representations at the same time. The Page Up and Page Down keys will arrange the 2 views either horizontally or vertically so you can see both workspaces simultaneously. To return to the tabbed display, simply click on the standard Windows Maximize button in the top right corner of either view window.
Many of the controls for manipulating the view in your project are similar in both 2D and 3D.
From within each view you can also directly interact with the objects that make up your job using the Object Selection Tools.
Material Setup - Flat
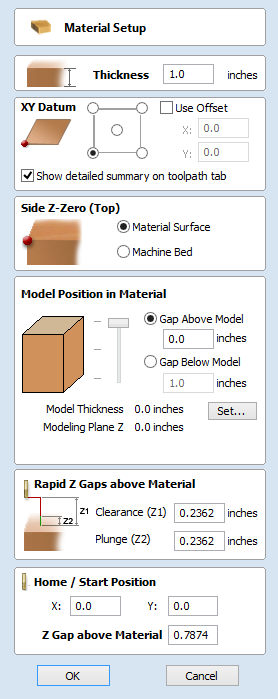
Thickness
Enter the thickness of the material being machined.
Show detailed summary on toolpath tab
This checkbox toggles the Material Setup summary layout on the Toolpaths tab between simple and detailed views.
Side Z-Zero
Select relative to the Material Surface or relative to the Machine Bed. This is a very important setting because the tooling used on the CNC machine must be setup in the same way, ensuring the toolpaths cut to the correct depth.
If you are working in a 2 Sided job, this will set the Z Zero for your current side only,
- The side you are setting up will be displayed in brackets e.g. (Top).
- You can set the Z-Zero for both sides through the Job Setup form.
Model Position in Material
The thickness of your model must be less than the thickness of the material you wish to cut it from. You can position your model within the material block wherever you wish by defining the gap distance either above or below your model. You can also double left click on either of the three lines next to the slider to position the model at the top, center or bottom of the material.
Note for Two-Sided Jobs
The gaps defined here are for the entire combined models from both sides (i.e. the final result you see when two-sided view is enabled). The above / below gaps do not depend on which side you are currently on. They represent the whole 2 sided model as if viewed in the correct orientation.
Gap Above Model
This distance positions your model according to the gap between the top of your model and the top surface of the material.
Gap Below Model
Alternatively you can position your model by defining the gap between the bottom of the model and the bottom surface of the material.
Model Thickness
This field simply reports the thickness of your composite model (as built from all your currently visible components).
Scale Model Height
The button can be used to change the Z Height of the Composite 3D Model (the visible Components) if it is not an appropriate height for your material thickness. Clicking this button will open the Set Model Height form which allows you to enter a new value for the overall height of the combined Components. After you have entered a new value hit and visually check the 3D model to ensure it still looks correct. Once you have found an appropriate value that looks good you can hit the button to continue in the Material Setup form. This height scaling function is also available from the Scale z height of model icon on the modeling toolbar.
Modeling Plane Z
Once you have positioned your model, this field will tell you the new height of your modeling base plane. This is for information only, and results from the gap settings above and cannot be edited directly.
Rapid Z Gaps above Material
Clearance (Z1)
This is the height above the job at which it is safe for the cutter to move at rapid or maximum feed rate. The software will raise the bottom of the cutter to this height when it traverses the material.
Plunge (Z2)
For all toolpaths, as well as specifying a rapid clearance gap for rapid positioning moves above the workpiece, the user can also specify a much smaller gap that the tool will rapid down to during plunge moves. By default the plunge gap is set to the same value as the Clearance gap which means that there will be no rapid plunges. If you set the plunge gap to a smaller value than the Clearance gap, the tool will plunge at rapid feed rate to the specified distance above the material surface before changing to the specified plunge rate. For jobs where a large value for Clearance gap has to be specified to avoid clamps etc, this feature can save a considerable amount of machining time if there are a lot of plunge moves in the job.
Note
Some engraving machines are not able to take advantage of this feature.
Home / Start Position
This is the absolute position that the tool will start moving from and where the tool can be programmed to return to at the end of cutting the job.
Extrude and Weave
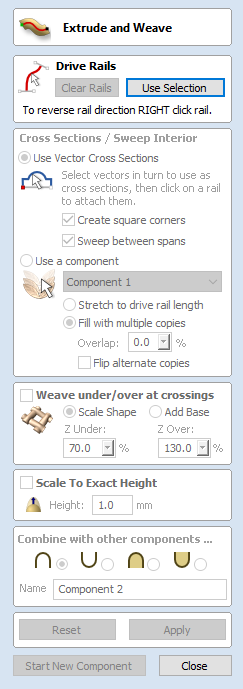
The Extrude and Weave feature is a very powerful and flexible modeling tool. It uses one or more vector drive-rails to define the path that the shape will follow, this allows you to extrude either vector cross-sections or 3D Components along these vectors to create the model.
The first stage is to select the drive rails and then choose whether you want to use either vectors or Components to extrude along your curves. There are many options both on the form and under the context sensitive right-click menus that can be used to control the shape that is created.
Drive Rail Selection
From the 2D View use the mouse to select one or more open or closed vectors you wish to use as the drive rails for you to extrude or weave along. Then click the button.
In the 2D view your rail vectors will be highlighted orange and now show a green square (start node) indicating the start of the vector from which the extruded shape will begin, and arrow markers along its length to show the direction of the extrusion.
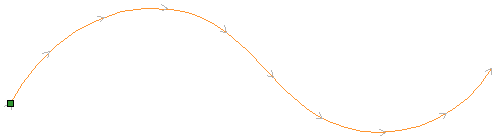
The default start point and direction shown may not be what you intended. To change the direction, right-click with the cursor on the vector line and select Reverse Rail from the context sensitive menu, you will now see the arrows on the drive rail change direction. On a closed vector you can change the start point by placing the cursor over an existing node in the drive-rail vector, right-clicking and selecting Make Start Point or you can right-click anywhere on the vector and select Insert Start Point to create a new node which will become the start point.
Note
Remember that you can hold down a Shift key while left-clicking on vectors in the 2D view to include more than one vector in the selection.
The button can be used at any time to empty your current selection. This will delete your current shape and deselect all the drive rail and cross section vectors. This can be used if you do not want to create a Component before you exit the form or if you want to select new vectors in the 2D view to use as the drive rail for your shape.
Using Vector Cross Sections
In this section of the form you can select whether to use vector cross sections or Components to extrude along your drive rails, select either Use Vector Cross Sections or Use a Component to make your choice.
Cross Section Selection
The next step is to select one or more cross-section vectors to sweep along your rails to form a 3D shape. In order for vectors to be used as valid cross-section shapes, they must be open.
Select a vector that you wish to use as a cross-section in the 2D View by left clicking on it with the mouse.
If you are using just a single cross section then you just need to make sure it is selected and then can proceed with the other settings in the form and calculate your shape. If you want to edit cross section positions or add more than one cross section then you will need to attach them to the drive rail.
Select a vector that you wish to use as a cross-section in the 2D View by left clicking on it with the mouse. Now click on the drive rail to attach the cross-section to that vector.
As you move the mouse over a selected drive rail it will indicate with a check mark ✓ that it is a valid place to add the cross section. Once a cross-section has been successfully attached to your drive rail, the 2D view will show a preview using line markers to indicate how the cross section will be positioned when it is extruded.
Two Cross-Sections are always created when you attach the first cross-section to the drive rail - one at the start and one at the end. The intermediate lines along the entire length of the rail indicate how the shape will flow between the defined cross sections. You can click the button to create your 3D swept shape.
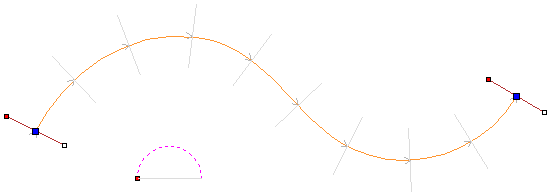
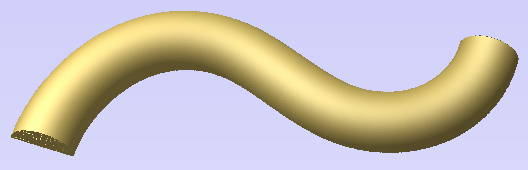
Using multiple cross-sections
It is possible to extrude between multiple cross section vectors along a drive rail blending from one vector shape to another.
Adding Cross-Sections
To add a new Cross-Section to an existing extrusion, simply select an open vector in the 2D View that you wish to use as a cross-section. With the vector selected, click on the point along the rail to which you wish it to be attached. A new Cross-Section will be inserted at this point. On applying the change, the resulting 3D sweep will blend seamlessly between all the defined Cross-Sections along the rail.
Note
To help differentiate which cross section is being used at each location the software will indicate a colored node at one end of each cross section and place the same colored node on the preview position. This node also indicates the direction the cross section is being 'hung' across the curve. The same cross section vector can be used in multiple locations along the drive rail.
In some cases it may be advantageous to add a cross section at all node positions on a drive curve, for example on a closed rectangular border. This can either be done manually, or automatically after you have added the first Cross-Section by right-clicking on the cross section you wish to duplicate and selecting Add To All Rail Nodes. This will add that same cross section to every node on that specific drive rail vector.
Removing Cross-Sections
To remove a Cross-Section, position the cursor over the cross section and click the right mouse button. Select the option to Delete Cross Section from the menu.
If you remove the start or end Cross-Section and fail to replace them with a new cross-section vector then the preview will no longer show intermediate lines to that point on its length. This means the shape will start or stop at that cross section and not go all the way to the start/end of the line. You can either add a new cross section or drag an existing one to that position if you need to resolve this.
You can remove all the Cross-Sections on a drive rail by positioning the mouse arrow over a part of the curve that does not contain a cross section. This will bring up a different context sensitive menu and you can select the options to Remove All Cross Sections.
Create sharp corners
If this option is checked, ✓ then the tool will create a sharp corner in the Component where there are discontinuities in the drive rail vector. When unchecked the shape will be rounded as it goes around the discontinuity. Below you can see a rectangular drive curve with a simple cross section being extruded around it, the one on the left has the Create sharp corners option selected and the one on the right without.
Sweep between spans
When checked ✓ this option will ensure that as the shape is extruded that it goes from a particular span/node in one cross section to the same span/node on the next cross section. For some applications this can give the user more control over the way the shape flows.
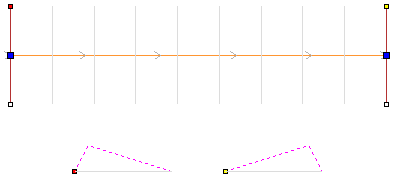
Using the above vector selection, the shape below left will be created with Sweep between spans checked ✓ and the shape on the right is created with the option un-checked. Note that on the left hand picture the crease in the shape goes from node to node in the cross sections as the spans flow exactly from one to the next. On the second picture the shape just linearly flows from one cross section to the next evenly with no additional control.
Smooth transition through the Cross Sections
As the extruded shape passes through each cross section the default is for it to flow smoothly through the profile. This can be edited by right-clicking over a cross section and unchecking the Smooth option. The middle node on the cross sections preview in the 2D View will be blue if it is smooth and white if it is un-smooth.
Using the above vector selection, the shape below left will be created with the Smooth option checked ✓ and the shape on the right is created with the option un-checked. Note that on the left hand picture the shape flows smoothly through each span, on the second it goes directly from cross section to cross section in a straight transition.
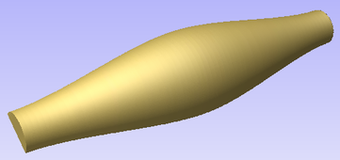
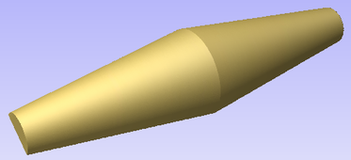
Extrude and Weave Components
The Extrude and Weave feature also allows the option to use a 3D Component instead of using vector cross sections to define the shape being created. To activate this feature choose the Use a Component option under the Cross Sections / Sweep Interior section of the form.
Once this option has been selected then you need to select a single Component that will be used for the operation. This can only be done within the form and not from either of the views or the Component Tree. Use the arrow at the side of the name in the drop down list to access a list of all the Components and select the one you want to use. By default the first Component name in the Component Tree will be shown in this section of the form. If the form is opened with a single Component selected, the selected Component will be the default in the list. Once selected a preview of the extrusion will be shown in the 2D view.
The orientation of the Component in your part will control how it flows along the vector. The direction along the X-axis of your Component will govern how it flows positively along the drive curve. Another way to think of it is you need to position your Component so it faces from left to right to orient how it will point along the curve.
Once your Component has been selected from the list you need to choose whether it will be used as a single copy stretched along the curve or repeated multiple times at its original size.
Stretch to drive rail length
Picking this option will take a single copy of the Component and stretch it along the full length of the selected drive rail vector.

Fill with multiple copies
Selecting this option will keep the Component at its original size and repeat it along the drive curve. Specifying an Overlap value will set each copy of the Component to overlap the previous one by this percentage of its length. Each overlapping piece will be merged together. In addition to overlapping the parts you can also check ✓ a box to flip alternate copies of the Component. This will flip every other copy of the original as if it had been mirrored vertically.


Weave under/over at crossings
With either vector or Component based extrusions you have the option to activate the Weave part of the function. This gives the ability to raise and lower the extruded shape at positions where the drive rail vector or vectors cross over. The effect of this is a Component that appears to be weaving the extruded shapes as you can see below.
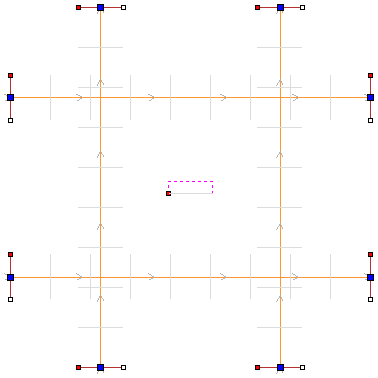
The order of the weave is determined by the direction of the first vector picked as part of the drive-rail selection. To change the order of which overlapping positions are raised up and lowered you can right mouse click on the first drive rail vector you selected and choose the option.
There are two options to control the way the shape is scaled at each overlapping point in the drive rail vectors, Scale Shape and Add Base.
Scale Shape
The Scale Shape option uses the percentage values entered into the form to scale the height of the original shape up and down at the cross-over positions. For example entering a Z Under percentage of 50% will force the locations which are being weaved under to be half their original height. Entering a Z Over percentage of 150% would force the locations of the shape which are being raised as they weave to be 1 ½ times their original height. This will distort the cross sections or Components to stretch or squash them.
The Scale Shape option will give a natural looking weave but for certain shapes will mean the detail in the shape may become heavily accentuated or reduced at the overlaps. In these situations the Add Base option may create a better result.
Add Base
The Add Base option will retain the height of the original cross section or Component and raise it up adding material under the shape depending on the percentage values indicated. This will typically create a higher final Component than using the Scale Shape option but gives a consistent shape to the strands of the weave.
Scale to Exact Height
Checking ✓ this option scales the shape calculated so its maximum height is the value entered in the Height area of the form.
Common Modeling Options
All of the main modeling tools in the software use a common set of commands to assign a name and combine mode to the component being created along with options to apply the settings in the form, reset the shape, start creating a new component and close to exit the function.
Combine with other components...
This section includes options to allow you to name your Component and control the way it will be combined with other objects in the Component Tree.

Reset
Clicking the button will remove the current shape, doing this before you Close the form will ensure that a component is not created from the current selection. Clicking this does retain the current set of selected vectors or Components.
Apply
Clicking the button will create a shape based on the settings you have chosen. You can continue making edits to the component by choosing different parameters within the form and hitting Apply to update it.
Start New Component
Clicking the button will save the state of the component that has been created, deselect all components/vectors and start the creation process again on a new component. The values and options within the form will be retained in this case until you Close it.
Close
Clicking the button will close the form returning to the Modeling Tab icons and the updated Component Tree, reflecting any changes that you have made. If you wanted to remove the shape you just created then you can hit the Undo icon or use the keyboard shortcut to undo, CTRL+Z.
Editing vectors while using the Extrude and Weave tool
It is possible to make edits to the vectors that you have selected while using the Extrude and Weave tool. To do this you can click in the whitespace of the 2D View to ensure you have focus on that window. Then on the keyboard hit either N to go into Node Editing mode or T to go into Transform mode.
You will notice the drive rails and cross sections will become deselected and the button will change to say . You can now make edits to the vectors using the dynamic Node Editing and Transform functions in the 2D view. When you are happy with your changes you can click on the button and the vectors will be selected in the same order they were before. Now you can click the button to create a new shape based on the edited vectors.
Subtract Vectors
Selected closed vectors that overlap can be merged together to create a new shape. These tools consider the closed vectors to be solid areas.
The following examples begin with these five vector shapes where the rectangle was selected last.
Areas in the first shapes that overlap the last selected shape are removed. In this case, the last selected shape was the rectangle, so the rectangle is cut away from the circles anywhere that overlaps.

Rotary Machining and Wrapping
Aspire for ALPHACAM can 'wrap' flat toolpaths around a cylinder to provide output to CNC machines which are configured with a rotary axis / indexer. The image below shows a flat toolpath wrapped around part of a cylinder.
Note
It is important to note that wrapping works in conjunction with specially configured post-processors which take the XYZ 'flat' toolpaths and wrap them around a rotary axis, replacing either the X or Y moves with angular moves.
The toolpaths can be visualized wrapped within the program when the Auto Wrapping mode is on.
Aspire for ALPHACAM can also visualize a wrapped model within the program by drawing the shaded composite model wrapped.
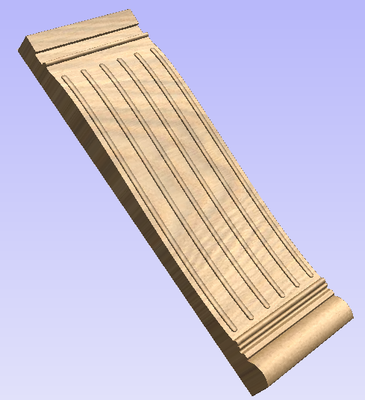

Aspire for ALPHACAM also has the ability to draw the toolpath simulation wrapped. Although this is very useful for getting a feel for how the finished product will look, it is important to realize that the wrapped simulation may not be a 100% accurate representation of how the finished product will look. An example of potential difference would be if you drilled holes in your rotary job. In the actual work piece these will obviously just be round holes, in the wrapped simulation these may appear as distorted ovals due to the 'stretching' process which takes place when we wrap the flat simulation model for display.
Note
If your rotary axis is aligned along your Y axis you would choose the Orientation Along Y Axis option during job setup. All the examples in this document will assume that the rotary axis is aligned along X.
It is important to realize that there are a huge number of possible combinations of machine controller and axis orientations for rotary axis / indexers. This means it is impractical for Vectric to supply a pre-configured post-processor for every possible combination as standard. We include some wrapping post-processors in the default post-processor list as standard.
We also ship a copy of those post-processors in the Application Data Folder which can be accessed from the File Menu ► Open Application Data Folder.
The example below uses wrapped post-processors in sub-folder '05-Wrapped' under C:\ProgramData\Vectric\Aspire\V[ProductVersion]\PostP\05-Wrapped.
Examining these posts may be helpful if you need to configure a post of your own. If Vectric have not supplied as standard a post for your machine configuration please refer to the Post Processor Editing Guide accessible from the Help menu of the program for information on how to configure a post-processor and also look at the standard rotary posts Vectric supply.
You should also look at the Vectric forum to see if anyone else has already configured a post for your configuration or one similar. If, after looking at these resources you are still unsure of what needs to be done for your machine, please feel free to contact support@vectric.com for help. However, please note that we cannot guarantee to write a custom rotary post-processor for every individual requirement.
Import Bitmap
This opens the File Open dialog window and allows image files to be selected and imported into the current open job. File types - BMP, JPG, TIF, GIF, PNG
Images are imported to sketch vectors over the top of them, generate traced vectors or to be used to generate a 3D Component directly from the image. These functions will be covered in more detail in the
Convert text to Curves
Converts selected text object into vector form, creating lines, arcs and Bezier spans that can be interactively edited. After conversion the text cannot be edited as a text object.
In most cases all the text created in Aspire for ALPHACAM can be VCarved, Engraved, Pocketed and Profile machined or used with the 3D modeling functions without converting to the curves.
Some fonts do occasionally include loops and problems that need fixing using the Node Editing tools before it can be utilized for other functions.
Create a New File
This option opens the Job Setup form, which is used to create a new blank job of the specified dimensions and type. The relative origins for X0, Y0 and Z0 are also specified at this point, and the measurement units can be set in either inches or metric. The Modeling Resolution and default 3D shading color/material can also be set at this stage.
Job Templates
Job templates are files which can hold frequently used dimensions, machine settings, or geometry. They are like regular .crv3d or .crv files apart from a few important differences:
- They have different file extensions (.crv3dt and .crvt)
- When templates are opened, if you then decided to save them they will not overwrite the template, they will behave as though they are new files.
- The default save and load location is shared only across templates
Creating a Job Template
To create a job template you will need to create a job like you usually would, with the required dimensions and machining setup. You can also add geometry that you want to form part of the template. Then click File > Save As Template and save the file in the desired location.
Using a Template
A template can be opened using the New file from template option on the start panel. Or alternatively from the File > New file from template top menu bar.
Editing an Existing Template
To edit an existing template open it up in the usual way, by going to File > New file from template, once you have made the changes to the template you can save over the existing file by going to File > Save As Template in the top menu bar.
Create Vector Boundary From Selected Components
This icon can be used to create a vector around the outermost boundary (silhouette) of one or more selected components. The most important use is to generate a vector that can be selected as a toolpath boundary, particularly for 3D Roughing, 3D Finishing and also Profile (cutout) toolpaths.
Aspire for ALPHACAM will create one or more closed vector boundaries around the edge of the selected components. If more than one closed vector is required to create the boundary, these will be created as a group to make it easier to select them. They would need to be ungrouped before they could be edited individually.
Mirror Mode
You can use this tool to create a vector boundary for a composition you have created in Mirror Mode. Simply select the components that are visible in the 2D View and apply the vector boundary.
Importing a 3D Model into Rotary job
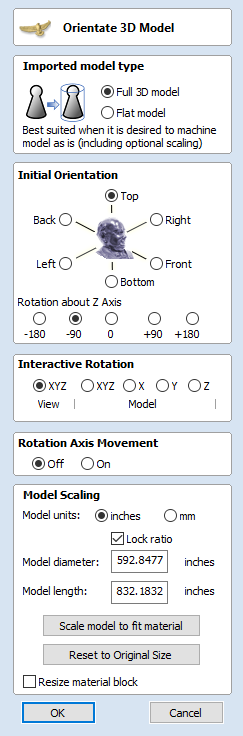
Imported model type
Allows the nature of the imported model to be specified. Depending on the selection, the form will change to allow the most appropriate workflow. You can choose from the following model types:
- Full 3D model - a model that is suitable for rotary machining as is,
- Flat model - a model that is only suitable as a part of design, similar to clipart provided with Aspire for ALPHACAM.
Initial Orientation
The purpose of this section is to roughly position the imported model within the material block. One can choose one of the 6 options to determine the most suitable direction on the model that defines the top surface (upper Z). This can be combined with one of the five options for Rotation about Z Axis.
Note
The software will try to guess the initial orientation that seems to be appropriate for the model, based on the model type selected in step one.
Interactive Rotation
This section can be used to fine-tune the model position in relation to the material block. The default choice XYZ-View allows the usual use of the mouse to rotate the 3D View, so the imported part can be seen from different angles. While this mode is selected, the orientation of the part will not change. Selecting one of the other four options above the word Model will enable adjustment of the actual positional orientation of the imported part. Choosing the XYZ option will allow rotation around all three axes simultaneously. Selecting X, Y or Z will only allow rotation around the specified axis. It will also automatically switch the 3D View to show the part from that axis.
Note
Selecting a different initial orientation will cancel any adjustments made by using Interactive Rotation.
Rotation Axis Movement (Full 3D model only)
This section can be used to adjust the position of the model in relation to the rotation centerline. By default Aspire for ALPHACAM will position the model in the center of the material block, so the material is used more efficiently.
When the Off option is selected, panning the 3D View will happen in the usual manner.
When the On option becomes selected, using the 3D View panning controls will move the rotation axis instead.
Model Scaling (Full 3D model)
This section allows the model scale to be adjusted as desired. The model bounding cylinder (blue) will be displayed around the imported model in the 3D View. The scaling is performed by means of length and diameter of the bounding cylinder. When the model orientation within the material block changes, so does the bounding cylinder. If that happens, the reported size of the model will change, although the model may not have been scaled.
Model units
By default Aspire for ALPHACAM assumes that the imported model is using the same units as specified during job setup. If that is not the case, the model units can be changed.
Note
If the model units are different than those selected during job setup, the imported model will be converted to use the units selected during job setup.
Lock ratio
When this option is selected, all scaling operations will maintain the current ratio between model length and diameter.
Scale model to fit material
This option can be used to resize the imported model so it will fit in the material block as defined during job setup.
Reset to Original Size
This option undoes any scaling applied to the model (apart from unit conversion), regardless of the model orientation.
Resize material block
When this option is selected, the project's material block will be resized to match the final dimensions of the imported model.
Model Scaling (Flat model)
This section allows the model scale to be adjusted as desired. A flat material block is displayed and the scaling can be performed by means of length in each of the three axes (X, Y and Z).
Model units
By default Aspire for ALPHACAM assumes that the imported model is using the same units as specified during job setup. If that is not the case, the model units can be changed.
Note
If the model units are different than those selected during job setup, the imported model will be converted to use the units selected during job setup.
Lock ratio
When this option is selected, all scaling operations will maintain the current ratio between the model length in each of the three axes.
Scale model to fit material
This option can be used to resize the imported model so it will fit in the material block as defined during job setup.
Reset to Original Size
This option undoes any scaling applied to the model (apart from unit conversion), regardless of the model orientation.
OK
Creates a 3D Component based on the settings in the form, the Component will have the same name as the imported file.
Cancel
Cancels the Import function and returns to the standard Modeling Tab icons.
3D View Controls
 | 3D Twiddle | Click and drag Left mouse button in the 3D window |
 | Zoom | Right mouse button - Push / Pull Mouse with Middle Wheel - Rotate wheel |
 | Pan | Click and drag Right mouse button and hold Ctrl. Click and drag Right and Left mouse button Click Middle mouse button |
 | Zoom to Fit | Zooms the whole 3D part to fit within the current 3D View window |
 | Isometric View | Shows the model in a 3D isometric view in the 3D window |
 | Plan View (Down Z) | Shows the top view of the model in the 3D View looking down the Z axis. Press Shift to show the bottom. |
 | Side View (Along X) | Shows the side view of the model in the 3D View looking along the X axis. Press Shift to show the opposite side. |
 | Side View (Along Y) | Shows the side view of the model in the 3D View looking along the Y axis. Press Shift to show the opposite side. |
 | Rotate around model (Rotary) | Rotate clockwise / anti-clockwise around the model (Available only in a Rotary project with Wrapped View |
Material Setup - Rotary
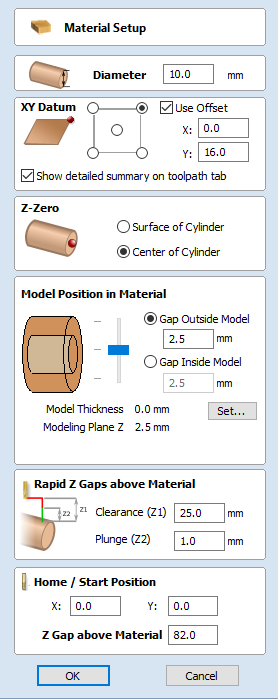
Diameter
Enter the diameter of the material being machined.
Show detailed summary on toolpath tab
This checkbox toggles the Material Setup summary layout on the Toolpaths tab between simple and detailed views.
Z-Zero
Select relative to the surface of the material cylinder or its center. This is a very important setting because the Tooling used on the CNC machine must be setup in the same way, ensuring the toolpaths cut to the correct depth.
Model Position in Material
The diameter of your model must be less than the diameter of the material you wish to cut it from. You can position your model within the material block wherever you wish by defining the gap distance either outside or inside your model. You can also double left click on either of the three lines next to the slider to position the model at the top, center or bottom of the material.
Gap Outside Model
This distance positions your model according to the gap between the top of your model and the surface of the material cylinder.
Gap Inside Model
Alternatively you can position your model by defining the gap between the bottom of the model and the center of the material.
Model Thickness
This field reports the thickness of the model (as built from all the currently visible components). The model can be scaled by clicking on the button.
Modeling Plane Z
Once you have positioned your model, this field will tell you the new height of your modeling base plane. This is for information only. It results from the gap settings above and cannot be edited directly.
Rapid Z Gaps above Material
Clearance (Z1)
This is the height above the job at which it is safe for the cutter to move at rapid or maximum feed rate. The software will raise the bottom of the cutter to this height when it traverses the material.
Plunge (Z2)
For all toolpaths, as well as specifying a rapid clearance gap for rapid positioning moves above the workpiece, the user can also specify a much smaller gap that the tool will rapid down to during plunge moves. By default the plunge gap is set to the same value as the Clearance gap which means that there will be no rapid plunges. If you set the plunge gap to a smaller value than the Clearance gap, the tool will plunge at rapid feed rate to the specified distance above the material surface before changing to the specified plunge rate. For jobs where a large value for Clearance gap has to be specified to avoid clamps etc, this feature can save a considerable amount of machining time if there are a lot of plunge moves in the job.
Note
Some engraving machines are not able to take advantage of this feature.
Home / Start Position
This is the absolute position that the tool will start moving from and where the tool can be programmed to return to at the end of cutting the job.
Save a File
This option opens the File Save As dialog window and allows the job to be saved as a Aspire file. Navigate to the required folder, enter a suitable name for the job and click the Save button.
You can also change the Save As Type using the Dropdown menu. This will allow you to save your file in the .CRV VCarve Pro file type. Saving with this file type will remove all 3D clipart and other 3D Data that is not usable in VCarve Pro, and will allow you to open a file from Aspire in VCarve Pro.
Alignment Tools
The Align Objects tool provides a number of options for accurately aligning the selected object to other objects in the selection, or to the available material.
Align to Material
The options in this section will align one or more selected objects within the material workspace defined when you setup your job (the white area in your 2D View).
Center in Material

This option moves the selected items to be positioned in the middle of the material. The short-cut key for this is F9.
Center in Material X only

Align items centrally in the material only moving them along the X axis so the vertical position will not be changed.
Center in Material Y only
Align items centrally in the material only moving them along the Y axis so the horizontal position will not be changed.
Align to Selection
The different items comprising your design in the 2D View can be aligned relative to one another using the following selection sequence:
- Select the item/s you wish to align / move (use single or multiple selection options).
- Hold the Shift key down.
- Select the final item - this is the object that the rest of the selected items will be aligned to Click the required alignment option.
There are 7 alignment options for aligning the selection to the inside edge:
Align Center

Center selected items in the middle (both horizontally and vertically) of the last selected item.
Align Vertical Center

Align the selected items vertically centered to the last selected item.
Align Horizontal Center

Align the selected items horizontally centered to the last selected item.
Align Left/Right


Align the selected items to the left or right edge of the last selected item.
Align Outside Top/Bottom


Align the selected items on the outside top or bottom edge of the last selected item.
Space Selection

The final section is different from the preceding two. The tools here evenly space the selected objects either horizontally or vertically whilst maintaining the relative X or Y positioning of the items. The top and bottom items (for vertical spacing) or left and right items (for horizontal spacing) will remain in place and the other items will be spaced evenly between them.
Alternatively if CTRL is pressed the order of selection will be taken into account and the selected objects will be spaced evenly between the first and last object selected.
If Inside last vector is checked the items will be evenly spaced within the bounds of the last object that was selected.
Show common tools on drawing tab
If this option is checked, ✓ the most common alignment tools will be displayed on the drawing tab in their own section called Align Objects. The Alignment form can still be accessed from the original icon in the 'Transform Objects' section (or by pressing F10).
Paste Operation
This Paste option places the contents of the clipboard (created by Cut or Copy) into the design, allowing elements to be re-used in different areas of a design or in other Aspire for ALPHACAM parts.
Level Clipping
Level Clipping allows you to dynamically trim models using closed vectors. When this option is enabled, the level will be constrained to the chosen vectors, without affecting the underlying components. Components can be rearranged to modify the underlying design and the results will be dynamically cropped.
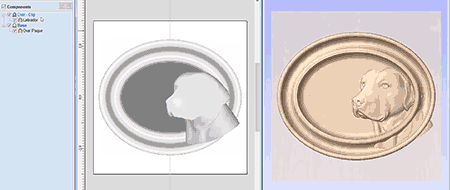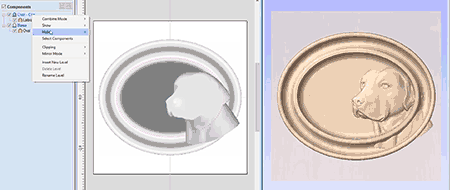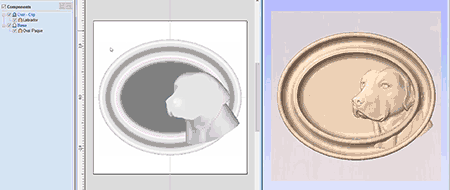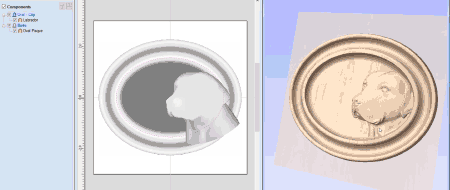
Apply
To apply level clipping vectors, select some vectors and then right click on the level that we want to trim:
Choose clipping and then apply to clip the level. When this happens then the components on the level are clipped. The areas of the model that lie within these vectors are left untouched, and all areas of the model that lie outside of the vectors are removed.
This clipping is dynamic, so the components on the level can be modified, rearranged, or transferred and the clipping automatically applies to the changed model on the Clipped Level.
Update
Once level clipping has been applied then changes to the underlying clipping vectors do not automatically result in changes to the clipping. To update the clipping boundary:
- Right click on the level and then choose Clipping > Update
- If no vector is selected and the previously used vector is still in the job then the previously used vector will be reused.
- If a different vector is selected then this will now be used as the clipping vector
Remove
To remove the clipping effect from the level, right click on the level and then choose Clipping > Remove.
Draw Rectangle
Rectangles can be created by using the Draw Polyline tool or using the Draw Rectangle Tool. The latter tool allows rectangles to be created interactively with the cursor and Quick Keys or by entering the exact coordinates, type of corners (square, internal or external radius) and Width and Height using typed input.
Interactive Creation
The quickest and simplest way to draw a rectangle is:
- Click and drag the left mouse button in the 2D View to begin drawing the rectangle from its first corner.
- While holding the left mouse button, drag to the required size.
- Releasing the left mouse button.
Note
Holding Alt and dragging creates a rectangle from the center. Holding Ctrl creates a square.
Quick Keys
Instead of releasing the left mouse button when you have dragged your shape to the required size, you can also type exact values during the dragging process and set properties precisely.
- Left-click and drag out your shape in the 2D View.
- With the left mouse button still pressed, enter a quick key sequence detailed below.
- Release the left mouse button.
Default
By default, two values separated by a comma, will be used to set width and height of your rectangle. One value will create a square with that side length. While you are dragging out the rectangle corner, type Width Value , Height Value Enter or Side Length , Enter to create a rectangle with the specified width and height.
Example
- 1 , 2 . 5 Enter - Creates a rectangle of width 1 and height 2.5
Specifying Further Properties
By using specific letter keys after your value, you can also indicate precisely which property it relates to.
- Value X - Creates a rectangle at the dragged height but with the width set to the entered value
- Value Y - Creates a rectangle at the dragged width but with the height set to the entered value
- Value R Value X - Create a rectangle with radius R and width X
- Value R Value Y - Create a rectangle with radius R and height Y
- Value W Value H - Create a rectangle with width W and height H
- Value R Value W Value H - Create a rectangle with width W and height H
Examples
- 1 X - Current dragged height with a width of 1
- 1 Y - Current dragged width with a height of 1
- 0 . 1 R 1 X - A corner radius of 0.1, a width of 1 and current dragged height
- 0 . 1 R 1 Y - A corner radius of 0.1, a width of 1 and current dragged height
Note
These key combinations must be pressed whilst dragging with the mouse to create the rectangle.
Exact Size
Rectangles can also be drawn by entering the required XY origin point with the Width and Height of the rectangle.
Corner Type
Corners of the rectangle can be Square, Radiused Externally or Radiused Internally.
Interactive Corner Radii
If you choose to have radiused corners then 4 additional green handles will appear on the previewed rectangle. These handles can be interactively dragged to modify the radii of the corners.
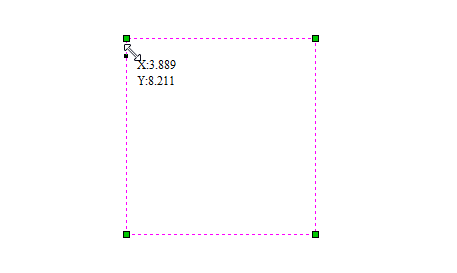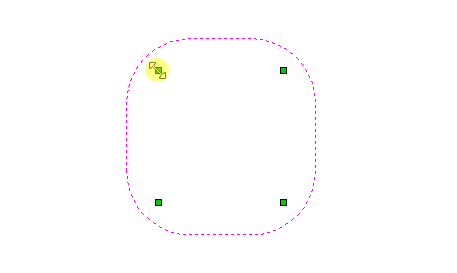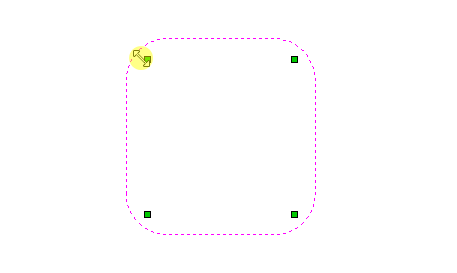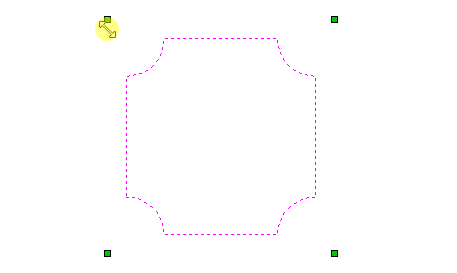
Editing Existing Rectangles
To edit an existing rectangle:
- Select the rectangle to modify and open the Draw Rectangle form.
- The selected shape is displayed as a dotted magenta line.
- Edit the Width and Height values.
- Click Apply to update the rectangle.
To modify another rectangle without closing the form hold a Shift key down and select the next rectangle.
Clipart Tab
The Clipart tab provides quick and convenient access to V3M files or 2D vector artwork.
This tab includes the library browser that allows you to add folders containing V3M Files into the software or you can use the local files option that allows you to quickly see the contents of several folders of V3M files in one place.
Importing Clipart
To import a file as a piece of clipart you can simply double click its thumbnail to position the clipart in the center of the job. You could also Right click on a piece of clip art and choose the option, this has a sub-menu that allows you to choose an existing Level or to create a New Level. When creating a New Level you will be prompted to enter a name and choose a combine mode. You can also click on a preview image and 'drag and drop' its thumbnail from the clipart browser, into the 2D or 3D View. To do this:
- Move your mouse over thumbnail image in the clipart browser.
- Press and hold down the left mouse button.
- While holding down the left mouse button, move the mouse back into the 2D or 3D View.
- A copy of the thumbnail image will be 'dragged' with the mouse pointer.
- Release the mouse button to 'drop' the clipart file into the 2D or 3D View.
The selected component clipart model or vector outline will be imported at the location of the dropped thumbnail and, if appropriate, added to your model's Component Tree
Library Browser
The library browser provides quicker access to folders on your computer which are in frequent use, or perhaps hold the data for the current project you are working on.
To add a folder into your library click on the button which opens up a dialog asking you to choose the folder you would like to add. Navigate through the tree to choose then folder and click OK. Unlike the Local Files browser the Library browser will only show the clipart that within this folder and folders within this folder. You will not be able to see the whole of the file tree beneath this folder.
Once you have populated your library with folders then clicking on a folder will populate the clipart browser with the objects which are contained in this folder and show you any subfolders immediately below it.
To better understand this, consider the following example: My current project is a western saloon themed sign. I have split up all the resources I am using for this creation into three folders, so that I have the following file folder structure:
Removing Folders
To remove a folder, select from the list of folders and click on the button. This will not delete clipart from your computer; it will just remove the library folder
Adding Folders
Folders may be added to the library from the local file browser by right clicking and selecting the Add folder to library option.
Local Files
The local files browser allows you to select a folder using the file explorer tree in the top section of the page. When you select a folder containing Vectric files (*.crv or *.v3m) the bottom section of the page will fill with thumbnail images of the V3M or CRV files within each folder.
Integrated Windows Explorer Thumbnail Support
V3M files automatically include thumbnails. Windows Explorer can make use of these thumbnails to show you a preview of each file when you browse a folder.
Drag and Drop
Aspire supports Windows drag and drop functionality to quickly add V3Ms into an existing model directly from Windows Explorer.
With Windows Explorer and Aspire both open, simply click and drag the V3M thumbnail of the file you want from the Explorer Window into either the 2D or 3D View window of Aspire. The selected V3M file will be imported automatically and added to the Component Tree
Replace Below
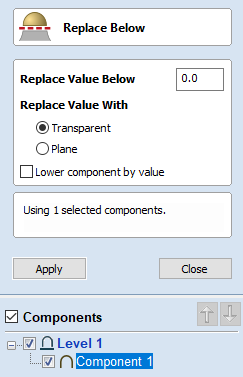
This feature allows you to trim (or flatten) the bottom off a component or multiple components. This could be useful if you've imported an STL model that has some undesired thickness, for example, when it has come from a 3D scan. Also, sometimes you could end up with an undesired negative part of the components (when sculpting, or combining with a deep subtracted model). This tool will allow you to remove anything below a certain height, and (optionally) drop the model by that height.
The result of the operation will be a component that will appear in the Component Tree.
- If only a single component is selected, it will be replaced.
- If multiple components are selected (or a level with more than one component is chosen), they will be baked into a single component, then the operation will applied to the baked component.
Note
Select one or more components, or use the active level to get started.
Options & Parameters
Replace Value Below
Replace areas that are below the given height with the height chosen by Replace Value With.
Replace Value With
This will control what value to replace those areas with.
- Transparent: Completely remove those areas, and replace them with transparency.
- Plane: Replaces those areas with a plane.The height of the plane is the height input above.
Lower Component by Value
When this option is checked, the model will be dropped by the given height. This is useful if the model is too thick and/or we want to get rid of some background (i.e. one that has come in with an STL model). If you set this to 0, it will remove everything below the Zero-Plane.
Selection
Height Value
The height value is local to the selected component(s). This is equivalent to the value you see if you hide everything but keep the components of interest visible. Therefore, it is easier to apply this to levels.
3D View Selection
You can double-click a point in the 3D view while the form is up to update the height value used.
Level & Component Selection
The effects of this operation are applied to the components and does not necessarily rely on the visible model.To apply this operation:
- Either have one (or more) component(s) selected, or
- Activate a level to select all visible components beneath it.